辽源网站建设公司足球积分排行榜最新
算法笔记-第九章-树的遍历
- 树遍历的知识点
- emplace_back()用法
- top和pop的用法
- 树的先根遍历
- 理解本题思路
- 树的后跟遍历
- 树的层序遍历
- 树的循环队列遍历
- 树的高度
- 树的高度分析
- 题目
- 树的结点层号
树遍历的知识点
大佬总结的实在是太好了
大佬讲解数遍历
(遍历树的前序,中序,后序遍历的递归法和迭代法)
emplace_back()用法
功能:和 push_back() 相同,都是在 vector 容器的尾部添加一个元素。
push_back() 向容器尾部添加元素时,首先会创建这个元素,然后再将这个元素拷贝或者移动到容器中(如果是拷贝的话,事后会自行销毁先前创建的这个元素),而 emplace_back() 在实现时,则是直接在容器尾部创建这个元素,省去了拷贝或移动元素的过程。
top和pop的用法
top()是取栈顶元素
pop()是弹出栈顶元素
stack a;
a.push(1); // 1
a.push(2); // 1 2
a.push(3); // 1 2 3
int c = a.top(); // c = 3
a.pop(); // 1 2
a.push(4); // 1 2 4
c = a.top(); // c = 4
树的先根遍历
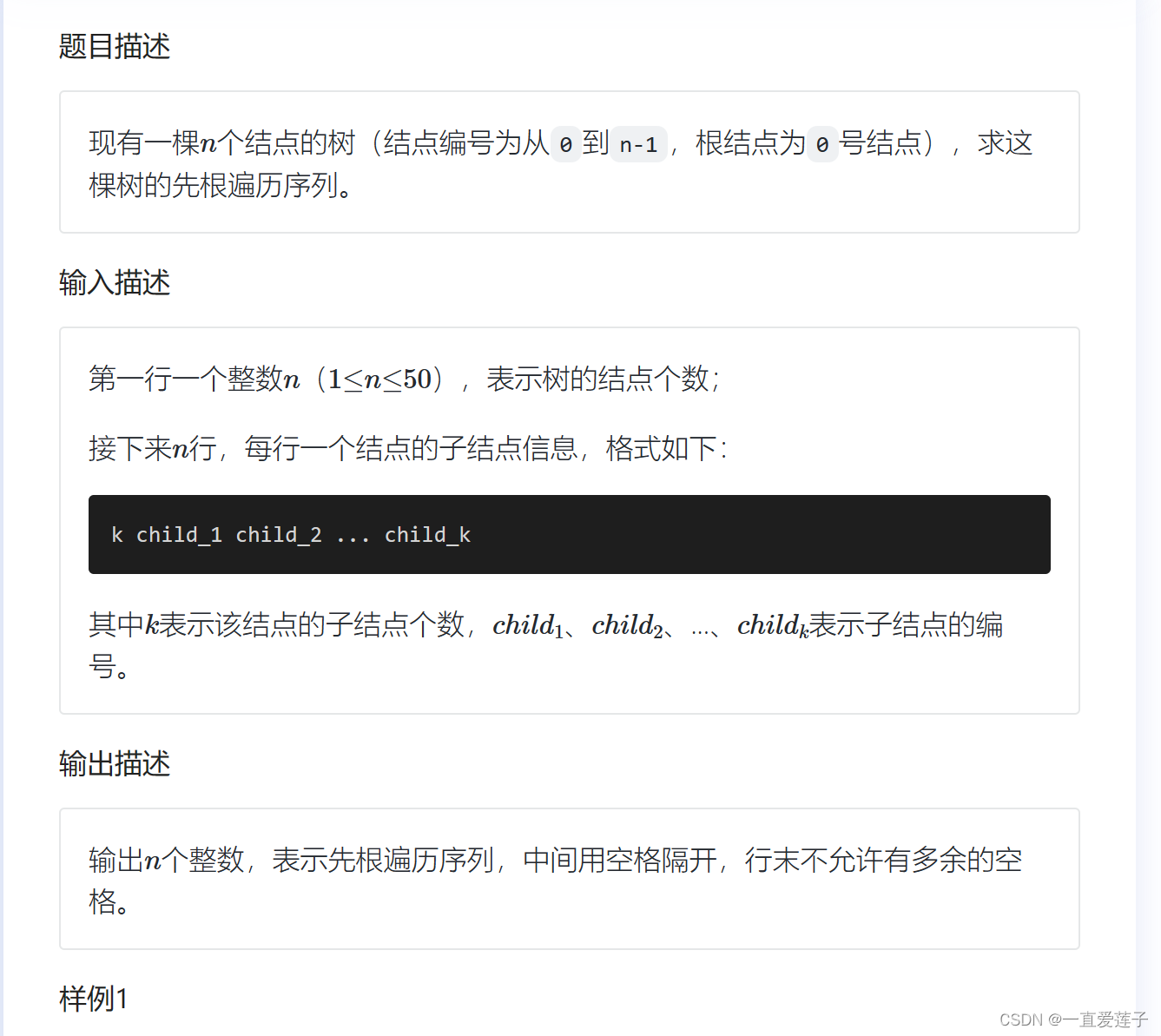
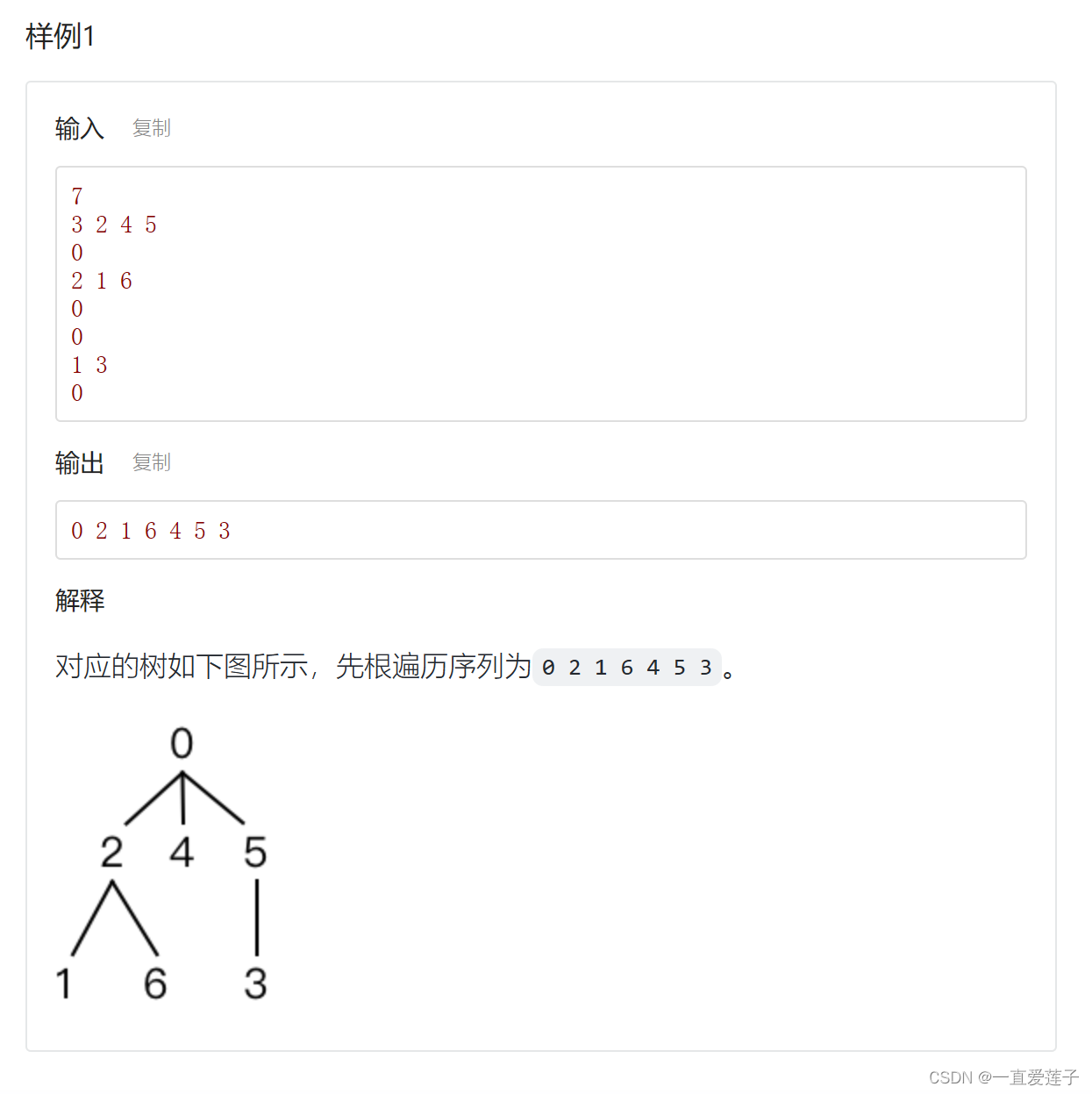
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 50;struct Node {vector<int> children;
} nodes[MAXN];vector<int> pre;void preOrder(int root) {pre.push_back(root);for (int i = 0; i < nodes[root].children.size(); i++) {preOrder(nodes[root].children[i]);}
}int main() {int n, k, child;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {scanf("%d", &k);for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {scanf("%d", &child);//每一行孩子节点信息nodes[i].children.push_back(child);//放到数组当中}}preOrder(0);//进行前序遍历for (int i = 0; i < pre.size(); i++) {printf("%d", pre[i]);if (i < (int)pre.size() - 1) {printf(" ");}}return 0;
}题目的思路不是递归也不是迭代,所有要理解的话,需要理解
理解本题思路
回顾二叉树节点的定义问题:是由数据域和指针域组成的,
指针域存放所有子结点的地址,或者可以存放所有子结点地址,
就是静态写法,用数组下标来代替所谓地址
struct node {typename data;//数据域int child[manx];//指针域,存放所有子结点下标
}node[maxn];//节点数组,maxn为结点上限个数
但是无法预知子节点的个数,所以只能将数组的个数加到不确定的位置
struct node
{typename data;vector child;
}node[maxn;与静态实现类似,当需要新建一个结点时,就按顺序从数组中取出一个下标
即可
int index = 0;
int newnode(int v)
{node[index].data = v;node[index].child.clear()return index++;
}一般来说,遍历二叉树的时候使用递归访问
但是对于根节点的子树来说,同样可以分为根节点和若干子树
这就是先根遍历
void preorder(int root)
{printf("%d ", node[root].data);//访问当前节点 for (int i = 0; i < node[data].child.size(); i++) {preorder(node[root].child[i]);//递归访问结点root的所有结点 }
}
树的后跟遍历
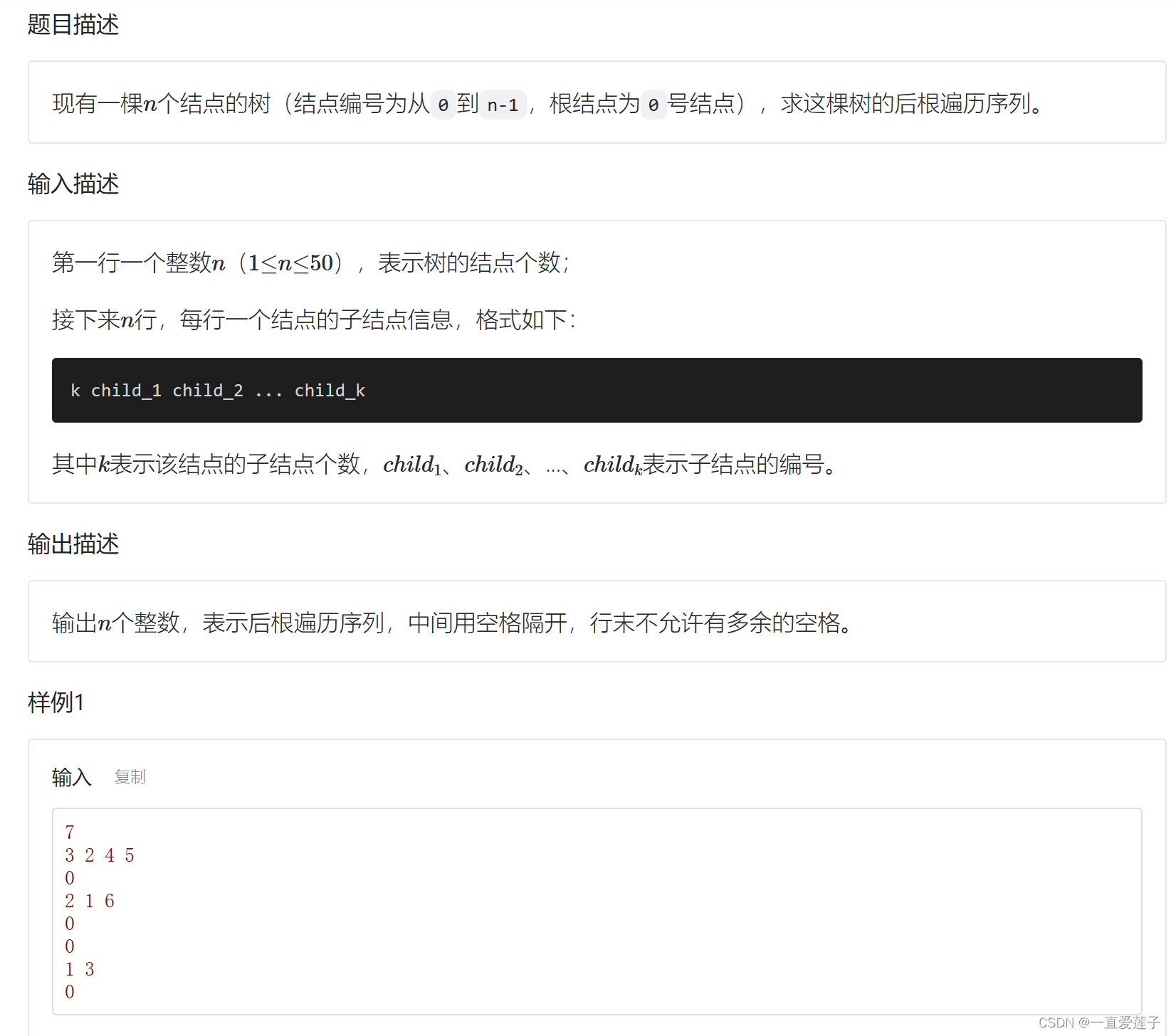
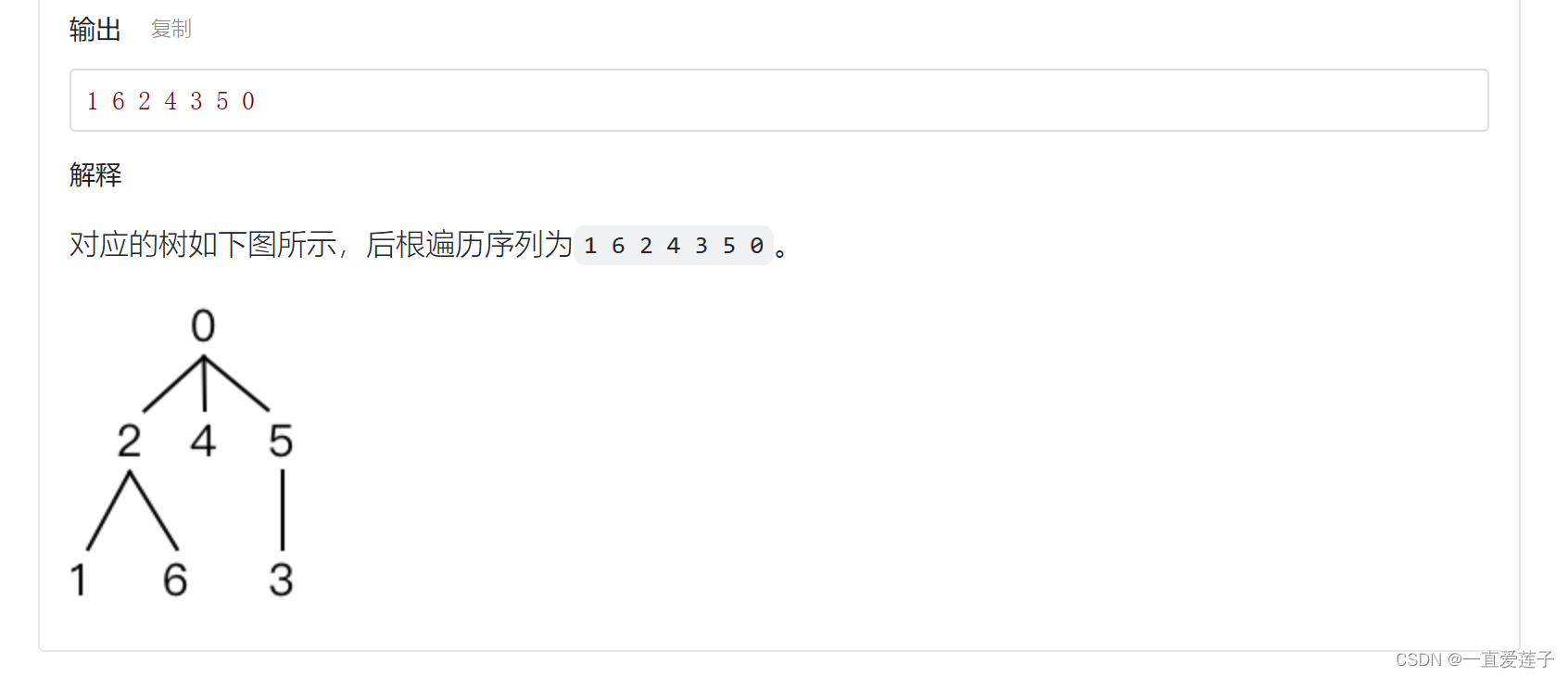
左右孩子,然后根结点
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 50;struct Node {vector<int> children;
} nodes[MAXN];vector<int> post;void postOrder(int root) {for (int i = 0; i < nodes[root].children.size(); i++) {postOrder(nodes[root].children[i]);}post.push_back(root);
}int main() {int n, k, child;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {scanf("%d", &k);for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) { scanf("%d", &child); nodes[i].children.push_back(child); }}postOrder(0); for (int i = 0; i < post.size(); i++) { printf("%d", post[i]); if (i < (int)post.size() - 1) { printf(" "); }}return 0;
}
树的层序遍历
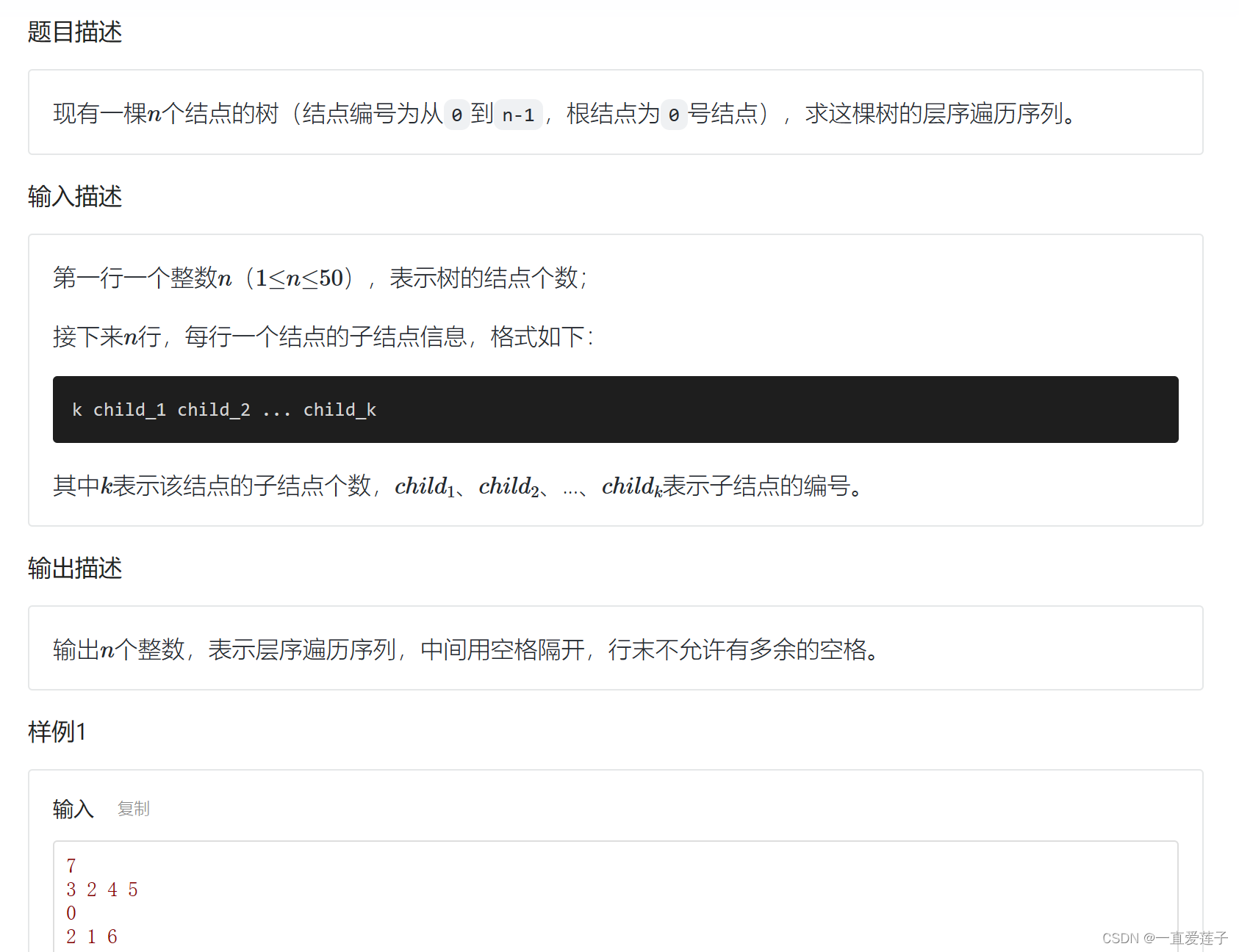
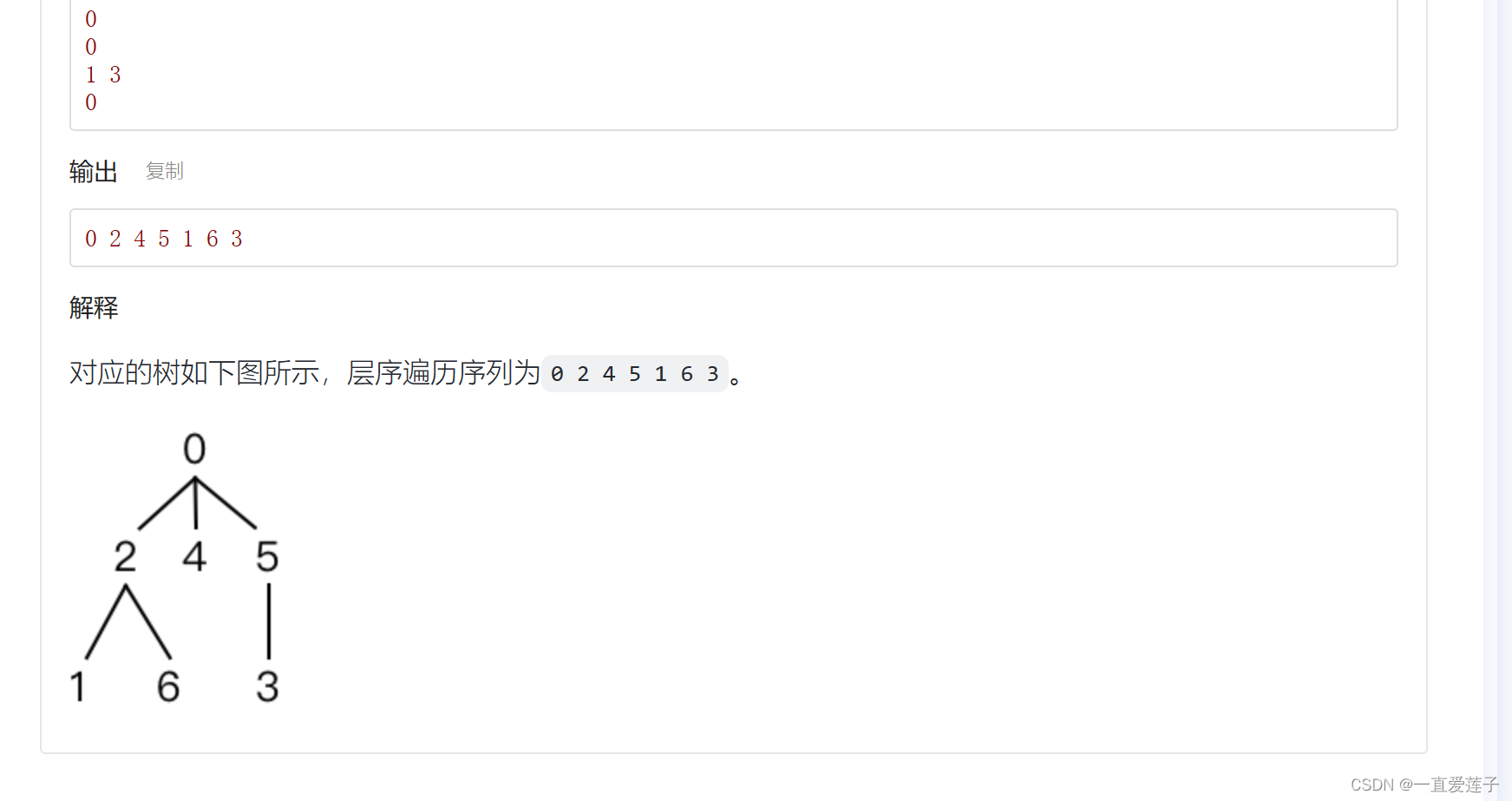
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 50;struct Node {vector<int> children;
} nodes[MAXN];vector<int> layer;void layerOrder(int root) {queue<int> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {int front = q.front();q.pop();layer.push_back(front);for (int i = 0; i < nodes[front].children.size(); i++) {q.push(nodes[front].children[i]);}}
}int main() {int n, k, child;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {scanf("%d", &k);for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {scanf("%d", &child);nodes[i].children.push_back(child);}}layerOrder(0);for (int i = 0; i < layer.size(); i++) {printf("%d", layer[i]);if (i < (int)layer.size() - 1) {printf(" ");}}return 0;
}
树的循环队列遍历
层次遍历
队列,循环加入到队列中
typedef struct
{BTNode* data[MaxSize];int front, rear;
}SqQueue;//层次遍历算法 结果:ABCDEFG
void LevelOrder(BTNode* b)
{BTNode* p;SqQueue* qu; //定义环形队列指针InitQueue(qu); //初始化队列enQueue(qu, b); //根结点进队while (!QueueEmpty(qu)) //队不空时循环 {deQueue(qu, p); //出队结点p printf("%c", p->data); //访问结点p if (p->lchild != NULL) //有左孩子时将其进队 enQueue(qu, p->lchild); if (p->rchild != NULL) //有右孩子时将其进队 enQueue(qu, p->rchild); }DestroyQueue(qu); //销毁队列
}
树的高度
树的高度分析
看大佬细致解释
思路:
树的高度就是表示树结点中最大层数
遍历到左子树和右子树,然后比较高度,层层的进行比较两边大小然后返回最大值
题目
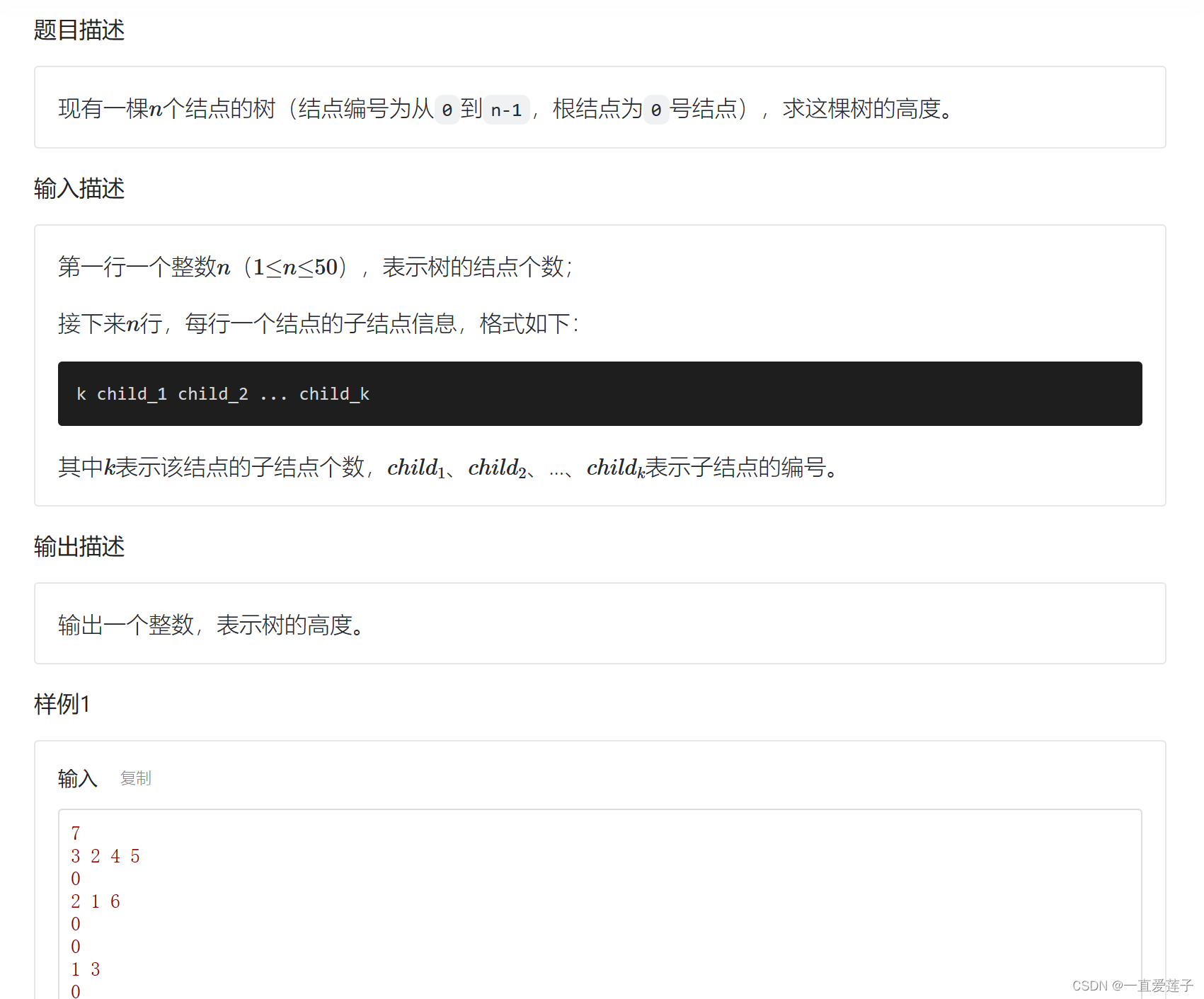
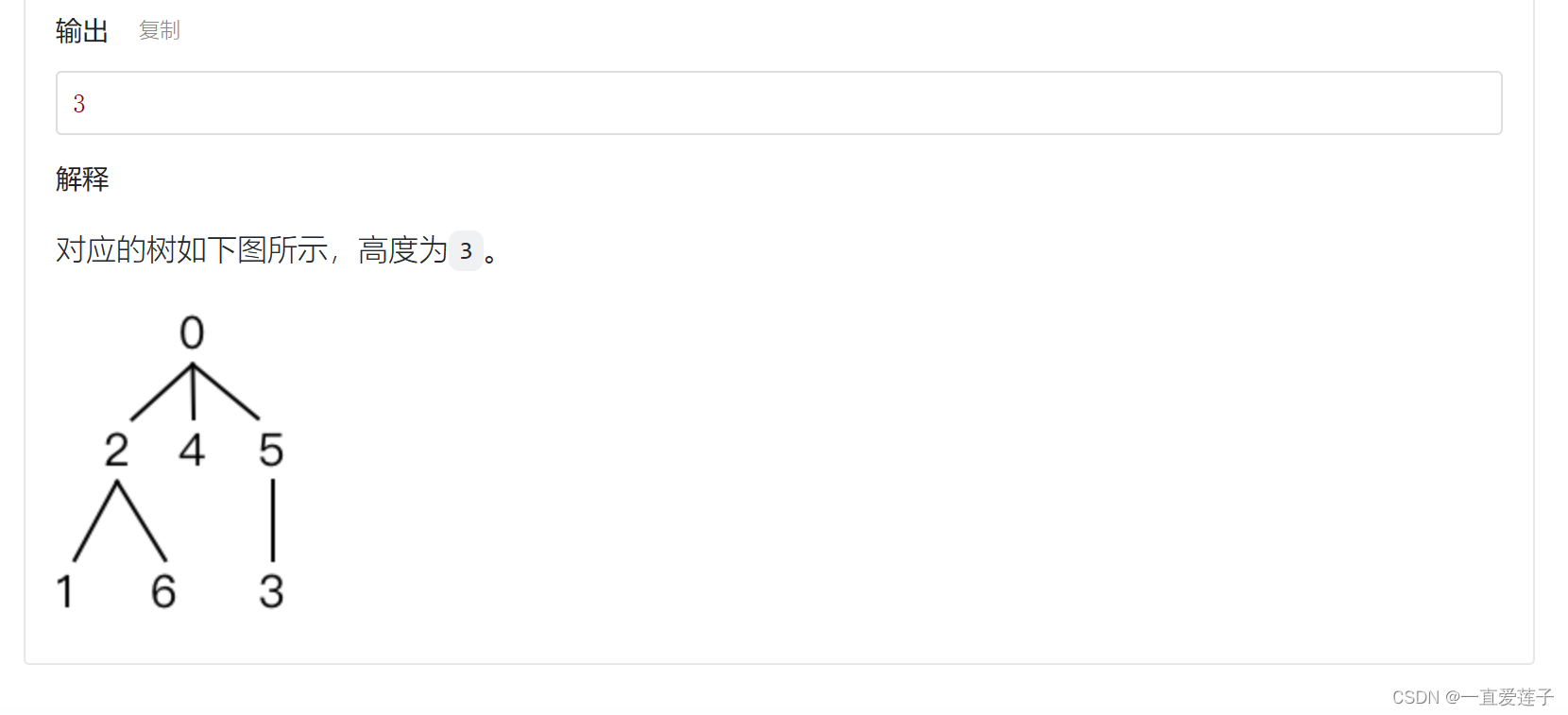
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 50;struct Node {vector<int> children;
} nodes[MAXN];int getHeight(int root) {int maxHeight = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nodes[root].children.size(); i++) {maxHeight = max(maxHeight, getHeight(nodes[root].children[i]));}return maxHeight + 1;
}int main() {int n, k, child;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {scanf("%d", &k); for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) { scanf("%d", &child); nodes[i].children.push_back(child); }}printf("%d", getHeight(0)); return 0;
}
树的结点层号
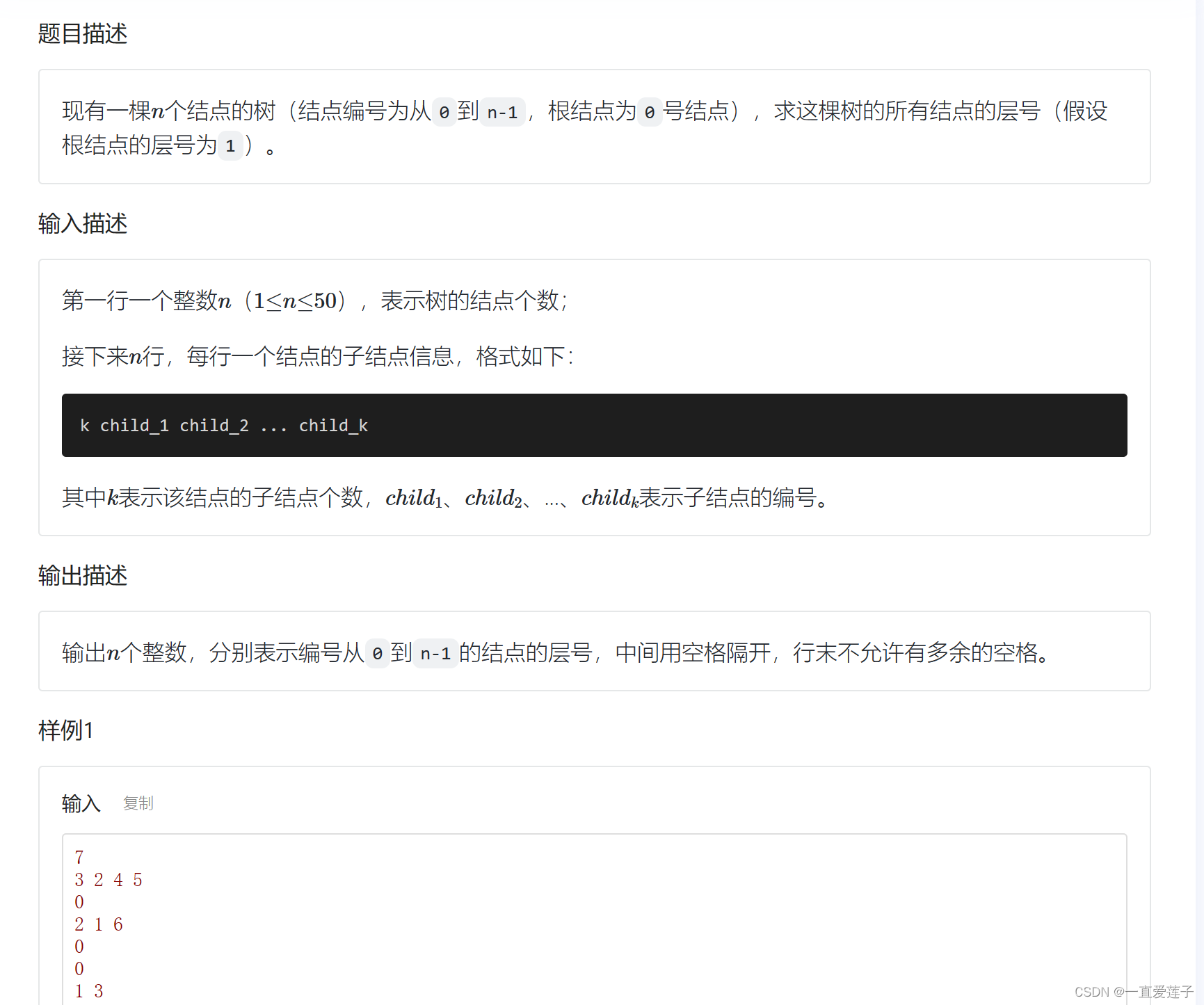
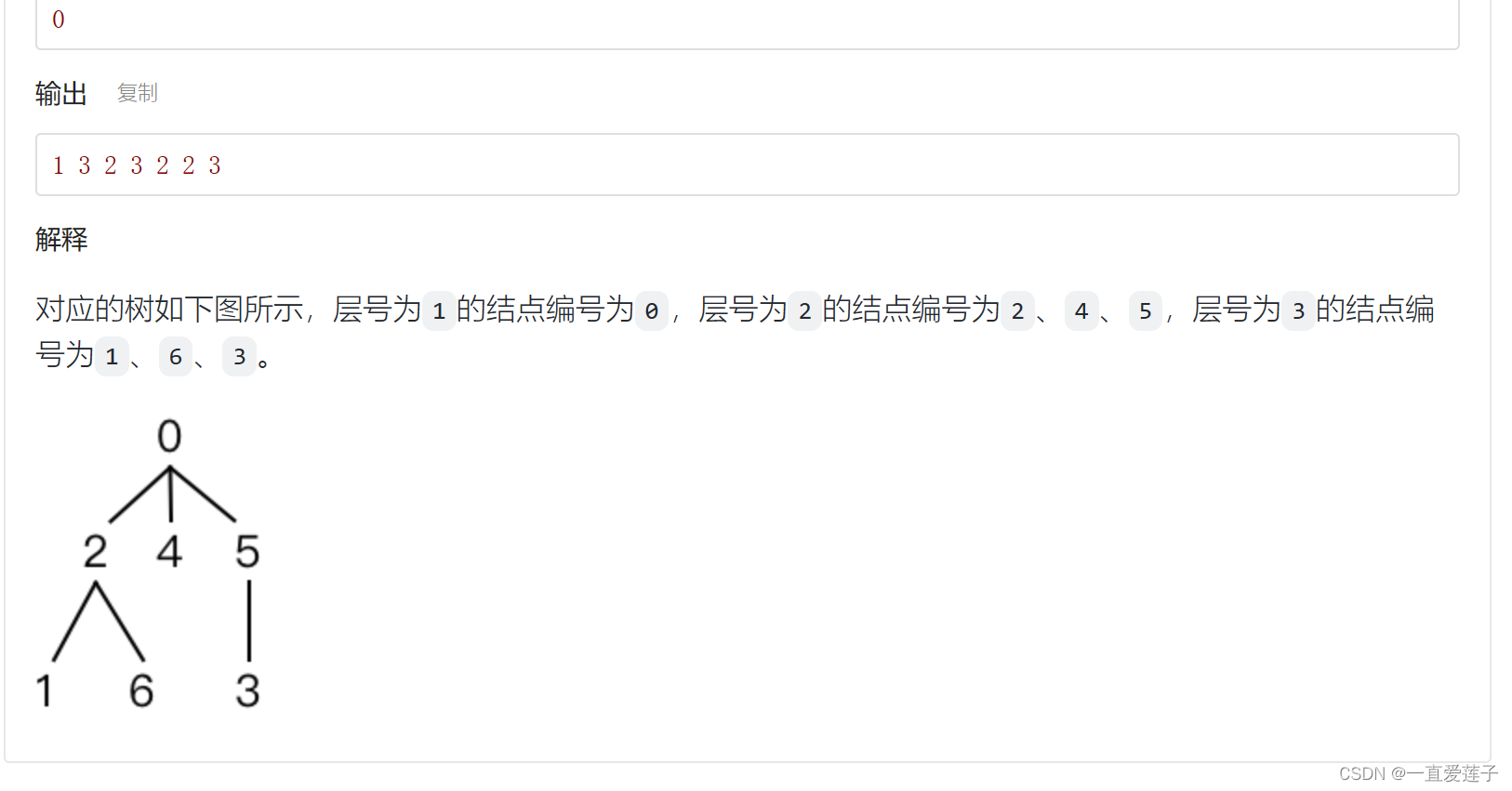
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;const int MAXN = 50;struct Node {vector<int> children;
} nodes[MAXN];//输入孩子结点int layers[MAXN];void layerOrder(int root) {queue<int> q;//队列q.push(root);int layer = 1;while (!q.empty()) {int cnt = q.size();for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {int front = q.front();q.pop();layers[front] = layer;for (int i = 0; i < nodes[front].children.size(); i++) {q.push(nodes[front].children[i]);}}layer++;}
}int main() {int n, k, child;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {scanf("%d", &k);for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {scanf("%d", &child);nodes[i].children.push_back(child);}}layerOrder(0);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {printf("%d", layers[i]);if (i < n - 1) {printf(" ");}}return 0;
}
