【Elasticsearch】文档(二):更新
文档(二):更新
- 1.创建测试数据
- 2.更新文档
- 2.1 在原有基础上新增字段
- 2.2 在原有字段基础上部分修改字段值
- 2.3 存在则更新,不存在则插入给定值(upsert)
- 2.4 全部文档更新(批量更新)
- 2.5 基于 Painless 脚本的批量更新
- 2.6 基于 Ingest 预处理管道的批量更新
- 2.7 取消更新
- 2.8 总结
在 Elasticsearch 中,更新文档 需要满足以下前置条件:
- 文档必须存在(除非使用
upsert操作) - 索引必须存在
- 用户需要有写入权限(
write或all权限) _version冲突检查(如果指定if_seq_no和if_primary_term)
1.创建测试数据
- 创建索引:
users
PUT /users
{"mappings": {"properties": {"name": { "type": "text" },"email": { "type": "keyword" },"age": { "type": "integer" },"created_at": { "type": "date" }}}
}

- 创建索引:
products
PUT /products
{"mappings": {"properties": {"name": { "type": "keyword" },"price": { "type": "double" },"category": { "type": "keyword" }}}
}

- 创建索引:
orders
PUT /orders
{"mappings": {"properties": {"order_id": { "type": "keyword" },"amount": { "type": "double" },"status": { "type": "keyword" },"discount": { "type": "double" }}}
}

- 创建索引:
books
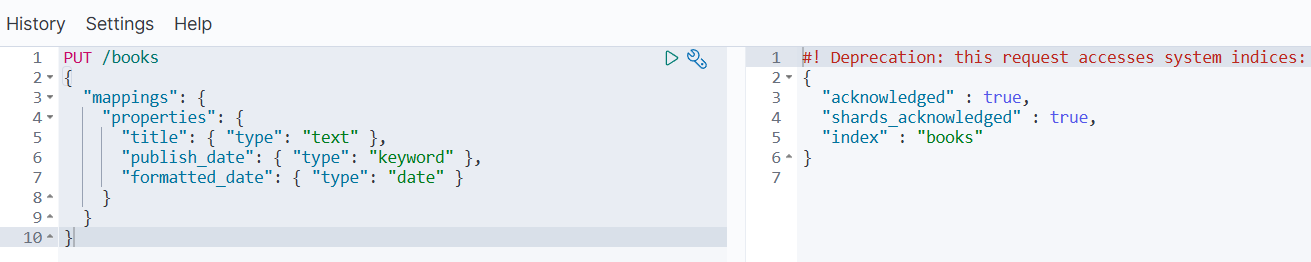
PUT /books
{"mappings": {"properties": {"title": { "type": "text" },"publish_date": { "type": "keyword" },"formatted_date": { "type": "date" }}}
}
2.更新文档
2.1 在原有基础上新增字段
写入数据。
POST /users/_doc/1
{"name": "John Doe","email": "john@example.com"
}

场景:给现有文档添加新字段。例如,给用户文档添加 age 字段。
POST /users/_update/1
{"doc": {"age": 30 # 新增字段}
}

2.2 在原有字段基础上部分修改字段值
写入数据。
POST /users/_doc/2
{"name": "Alice","email": "alice@old.com","age": 25
}

场景:修改文档的某个字段。例如,更新用户的 email。
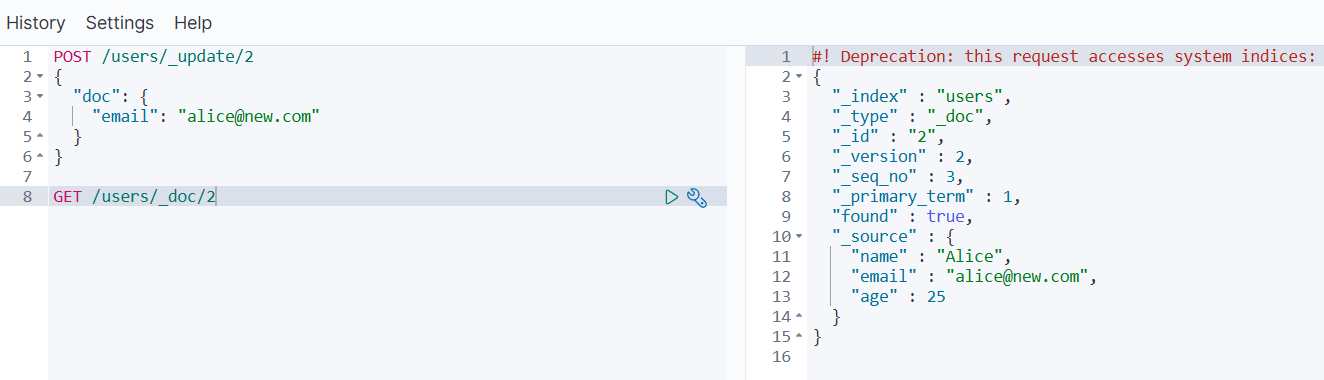
POST /users/_update/2
{"doc": {"email": "alice@new.com"}
}
2.3 存在则更新,不存在则插入给定值(upsert)
如果文档不存在,直接更新会报错。

场景:如果文档存在则更新,否则插入(upsert)新文档(类似 INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE)。
POST /users/_update/3
{"doc": {"name": "Bob","age": 40},"upsert": {"name": "Bob","age": 40,"created_at": "2023-01-01"}
}

2.4 全部文档更新(批量更新)
写入数据。
POST /products/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"Laptop","price":1000,"category":"Electronics"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"Coffee","price":5,"category":"Food"}

场景:更新索引中的所有文档(例如,将所有商品的 price 增加 10 % 10\% 10%),使用 _update_by_query。
POST /products/_update_by_query
{"query": { "match_all": {} }, # 匹配所有文档"script": {"source": "ctx._source.price = ctx._source.price * 1.1D", # 价格增加 10%,D表示double"lang": "painless"}
}

2.5 基于 Painless 脚本的批量更新
写入数据。
POST /orders/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"O1001"}}
{"order_id":"O1001","amount":1500,"status":"pending"}
{"index":{"_id":"O1002"}}
{"order_id":"O1002","amount":800,"status":"pending"}

场景:使用脚本动态更新文档。例如,根据条件修改 status。
POST /orders/_update_by_query
{"query": { "range": { "amount": { "gte": 1000 } } # 金额 >= 1000 的订单},"script": {"source": """ctx._source.status = "VIP"; # 更新 statusctx._source.discount = 0.1; # 新增 discount 字段""","lang": "painless"}
}

2.6 基于 Ingest 预处理管道的批量更新
写入数据。
POST /books/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"B001"}}
{"title":"Elasticsearch Guide","publish_date":"2023-05-20"}
{"index":{"_id":"B002"}}
{"title":"Kibana Handbook","publish_date":"2023-08-15"}

场景:在写入或更新时自动处理数据。例如,标准化日期格式。
步骤 1:创建预处理管道
PUT _ingest/pipeline/format_date_pipeline
{"description": "标准化日期格式","processors": [{"date": {"field": "publish_date","target_field": "formatted_date","formats": ["yyyy-MM-dd"],"timezone": "UTC"}}]
}

步骤 2:使用管道更新文档
POST /books/_update_by_query?pipeline=format_date_pipeline
{"query": { "match_all": {} }
}

2.7 取消更新
场景:在更新过程中取消任务(如长时间运行的 _update_by_query)。
步骤 1:准备测试数据(10万条文档)
POST /products/_bulk
{"index":{}}
{"name":"Test","price":10,"category":"A"}
{"index":{}}
{"name":"Test","price":10,"category":"B"}
...(重复直到文档数足够多)
步骤 2:发起一个真实的长任务
POST /products/_update_by_query?wait_for_completion=false
{"query": { "match_all": {} },"script": {"source": "ctx._source.price += 0.1","lang": "painless"}
}
步骤 3:查找任务 ID
GET _tasks?actions=*update_by_query
{"nodes": {"node-1": {"tasks": {"abc123": { # 任务 ID"action": "indices:data/write/update/byquery","description": "update_by_query [products]"}}}}
}
步骤 4:取消任务
POST _tasks/abc123/_cancel
{"acknowledged": true,"task_failures": []
}
2.8 总结
| 更新类型 | 适用场景 | API |
|---|---|---|
| 新增字段 | 扩展文档结构 | POST /index/_update/{id} |
| 修改字段 | 部分更新 | POST /index/_update/{id} |
| 存在则更新,否则插入 | 避免重复插入 | POST /index/_update/{id} + upsert |
| 批量更新 | 全量修改 | POST /index/_update_by_query |
| 脚本更新 | 复杂逻辑 | POST /index/_update_by_query + Painless |
| Ingest 管道 | 数据预处理 | POST /index/_update_by_query?pipeline=xxx |
| 取消更新 | 终止任务 | POST _tasks/{task_id}/_cancel |
这些方法覆盖了 Elasticsearch 文档更新的主要需求,可根据业务场景选择合适的方式。
