前言
前提要求
- 安装 virtualbox 和vagrant<vagrant-disksize> (Linux 方式 Windows 方式)
创建一键部署ubuntu虚拟机
- /opt/vagrant 安装目录
- /opt/VirtualBox 安装目录
- /opt/ubuntu22/Vagrantfile (可配置网络IP,内存,cpu,磁盘及分区,启动项,虚拟化开启,usb3.0,安装软件) 参考
- 用户名密码 root:1234@com,vagrant:1234@com 远程连接端口 2221
- /usr/lib/systemd/system/vagrant-autostart.service 开机启动脚本
- /usr/bin/vagrant_start.sh 启动脚本,可以执行批量启动关闭
- /usr/bin/vagrant_stop.sh 关闭脚本,可以执行批量启动关闭
- /var/log/vagrant_startup.log 启动日志记录
- /var/log/vagrant_shutdown.log 关闭日志记录
- box 导入参数参考
- 导出参考
- box images download
vim /vagrant_import_ubuntu.sh
#!/bin/bash
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: make.han
# Date: 2025/04/14
# vagrant ubuntu
<<!
# vagrant vm
https://portal.cloud.hashicorp.com/vagrant/discover
# ubuntu box download
https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/
# vagrant docs
https://developer.hashicorp.com/vagrant/docs
# vagrant download
https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant
# vagrant gitlab
https://github.com/hashicorp/vagrant/releases
# vagrantfile config
https://developer.hashicorp.com/vagrant/docs/vagrantfile/machine_settings
# vagrant 常用命令参考
vagrant init # 初始化
vagrant up # 启动虚拟机
vagrant halt # 关闭虚拟机
vagrant reload # 重启虚拟机
vagrant ssh # SSH 至虚拟机
vagrant suspend # 挂起虚拟机
vagrant resume # 唤醒虚拟机
vagrant status # 查看虚拟机运行状态
vagrant destroy # 销毁当前虚拟机
#box管理命令
vagrant box list # 查看本地box列表
vagrant box add # 添加box到列表
vagrant box remove # 从box列表移除
!
echo "create ubuntu directory"
mkdir -p /opt/ubuntu-22.04
cd /opt/ubuntu-22.04
echo "add init config"
cat <<'EOF'>>/opt/ubuntu-22.04/Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "ubuntu-22.04"
# hosts name
config.vm.hostname = "ubuntu-22.04"
# Default boot disk size
config.vm.disk :disk, size: "100GB", primary: true
# Add new disks (vagrant plugin install vagrant-disksize)
#config.disksize.size = "80GB"
# Set the guest operating system type (:linux :windows)
config.vm.guest = :linux
# Configure SSH username and password
config.ssh.username = "vagrant" # Default User
#config.ssh.password = "1234@com" # config password
# Password login
config.ssh.keys_only = false # Disable key authentication
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
config.vm.network :forwarded_port, guest: 22, host: 2221, host_ip: "0.0.0.0"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# Configure as a public network, the virtual machine will obtain an IP address in the same network segment as the host through DHCP
# config.vm.network "public_network"
#config.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.11.82"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Disable the default share of the current code directory. Doing this
# provides improved isolation between the vagrant box and your host
# by making sure your Vagrantfile isn't accessible to the vagrant box.
# If you use this you may want to enable additional shared subfolders as
# shown above.
# config.vm.synced_folder ".", "/vagrant", disabled: true
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
vb.gui = false
#
# Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
vb.memory = "8096"
# 42 CPU cores
vb.cpus = 2
# Enable nested virtualization (optional)
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--nested-hw-virt", "on"]
# vm name
vb.name = "ubuntu-22.04"
# Startup Item Settings
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--boot1", "disk"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--boot2", "dvd"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--boot3", "floppy"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--boot4", "net"]
# Enable USB controller (USB 2.0)
#vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--usb", "on"]
#vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--usbehci", "on"]
# Enable USB controller (USB 3.0)
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--usb", "on"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--usbxhci", "on"]
# Enable bidirectional shared clipboard and drag and drop functionality
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--clipboard", "bidirectional"]
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--draganddrop", "bidirectional"]
end
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Define a Vagrant Push strategy for pushing to Atlas. Other push strategies
# such as FTP and Heroku are also available. See the documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com/v2/push/atlas.html for more information.
# config.push.define "atlas" do |push|
# push.app = "YOUR_ATLAS_USERNAME/YOUR_APPLICATION_NAME"
# end
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
echo "root:1234@com" | chpasswd
echo "vagrant:1234@com" | chpasswd
# add key
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAqeHJeGkyl1V+04VQ3TN5vfp1tROhrpxFIkxunJszRJpNakDjolZRDRfrKNTdn1D7z6rq1LLImZSqEj2AnNKA7OONGH73hHNVx6StCRjQo4UDy6bKBoToGjdb74D4zVFPuFqNfRX4i9yFi6Ujadf9Dsk4IeR/juD5stquE65kAB1q8S8zMdnPyZNt3JNhMh0aU23C6JTvUnqeeNQcYrhLOSPjQYZgNl4G2x6EYVRECokhTtw==" >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
# config DNS
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" > /etc/resolv.conf
echo "nameserver 8.8.4.4" >> /etc/resolv.conf
cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak
sed -i \
-e 's#http://archive.ubuntu.com/#https://mirrors.aliyun.com/#g' \
-e 's#http://security.ubuntu.com/#https://mirrors.aliyun.com/#g' \
-e 's#https://archive.ubuntu.com/#https://mirrors.aliyun.com/#g' \
-e 's#https://security.ubuntu.com/#https://mirrors.aliyun.com/#g' \
/etc/apt/sources.list
apt update
apt install -y openssh-server
sed -i 's/^#*PasswordAuthentication .*/PasswordAuthentication yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sed -i 's/^#*PermitEmptyPasswords .*/PermitEmptyPasswords no/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sed -i 's/#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password/PermitRootLogin yes/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config
systemctl restart ssh
SHELL
end
EOF
echo "download ubuntu vagrant"
curl -o /opt/ubuntu-22.04/ubuntu-22.04-server-cloudimg-amd64-vagrant.box https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/jammy/20250327/jammy-server-cloudimg-amd64-vagrant.box
echo "add vagrant list"
vagrant box add --name ubuntu-22.04 /opt/ubuntu-22.04/ubuntu-22.04-server-cloudimg-amd64-vagrant.box
# 在线下载
#vagrant init generic/ubuntu2204 --box-version 4.3.12
#echo "init vagrant-disksize"
#vagrant plugin install vagrant-disksize
#vagrant plugin install --plugin-clean-sources --plugin-source https://gems.ruby-china.com/ vagrant-disksize
echo "start ubuntu vm"
vagrant up
#echo "进入"
#vagrant ssh
echo "查看"
vagrant box list
echo "port firewall"
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=2221/tcp --permanent && firewall-cmd --reload
echo "vagrant service"
cat <<'EOF'>>/usr/lib/systemd/system/vagrant-autostart.service
[Unit]
Description=Auto-start Vagrant VM on boot
After=network.target vboxdrv.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vagrant_start.sh
ExecStop=/usr/bin/vagrant_stop.sh
RemainAfterExit=true
User=root
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
echo "Vagrant startup script"
cat <<'EOF'>>/usr/bin/vagrant_start.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 定义 Vagrant 项目目录列表
VAGRANT_PROJECTS=(
"/opt/ubuntu-22.04"
)
# 遍历每个 Vagrant 项目并启动虚拟机
for project in "${VAGRANT_PROJECTS[@]}"; do
echo "切换到 Vagrant 项目目录: $project 并启动虚拟机..."
if [ -d "$project" ]; then
cd "$project" || { echo "无法进入目录: $project"; continue; }
vagrant up >> /var/log/vagrant_startup.log 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "虚拟机启动成功: $project"
else
echo "虚拟机启动失败: $project"
fi
else
echo "项目目录不存在: $project"
fi
done
EOF
echo "Vagrant close script"
cat <<'EOF'>>/usr/bin/vagrant_stop.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 定义 Vagrant 项目目录列表
VAGRANT_PROJECTS=(
"/opt/ubuntu-22.04"
)
# 遍历每个 Vagrant 项目并关闭虚拟机
for project in "${VAGRANT_PROJECTS[@]}"; do
echo "切换到 Vagrant 项目目录: $project 并关闭虚拟机..."
if [ -d "$project" ]; then
cd "$project" || { echo "无法进入目录: $project"; continue; }
vagrant halt >> /var/log/vagrant_shutdown.log 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "虚拟机关闭成功: $project"
else
echo "虚拟机关闭失败: $project"
fi
else
echo "项目目录不存在: $project"
fi
done
EOF
echo "赋予脚本权限"
chmod +x /usr/bin/{vagrant_start.sh,vagrant_stop.sh}
echo "启动服务,开机自启动"
systemctl enable vagrant-autostart.service
systemctl status vagrant-autostart.service
执行一键安装
bash /vagrant_import_ubuntu.sh
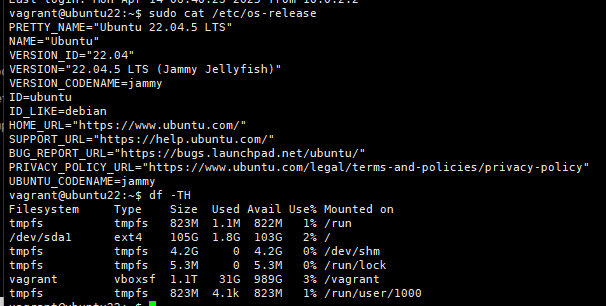
进入ubuntu 22系统
cd /opt/ubuntu22
vagrant ssh
进入virtualbox 管理界面
virtualbox
远程连接 MobaXterm或者Xmanager
- 端口 2221
- root:1234@com,vagrant:1234@com
- 创建好主机的ssh 密钥key 远程连接用到 上述脚本180行更换自己的公钥