单周期Risc-V指令拆分与datapath绘制
功能性单周期Risc-V 处理器设计
目标:
对照risc-v手册,实现并调试自研单、多周期处理器
本次实验要实现下面指令:
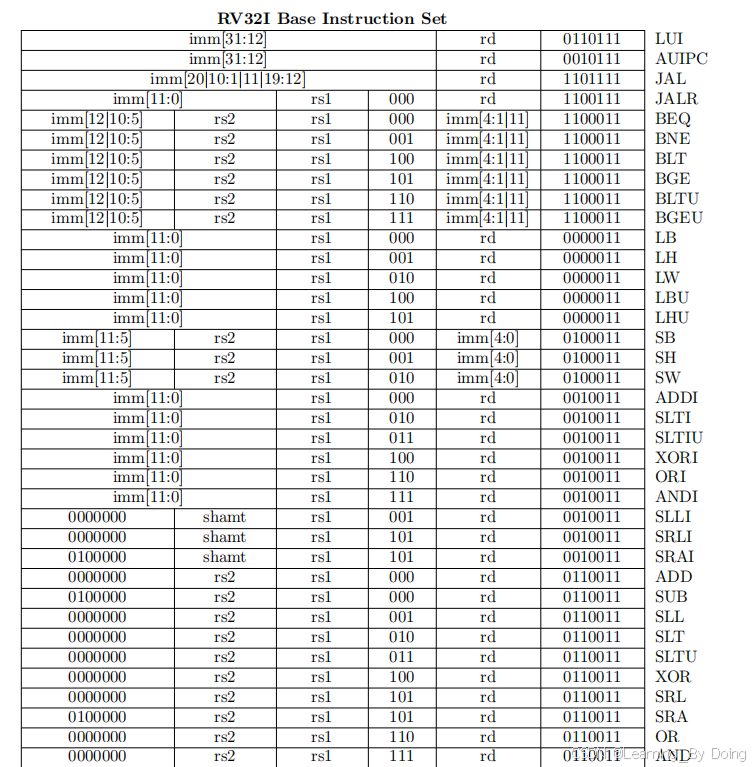
单周期实验目标模块
注意
Risc-V的指令构成与MIPS指令并不一样:
I-Type 指令:
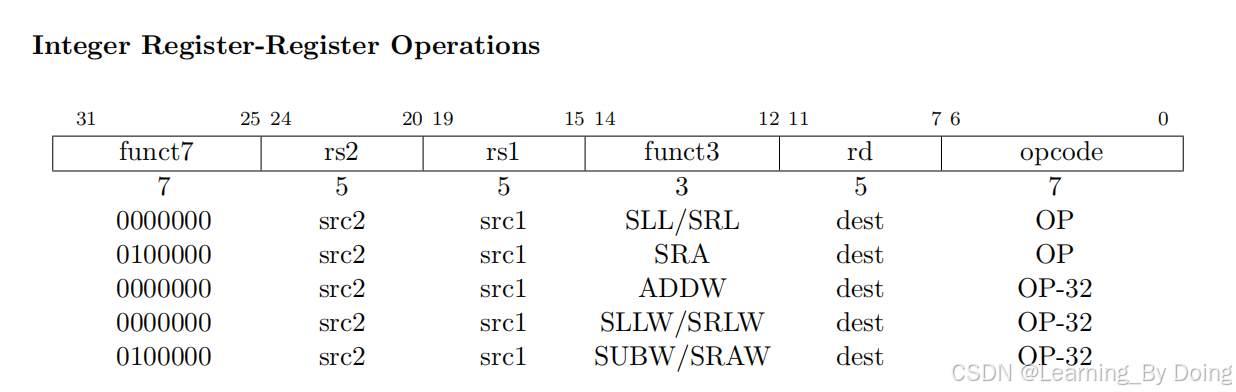
根据这个表来扩展立即数
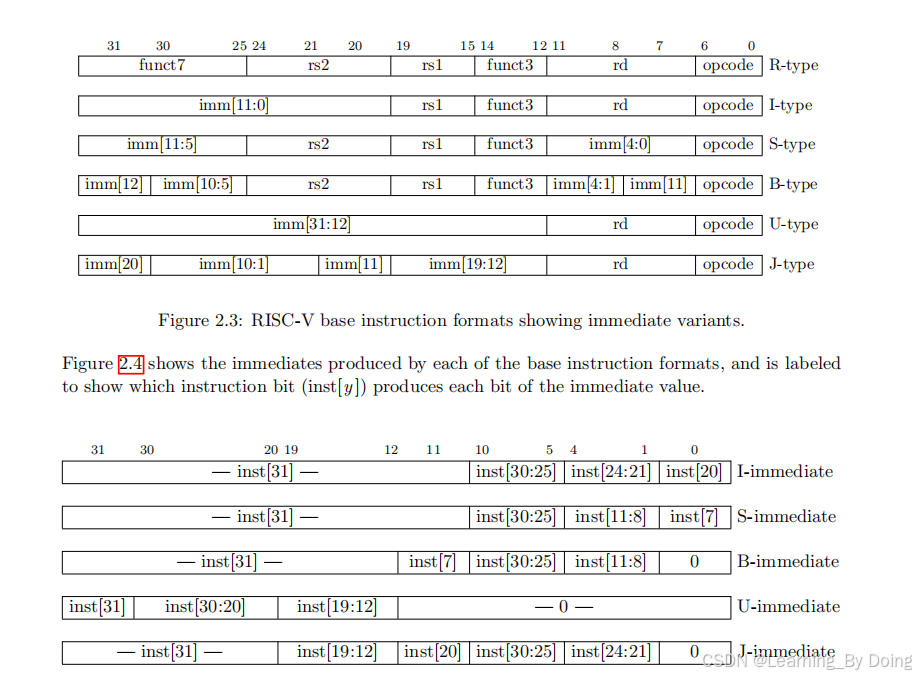
查看文献总结37条指令执行公式:
- 通过I-type格式的特殊化来实现常数位移操作(Shifts by a constant)。
- rs1 是被操作数,imm 是位移量,shift mount 在 imm 的低 5 位中。
- The right shift type is encoded in a high bit of the I-immediate.
- 0 表示逻辑右移(逻辑右移是在高位补 0),1 表示算术右移(算术右移是在高位补符号位)。
I-type 指令执行公式:
- ADDI : rd = rs1 + imm (sign_extend);
- SLTI :rd = rs1 < imm (sign_extend)? 1 : 0;
- SLTIU: rd = rs1 < imm (unsign_extend)? 1 : 0;
- ANDI : rd = rs1 & imm (sign_extend);
- ORI : rd = rs1 | imm (sign_extend);
- XORI : rd = rs1 ^ imm (sign_extend);(rs1 ^ -1 会得到 ~rs1)
- SLLI : rd = rs1 << imm[4:0] (sign_extend);
- SRLI : rd = rs1 >> imm[4:0] (sign_extend);
right shift type is encoded in the high bit of the I-immediate.
- SRAI : rd = rs1 >>> imm[4:0] (sign_extend);
the original sign bit is copied into the vacated upper bits
U-type 指令执行公式:
10. LUI : rd = imm[31:12] << 12 (sign_extend);
LUI places the U-immediate value in the top 20 bits of the destination register rd, filling in the lowest 12 bits with zeros.
- AUIPC : rd = imm + PC (sign_extend);

R-type : rd = rs1 op rs2 (sign_extend);
All operations read the rs1 and rs2 registers as source operands and write the result into register rd.The funct7 and funct3 fields select thetype of operation.
- ADD: rd = rs1 + rs2 (sign_extend);
- SUB: rd = rs1 - rs2 (sign_extend);
- SLT: rd = rs1 < rs2 (sign_extend)? 1 : 0;
- SLTU : rd = rs1 < rs2 (unsign_extend)? 1 : 0;
- AND: rd = rs1 & rs2 (sign_extend);
- OR: rd = rs1 | rs2 (sign_extend);
- XOR: rd = rs1 ^ rs2 (sign_extend);
- SLL: rd = rs1 << rs2[4:0] (sign_extend);
- SRL: rd = rs1 >> rs2[4:0] (sign_extend);
- SRA: rd = rs1 >>> rs2[4:0] (sign_extend);
SLL, SRL, and SRA perform logical left, logical right, and arithmetic right shifts on the value in register rs1 by the shift amount held in the lower 5 bits of register rs2.
J-type 指令执行公式:
- JAL : rd = PC + 4; Target PC = imm + PC (sign_extend);
通过 immimmimm 扩展到 32 位,然后左移 1 位,与当前 PCPCPC 相加得到下一个 PCPCPC,就是目标跳转地址。
然后当前 PC+4PC+4PC+4 存储在 rdrdrd 寄存器中。
- JALR : rd = PC + 4; PC = (rs1 + imm)&~1 (sign_extend); I-type Instruction 间接跳转指令
B-type 指令执行公式(与 Zero 相关 ):
24. BEQ : if (rs1 == rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (sign_extend and unsigned);
25. BNE : if (rs1 != rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (sign and unsign_extend);
26. BLT : if (rs1 < rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (sign_extend);
27. BGE : if (rs1 >= rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (sign_extend;
28. BLTU : if (rs1 < rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (unsign_extend);
29. BGEU : if (rs1 >= rs2) then PC = PC + imm else PC = PC + 4 (unsign_extend);
Note, BGT, BGTU, BLE, and BLEU can be synthesized by reversing the operands to BLT, BLTU, BGE, and BGEU, respectively.
Load and Store Instructions
Load and store instructions transfer a value between the registers and memory.
Loads are encoded in the I-type format and stores are S-type.
Loads copy a value from memory to register rd. Stores copy the value in register rs2 to memory.
Effective Address=rs1+SignExtend(12-bit offset)\text{Effective Address} = rs1 + \text{SignExtend}(\text{12-bit offset})Effective Address=rs1+SignExtend(12-bit offset)
- LW: rd = mem[rs1 + imm] ; 数据无需扩展
- LH: rd = mem[rs1 + imm] ; 数据符号扩展到32位
- LB: rd = mem[rs1 + imm] ; 符号扩展到32位
- LHU: rd = mem[rs1 + imm] ; 数据零扩展到32位
- LBU: rd = mem[rs1 + imm] ; 数据零扩展到32位
- SW: mem[rs1 + imm] = rs2 ; 数据无需扩展
- SH: mem[rs1 + imm] = rs2[15:0];
- SB: mem[rs1 + imm] = rs2[7:0] ;
simple-cpu 流程图
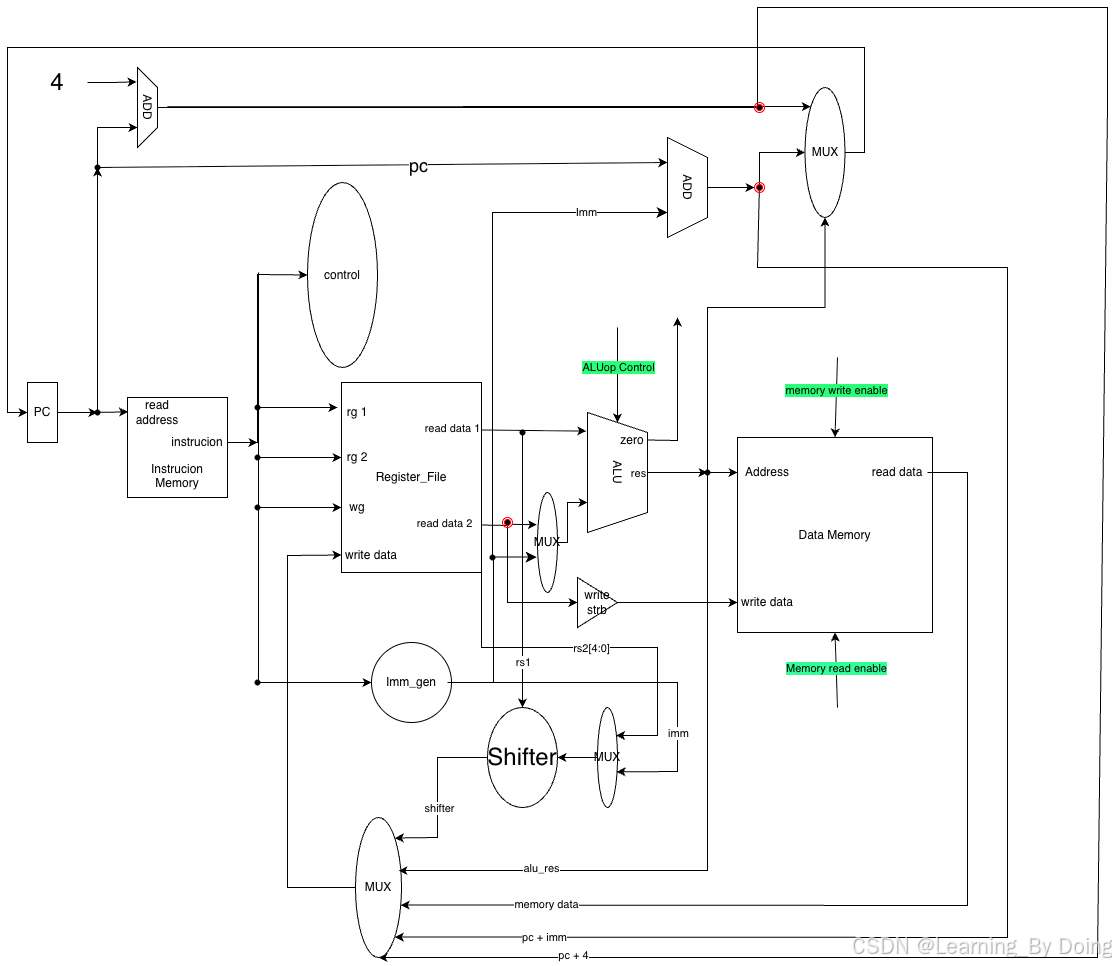
很早就绘制好了这个datapath,现在再复盘发现还是要花点时间的,所以按照指令绘制datapath会提高写verilog代码的效率,如果只看图会乱。研究过指令后再看图会好一点。
