STL之priority_queue的用法与实现
目录
1. priority_queue的介绍
1.1. priority_queue的概念
1.2. priority_queue的特点
2. 仿函数
2.1. 仿函数的概念
2.2. 仿函数的应用
2.3 仿函数的灵活性
3. priority_queue的用法
4. 模拟实现priority_queue
4.1. 插入
4.2. 删除
5. 源码
priority_queue.h
test.cpp
结果
💓 博客主页:C-SDN花园GGbond
⏩ 文章专栏:玩转c++
1. priority_queue的介绍
1.1. priority_queue的概念
priority_queue即为**优先级队列,**它是STL对数据结构中堆的具体封装,因为priority_queue的头文件倍包含在queue的头文件中,所以使用时只需要包含头文件#include<queue>,并且使用优先级队列建堆,默认为大堆。
探索数据结构与算法】堆的具体实现和应用
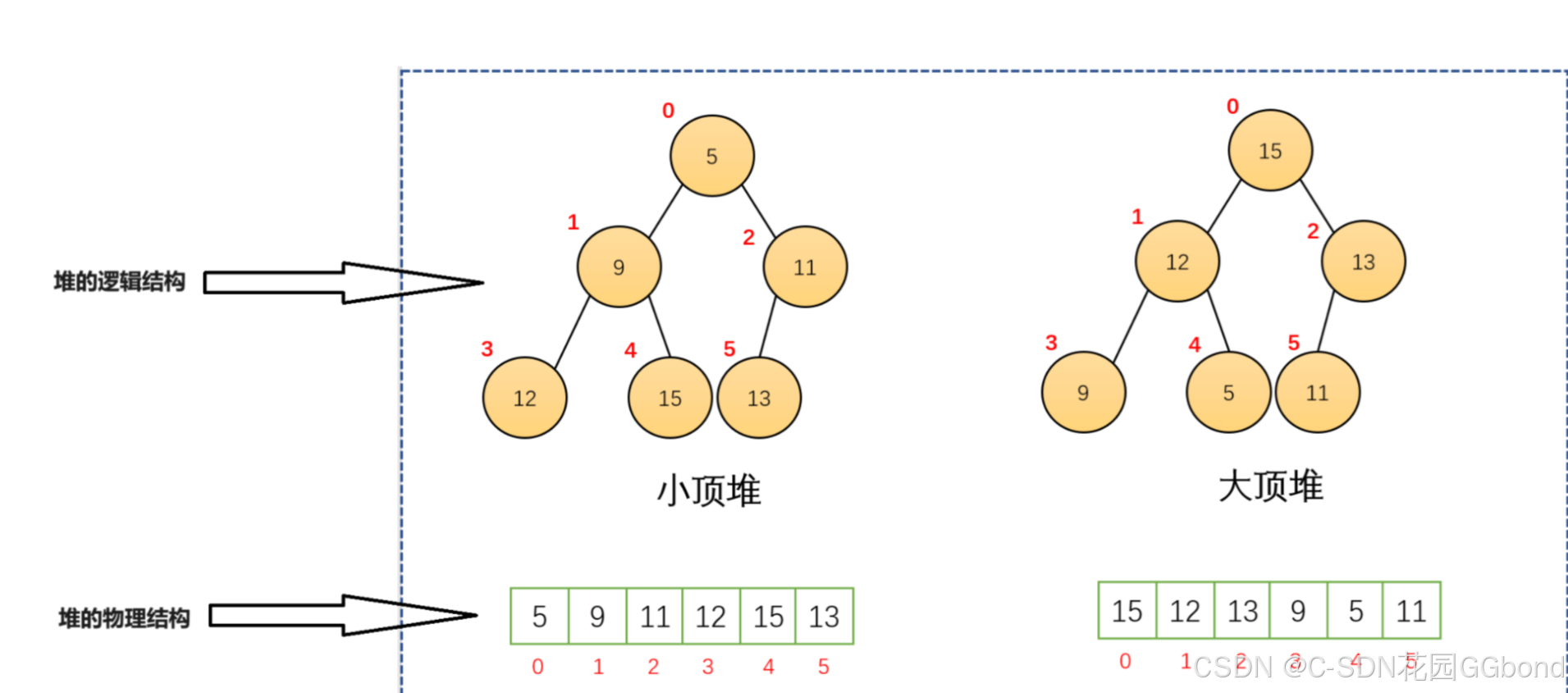
1.2. priority_queue的特点
priority_queue的模版参数有三个,第一个T是我们的元素类型,第二个Container是我们的容器适配器,第三个Compare是我们的仿函数。
priority_queue参考文档

2. 仿函数
2.1. 仿函数的概念
**仿函数(Functor)**是一种行为类似函数的对象,它可以被用作函数并接受参数。在 C++ 中,仿函数通常是重载了函数调用运算符 operator()的类对象。通过重载 operator(),仿函数可以像函数一样被调用,并且可以保存状态信息。
下面是一个具体的仿函数例子:
// 定义一个比较小于的仿函数
template<class T>
struct Less
{
//重载函数调用运算符
bool operator()(const T&a, const T&b)
{
return a < b;
}
};
int main()
{
Less<int> le;//定义一个仿函数对象
int a = 5, b = 9;
cout << le(a, b) << endl;//采用仿函数比较
cout << (Less<int>().operator()(a,b)) << endl;//完整调用
return 0;
}
我们可以通过定义对象的方式调用,也可以通过完整的类调用函数方式调用。
2.2. 仿函数的应用
在C++的标准库中,仿函数的使用就较为普遍,一般都作为模版参数进行传参。比如说算法库algorithm中的排序算法sort,默认排序就是升序,如果需要降序排序就需要传仿函数
这个仿函数或者函数我们可以自己定义,也可以借用标准库中提供的函数。其中比较常用的就是比较小于的less,比较大于的greater。使用时需要包含头文件#include<functional>。

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
template<class T>
struct Less
{
bool operator()(const T&a,const T&b)
{
return a < b;
}
};
template<class T>
struct Greater
{
bool operator()(const T& a, const T& b)
{
return a > b;
}
};
int main()
{
int a = 5,b = 9;
less<int> Ls;
cout << Ls(b, a) << endl;//采用仿函数比较
cout << less<int>().operator()(a, b) << endl;
//
vector<int> v = { 2,3,1,7,5,6,9,8 };
//sort(v.begin(), v.end());//默认升序
sort(v.begin(), v.end(),greater<int>());//降序
for (int& e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.3 仿函数的灵活性
仿函数 可以具有任意数量的参数,并可以用于各种不同的操作。这使得它们非常灵活,可以根据需要进行定制。
在这个示例中,我们创建了两个不同的仿函数,一个用于加法(MyAdditionFunc),一个用于减法( MySubtractionFunc ),它们可以根据需要进行切换。
class MyAdditionFunc
{
public:
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
};
class MySubtractionFunc
{
public:
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
};
int main()
{
MyAdditionFunc add;
MySubtractionFunc subtract;
int result1 = add(5, 3); // 8
int result2 = subtract(5, 3); // 2
std::cout << "Result of addition: " << result1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "Result of subtraction: " << result2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}

3. priority_queue的用法
priority_queue提供的接口相比较与其他容器也明显较少,这是由于其结构决定的,并且由于priority_queue也并不需要遍历,所以也不存在迭代器的概念。
以下就是priority_queue的接口:

我们学习过数据结构中的堆,所以使用这里的接口的成本也比较低。
void Test1()
{
priority_queue<int> heap;
heap.push(1);
heap.push(2);
heap.push(3);
heap.push(4);
heap.push(5);
heap.push(6);
cout << heap.size() << endl;
cout << heap.top() << endl;
while (!heap.empty())
{
cout << heap.top() << " ";
heap.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}
我们也可以使用greater仿函数让其变为小堆。
void Test1()
{
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> heap;//第三个模板参数为仿函数类型
heap.push(1);
heap.push(2);
heap.push(3);
heap.push(4);
heap.push(5);
heap.push(6);
cout << heap.size() << endl;
cout << heap.top() << endl;
while (!heap.empty())
{
cout << heap.top() << " ";
heap.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}
4. 模拟实现priority_queue
我们学习过堆这个数据结构,所以封装priority_queue会非常简单,只需要在原有的基础上增加一个仿函数即可
4.1. 插入
向堆的末尾插入新的元素,然后与父节点比较,然后判断是否需要向上调整。假设插入元素23,如下图:


//向上调整
void adjust_up(size_t child)
{
Compare com;//使用仿函数,
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
4.2. 删除
先将堆顶元素与最后一个元素交换,将删除堆顶元素转化为删除末尾元素,然后再对堆顶元素进行向下调整。



//向下调整
void adjust_down(size_t parent)
{
Compare com;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
while (child < _con.size())
{
//选出较大(小堆则较小)的那个孩子
if (child + 1 < _con.size()&& com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
child++;
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
}
剩余的size(),empty(),top()等接口实现就非常容易了,这需要复用我们容器适配器的接口即可。
const T& top()const
{
return _con[0];
}
size_t size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
5. 源码
priority_queue.h
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
namespace HTD
{
//template<class T,class Container=vector<T>,class compare=Greater<T>>
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class compare =Less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if(com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
compare com;
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child ] < _con[child+1])
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child],_con[child+1])) // 选出较大(小堆则较小)的那个孩子
{
child++;
}
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
if(com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}test.cpp
#include"priority_queue.h"
int main()
{
//priority_queue<int, vector<int>> pq;
HTD:: priority_queue<int, vector<int>> pq;
pq.push(4);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(7);
pq.push(9);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}结果

