C++回顾 Day7
调用子类构造器之前就会调用父类构造器
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class father
{public:father(){cout << "father()" << endl;}private:int a;
};class son : public father
{public:son(){cout << "son()" << endl;}
};class grandson : public son
{public:grandson(){cout << "grandson()" << endl;}
};int main()
{father f;cout << "---------------" << endl;son s;cout << "---------------" << endl;grandson g;return 0;
}//结果
//father()
//---------------
//father()
//son()
//---------------
//father()
//son()
//grandson()同时还要注意,子类只需要管好父类的构造器就可以了
class father
{public:father(int a):a(a){cout << "father()" << endl;}private:int a;
};class son : public father
{public:son():father(4) //father类没有无参构造所以必须显式调用{cout << "son()" << endl;}
};class grandson : public son
{public:grandson() //son类有无参构造所以不必显式调用{cout << "grandson()" << endl;}
};
当然了,如果son类通过son(int a):father(a)这种传入参数的方式对father类进行初始化,并且son类不包含其他的默认构造参数,那么grandson类的构造器也必须显式调用son类的构造器
初始化顺序:父类的初始化,类对象的初始化,本类的初始化
遵循一个原则:想要初始化一个类就要先初始化其父类的全部,再初始化其类对象
继承后的拷贝构造器
子类没有自实现拷贝构造器则使用子类的默认拷贝构造器,而子类的默认拷贝构造器会调用父类的拷贝构造器
若实现了则使用自实现的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class student
{public:student(string sn,int ia,string sg):name(sn),age(ia),gender(sg){}student(const student &another):name(another.name)//写成参数列表运行快就是因为还未生成this指针就进行了赋值 {this->age = another.age;this->gender = another.gender;}void show(){cout << "name :" << name << endl;cout << "age :" << age << endl;cout << "gender:" << gender << endl;}private:string name;int age;string gender;
};class graduate : public student
{public:graduate(string sn,int ia,string sg,int ss):student(sn,ia,sg),salary(ss){}graduate(const graduate &another):student(another),salary(another.salary)//这里调用了 父类构造器,传入子类用来初始化父类,这是赋值兼容 //赋值兼容:子类的引用或指针能够赋给父类对象的引用或指针 {//this->name = another.name;//这是不合法的,因为name是父类的private成员,对子类是不可见的 }void print(){show();cout << "salary:" << salary << endl;}private:int salary;
};int main()
{student s1("bob",18,"男");s1.show();cout << "----------------" << endl; student s2 = s1;s2.show();cout << "----------------" << endl; graduate g1("dick",22,"女",23000);g1.print();cout << "----------------" << endl; graduate g2 = g1;g2.print();return 0;
}继承后的赋值重载
子类没有自实现赋值重载则使用子类的默认赋值重载,而子类的默认赋值重载会调用父类的赋值重载
若实现了则使用自实现的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class student
{public:student(string sn,int ia,string sg):name(sn),age(ia),gender(sg){}student(const student &another):name(another.name){this->age = another.age;this->gender = another.gender;}student& operator=(const student& another){cout << "student& operator=(const student& another)" << endl;if(this == &another)return *this;this->name = another.name;this->age = another.age;this->gender = another.gender;return *this;}void show(){cout << "name :" << name << endl;cout << "age :" << age << endl;cout << "gender:" << gender << endl;}private:string name;int age;string gender;
};class graduate : public student
{public:graduate(string sn,int ia,string sg,int ss):student(sn,ia,sg),salary(ss){}graduate(const graduate &another):student(another),salary(another.salary){}graduate& operator=(const graduate& another){if(this == &another)return *this;//不写也可以,因为父类赋值重载有自赋值检查,但是加上会使得代码更加健壮 student::operator=(another);//调用了父类的赋值重载,必须加作用域,//不然对于重名的成员,子类会把父类中重名的成员shadow掉//shadow与重载不同,只和参数名有关//同时,这里也发生了一次赋值兼容//这里就会导致递归,程序崩溃 this->salary = another.salary;} void print(){show();cout << "salary:" << salary << endl;}private:int salary;
};int main()
{student s1("bob",18,"男");s1.show();cout << "----------------" << endl; student s2("111",1,"1");s2.show();cout << "----------------" << endl; s2 = s1;s2.show();cout << "----------------" << endl; graduate g1("dick",22,"女",23000);g1.print();cout << "----------------" << endl; graduate g2("222",2,"2",2);g2.print();cout << "----------------" << endl; g2 = g1;g2.print();return 0;
}注意:
绝不要使得子类中的成员和父类中的成员同名
如果同名发现冲突,要加上作用域(命名空间)
继承后的友元函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class father
{public:father(int _a,int _b):a(_a),b(_b){}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &os,father &f);private:int a;int b;
};ostream& operator<<(ostream &os,father &f)
{os << f.a << endl << f.b << endl;
}class son : public father
{public:son(int _a,int _b,int _c):father(_a,_b),c(_c){}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,son &s);private:int c;
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,son &s)//只写函数不写具体实现cout << s就不输出了,//因为严格匹配到了这个函数,不再赋值兼容
{cout << static_cast<father&>(s);//static_cast<father>(s)的话就要//将之前的函数的参数变成const father &f //father::operator<<(cout,s);不对 //友元函数并不是类的一个成员函数,而是与类相关联的一个函数//因此,它不能通过类的作用域解析运算符 :: 直接作为成员函数来调用os << s.c << endl;
}int main()
{father f(1,2);cout << f;son s(3,4,5);//cout << s;//这里会输出3和4,是因为发生了一次赋值兼容 cout << s;return 0;
}注意:
继承不会继承友元关系;
不能通过域解析运算符 :: 调用父类中的同名的友元函数
析构函数调用的顺序和构造函数相反
先析构子类,再析构对象成员,最后析构父类
对于不同的继承方式
99%使用的都是public继承
不同访问权限的作用
public用来提供接口
protected用来隐藏数据,传承数据
private用来隐藏数据
继承方式总结
public继承了接口,也传承了数据
protected只传承了数据
private既没有继承接口,也没有传承数据
多继承
当一个子类继承自多个父类,而父类之间又有重名的成员,便会出现冗余数据(数据保存了两份),还会给使用者带来不便利(使用前必须加上作用域(类名::))
为了解决这种问题,出现了虚基类和虚继承
就是将这两个父类中共有的东西提取出来放到一个类M里面,然后让这两个父类都虚继承自这个虚基类M。这样数据就只有一份,访问也不会有冲突
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class M
{public:int m;M(int _m):m(_m){}void show(){cout << m << endl;}
}; class A : virtual public M
{public:A(int a):M(a){}void M_set(int x){m = x;}
};class B : virtual public M
{public:B(int b):M(b){}void M_get(){cout << m << endl;}
};class myclass : public A,public B
{public:myclass(int x):A(2),B(3),M(x){}//这里必须把M的初始化也完成,并且A、B的初始化本质上对m的值没有影响,只是陪跑的void print(){cout << m << endl;}
};int main()
{
// A a(10);
// cout << "A a(10);" << endl;
// B b(20);
// cout << "B b(20);" << endl;
// myclass c(30);
// cout << "myclass c(30);" << endl;
// a.M_set(100);
// cout << "a.M_set(100);" << endl;
// cout << "b.M_get() = ";
// b.M_get();
// cout << "c.print() = ";
// c.print();
// c.m = 999;
// cout << "c.m = 999;" << endl;
// cout << "c.print() = ";
// c.print();
// cout << "b.M_get() = ";
// b.M_get();myclass t(20);t.show();t.print();t.M_set(10);t.show();t.print();t.m = 999;t.show();t.print();//由于只有M里面存着一份,所以使用A类继承过来的赋值进行赋值还是使用直接赋值都只有一份结果return 0;
}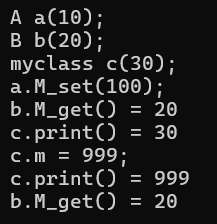
注意:当同时存在A、B和myclass类时,里面的m是互不干扰的
当只有一个myclass类时,可以理解为将M、A、B的内容都聚合到了一起,只有一份存储
