神经网络常见激活函数 15-B-SiLU 函数
文章目录
- B-SiLU (Bounded Sigmoid Linear Unit)
- 函数+导函数
- 函数和导函数图像
- 优缺点
- PyTorch 中的 B-SiLU
- TensorFlow 中的 B-SiLU
- 备注
B-SiLU (Bounded Sigmoid Linear Unit)
-
论文
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.22074
结合了 SiLU 的自门控特性与可调下限参数,B-SiLU 通过 SUGAR(Surrogate Gradient for ReLU)方法用于解决 ReLU 的「死亡 ReLU 问题」,在前向传播中保持 ReLU 的稀疏性,而在反向传播中 作为 ReLU 的平滑导数替代函数。实验表明,SUGAR 结合 B-SiLU 在 CIFAR-10 和 CIFAR-100 数据集上显著提升了 VGG-16 和 ResNet-18 的测试准确率,分别提升 10-16 个百分点,优于其他替代函数(如 ELU、SELU、LeakyReLU 等。
-
这篇中,作为ReLU的梯度替代,同时还有一个NELU被提出,但是感觉效果不太好,后续就不写了
函数+导函数
-
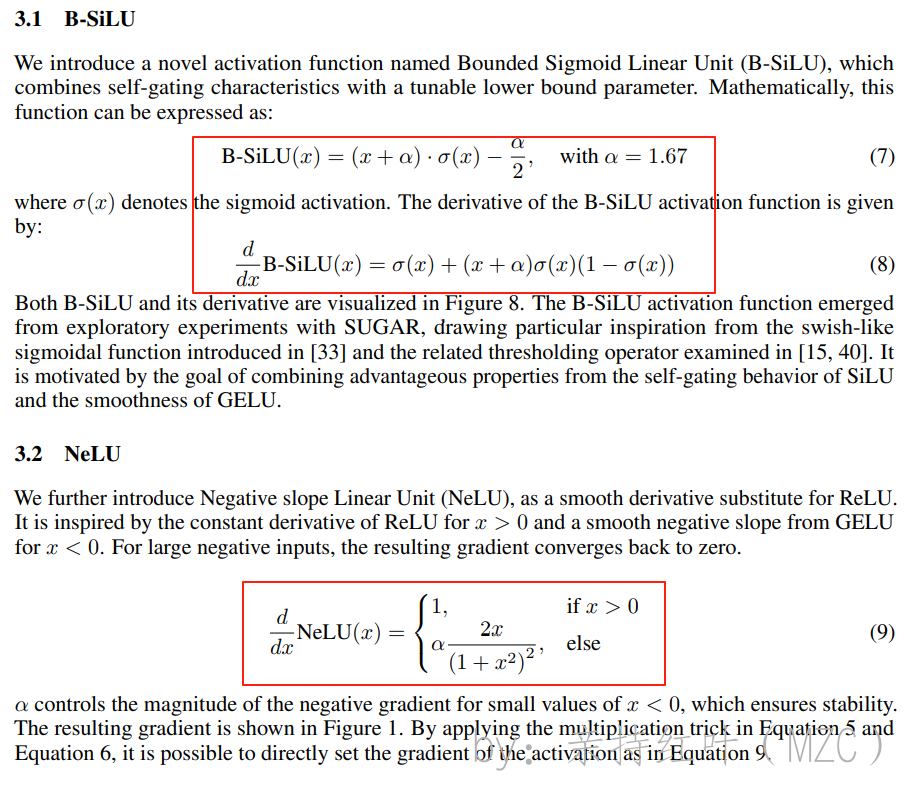
B-SiLU函数
B-SiLU(x)=(x+α)⋅σ(x)−α2=x+α1+e−x−α2\begin{aligned} \mathrm{B\text{-}SiLU}(x) &= (x + \alpha) \cdot \sigma(x) - \frac{\alpha}{2} \\ &= \frac{x + \alpha}{1 + e^{-x}} - \frac{\alpha}{2} \end{aligned} B-SiLU(x)=(x+α)⋅σ(x)−2α=1+e−xx+α−2α
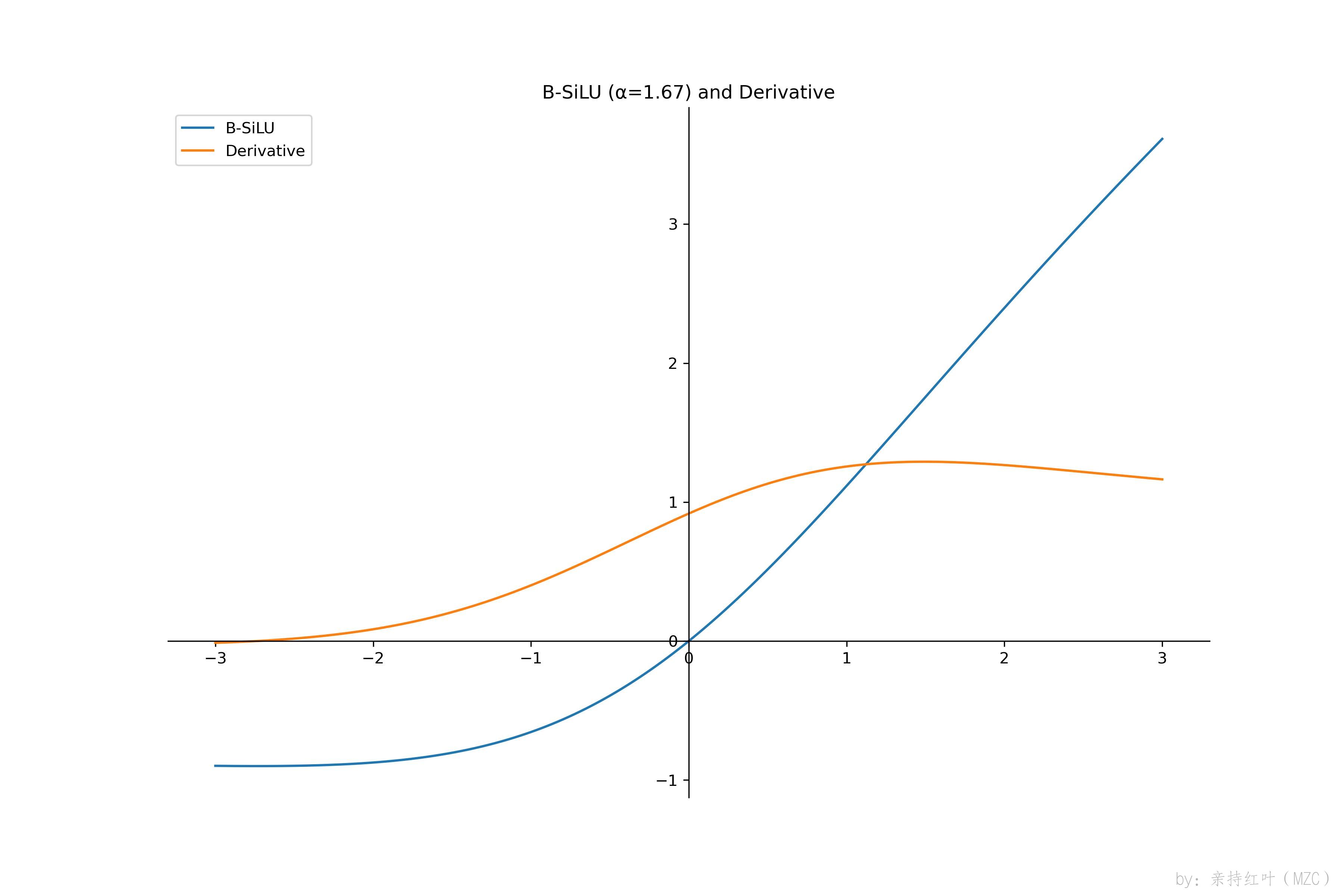
当 α=0 时,B-SiLU 退化为 SiLU/Swish-1。 -
B-SiLU函数导数
ddxB-SiLU(x)=[(x+α)⋅σ(x)−α2]′=σ(x)+(x+α)ddxσ(x)=σ(x)+(x+α)⋅σ(x)(1−σ(x))\begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx} \mathrm{B\text{-}SiLU}(x) &= \left[(x + \alpha)\cdot\sigma(x) - \frac{\alpha}{2}\right]' \\ &=\sigma(x) + (x+\alpha) \frac{d}{dx}\sigma(x)\\ &= \sigma(x) + (x + \alpha)\cdot\sigma(x)\bigl(1 - \sigma(x)\bigr) \end{aligned} dxdB-SiLU(x)=[(x+α)⋅σ(x)−2α]′=σ(x)+(x+α)dxdσ(x)=σ(x)+(x+α)⋅σ(x)(1−σ(x))
其中 σ(⋅)\sigma(\cdot)σ(⋅) 为 Sigmoid 函数,α=1.67\alpha=1.67α=1.67(论文建议值)。且
ddxσ(x)=σ(x)(1−σ(x))\frac{d}{dx}\sigma(x) = \sigma(x)(1-\sigma(x)) dxdσ(x)=σ(x)(1−σ(x))
函数和导函数图像
-
画图
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as pltdef b_silu(x, alpha=1.67):return (x + alpha) / (1 + np.exp(-x)) - alpha / 2def b_silu_derivative(x, alpha=1.67):sig = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))return sig + (x + alpha) * sig * (1 - sig)x = np.linspace(-6, 6, 1000) y = b_silu(x) y1 = b_silu_derivative(x)plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) ax = plt.gca() plt.plot(x, y, label='B-SiLU') plt.plot(x, y1, label='Derivative') plt.title('B-SiLU (α=1.67) and Derivative')ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))plt.legend(loc=2) plt.savefig('./b_silu.jpg') plt.show()
优缺点
-
B-SiLU 的优点
- 有界输出:下限 −α/2-\alpha/2−α/2、上限趋于 +∞+\infty+∞。
- 平滑可导:避免 ReLU 的“死亡”现象,反向传播更稳定。
- 非单调性:负区间小负值仍保留部分梯度,有利于信息流动。
- 兼容 ReLU:前向与 ReLU 近似,易于替换且无需大幅调参。
-
B-SiLU 的缺点
- 计算量略高:相比 ReLU 多了 sigmoid 运算。
- 超参数 α\alphaα:需要针对任务微调,通用性稍逊。
- 研究阶段:目前应用案例不如 ReLU/Swish 丰富。
PyTorch 中的 B-SiLU
-
代码
import torch import torch.nn.functional as Ftorch.manual_seed(1024)def b_silu(x, alpha=1.67):return (x + alpha) * torch.sigmoid(x) - alpha / 2x = torch.randn(3) y = b_silu(x) print("x:", x) print("B-SiLU(x):", y)输出示例
x: tensor([-1.4837, 0.2671, -1.8337]) B-SiLU(x): tensor([-0.8006, 0.2622, -0.8576])
TensorFlow 中的 B-SiLU
-
代码
import tensorflow as tf@tf.function def b_silu(x, alpha=1.67):return (x + alpha) * tf.nn.sigmoid(x) - alpha / 2x = tf.constant([-1.4837, 0.2671, -1.8337], dtype=tf.float32) y = b_silu(x) print("x:", x.numpy()) print("B-SiLU(x):", y.numpy())输出示例
x: [-1.4837 0.2671 -1.8337] B-SiLU(x): [-0.80055887 0.2621364 -0.85755754]
备注
- 这篇论文发布于2025年5月,目前这个B-SiLU 在反向传播中 作为 ReLU 的平滑导数替代函数。所以暂时这里只关注
