XML 和 JSON -----几种重要模式
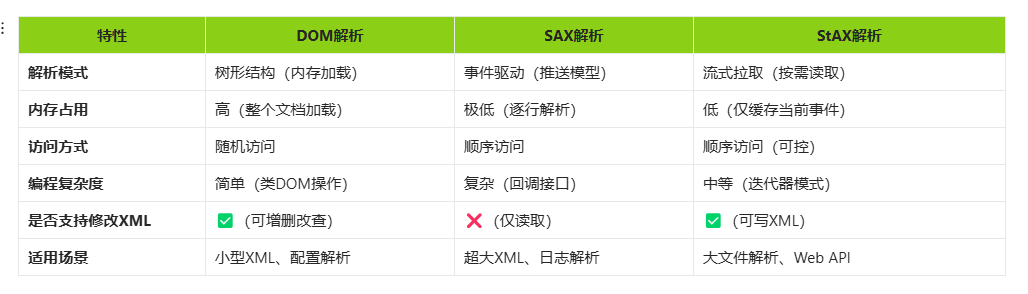
1.XML的三种解析:
DOM解析:
将xml文件全部加载到内存中,对内存开销较大,支持随意的访问,增删改查,解析速度慢。
SAX解析:
基于事件驱动,逐行读取xml,不占用内存,速度比较快,无法随机访问,不能修改。
StAX解析:
位于这两者之间,基于拉取模式,支持xml写入,支持选择性解析。
2.DOM + XPath 解析 (重点掌握)

// 1. 创建SAXReader对象// 注意:DOM4J 的 SAXReader 不是纯 SAX 解析,而是 SAX + DOM 混合模式。// 它底层用 SAX 高效读取 XML,但最终构建 DOM4J 的 Document 对象,支持 XPath 查询。SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();InputStream is = Test02.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.xml");//获取文件 xmlDocument readfile = reader.read(is);String sle = "//book/title"; // //book/titleList<Node> list = readfile.selectNodes(sle);for (Node A:list){System.out.println(A);
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Node;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;public class Dom4jXpathExample {public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 1. 创建SAXReader对象// 注意:DOM4J 的 SAXReader 不是纯 SAX 解析,而是 SAX + DOM 混合模式。// 它底层用 SAX 高效读取 XML,但最终构建 DOM4J 的 Document 对象,支持 XPath 查询。SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();// 2. 加载XML文件File file = new File("books.xml");Document document = reader.read(file);System.out.println("=== 所有书籍标题 ===");// 3. 使用XPath选择所有title元素List<Node> titleNodes = document.selectNodes("//book/title");for (Node node : titleNodes) {System.out.println(node.getText());}System.out.println("\n=== 价格超过35的书籍 ===");// 4. 使用XPath选择价格>35的书籍List<Node> expensiveBooks = document.selectNodes("//book[price>35]");for (Node book : expensiveBooks) {String title = book.selectSingleNode("title").getText();String price = book.selectSingleNode("price").getText();System.out.println(title + " - 价格: " + price);}System.out.println("\n=== WEB类别的书籍 ===");// 5. 使用属性选择List<Node> webBooks = document.selectNodes("//book[@category='WEB']");for (Node book : webBooks) {String title = book.selectSingleNode("title").getText();String author = book.selectSingleNode("author").getText();System.out.println(title + " - 作者: " + author);}// 6. 获取单个节点Node firstBook = document.selectSingleNode("//book[1]");System.out.println("\n第一本书的类别: " + firstBook.valueOf("@category"));} catch (DocumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}3.java解析JSON常用的库:
(常用) Jackson:
String jsonString = """{"name" : "Bob","age" : 25}""";ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();Student student = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Student.class);System.out.println(student);String s = mapper.writeValueAsString(student);System.out.println(s);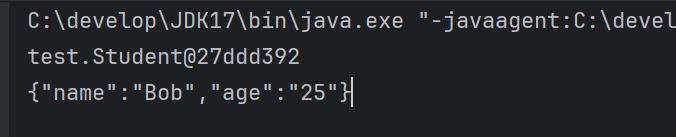
就两行代码,两个方法:
创建:ObjectMapper 对象 ,调用下面两个方法即可。
1.将对象转换为 JSON格式:writeValueAsString(对象)
2.将JSON转换为java对象:readValue(json字符,类的信息)
(常用)Gson:
Gson gson = new Gson();Student user = gson.fromJson(jsonString, Student.class); // JSON转对象System.out.println(user);String json = gson.toJson(user); // 对象转JSONSystem.out.println(json);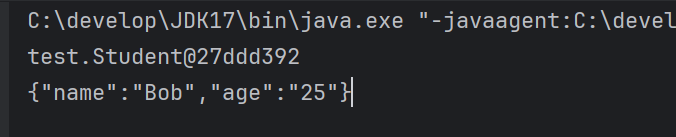
也是两行代码:
创建gson对象
1.使用fromJson:将json转换为对象
2.使用toJson:将对象转换为json
