不止于 API 调用:解锁 Java 工具类设计的三重境界 —— 可复用性、线程安全与性能优化
在 Java 开发的世界里,工具类就像瑞士军刀,看似简单却蕴含着开发者的设计智慧。每个项目中都充斥着各种 Utils 类,但能真正做到 "一次编写,到处复用" 且兼顾线程安全与性能的却寥寥无几。本文将带你超越简单的 API 封装,深入探索 Java 工具类设计的精髓所在,从可复用性构建、线程安全保障到性能极致优化,全方位剖析如何打造经得起考验的高质量工具类。
一、工具类设计的基石:理解本质与原则
工具类(Utility Class)是 Java 开发中最常见的类之一,它通常包含一组静态方法,用于提供通用功能。但优秀的工具类绝不仅仅是静态方法的简单堆砌,而是需要遵循特定的设计原则和模式。
1.1 工具类的本质特征
一个设计良好的工具类应具备以下特征:
- 无状态性:不保存实例变量,所有方法都基于输入参数完成操作
- 不可实例化:通过私有构造方法防止被实例化
- 功能单一性:专注于某一领域的功能实现
- 高内聚性:相关功能紧密结合,减少外部依赖
/*** 字符串处理工具类* 遵循工具类设计基本原则:不可实例化、无状态、功能单一* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class StringProcessUtils {/*** 私有构造方法,防止类被实例化*/private StringProcessUtils() {// 抛出异常防止通过反射实例化throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}// 工具方法实现...
}
1.2 工具类设计的核心原则
工具类设计需遵循以下核心原则,这些原则将指导我们后续的可复用性、线程安全和性能优化实践:
- 单一职责原则:一个工具类应专注于解决某一领域的问题,如日期处理、加密解密等
- 最小知识原则:减少与其他类的交互,降低耦合度
- 不可变性原则:避免维护内部状态,确保方法调用的结果只依赖于输入参数
- 防御性编程原则:对输入参数进行校验,确保方法在各种情况下的稳定性
- 命名直观原则:方法名应清晰表达其功能,让使用者一目了然
二、可复用性设计:让工具类真正 "通用"
可复用性是衡量工具类质量的首要标准。一个高可复用性的工具类能够在不同项目、不同场景下被轻松使用,显著提高开发效率。
2.1 接口与实现分离:隐藏细节,暴露契约
通过接口定义工具类的功能契约,具体实现可以灵活变化,这是提高可复用性的关键策略。
/*** 数据加密工具接口* 定义加密解密功能契约* @author ken*/
public interface EncryptionUtils {/*** 对字符串进行加密* @param content 待加密的内容* @param key 加密密钥* @return 加密后的字符串* @throws EncryptionException 加密过程中发生的异常*/String encrypt(String content, String key) throws EncryptionException;/*** 对字符串进行解密* @param encryptedContent 加密后的内容* @param key 解密密钥* @return 解密后的原始字符串* @throws EncryptionException 解密过程中发生的异常*/String decrypt(String encryptedContent, String key) throws EncryptionException;
}/*** AES加密算法实现类* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class AesEncryptionUtils implements EncryptionUtils {private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES";private static final String TRANSFORMATION = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding";private AesEncryptionUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}@Overridepublic String encrypt(String content, String key) throws EncryptionException {StringUtils.hasText(content, "加密内容不能为空");StringUtils.hasText(key, "加密密钥不能为空");try {SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM);Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION);cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encrypted);} catch (Exception e) {log.error("AES加密失败", e);throw new EncryptionException("AES加密失败: " + e.getMessage(), e);}}@Overridepublic String decrypt(String encryptedContent, String key) throws EncryptionException {StringUtils.hasText(encryptedContent, "解密内容不能为空");StringUtils.hasText(key, "解密密钥不能为空");try {SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ALGORITHM);Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(TRANSFORMATION);cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedContent));return new String(decrypted, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);} catch (Exception e) {log.error("AES解密失败", e);throw new EncryptionException("AES解密失败: " + e.getMessage(), e);}}
}/*** 加密工具工厂类* 提供不同加密算法的实例* @author ken*/
public final class EncryptionUtilsFactory {private EncryptionUtilsFactory() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 获取AES加密工具实例* @return AES加密工具实例*/public static EncryptionUtils getAesEncryptionUtils() {return AesEncryptionUtils.INSTANCE;}// 可以添加更多加密算法的获取方法
}
2.2 配置化与参数化:适应不同场景
将工具类中可能变化的部分通过参数或配置文件进行控制,而不是硬编码,能极大提高工具类的灵活性和复用性。
/*** 日期处理工具类* 支持多种日期格式,通过参数化配置适应不同场景* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class DateUtils {// 默认日期格式public static final String DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd";public static final String DEFAULT_DATETIME_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";private DateUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 将日期转换为字符串* @param date 日期对象,不能为null* @param pattern 日期格式,若为null则使用默认格式* @return 格式化后的日期字符串*/public static String format(Date date, String pattern) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(date, "日期对象不能为空");String usePattern = StringUtils.hasText(pattern) ? pattern : DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT;try {SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(usePattern);return sdf.format(date);} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {log.error("日期格式化失败,格式: {}", usePattern, e);throw new InvalidDateFormatException("无效的日期格式: " + usePattern, e);}}/*** 将字符串转换为日期* @param dateStr 日期字符串,不能为null或空* @param pattern 日期格式,若为null则使用默认格式* @return 解析后的日期对象*/public static Date parse(String dateStr, String pattern) {StringUtils.hasText(dateStr, "日期字符串不能为空");String usePattern = StringUtils.hasText(pattern) ? pattern : DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT;try {SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(usePattern);return sdf.parse(dateStr);} catch (ParseException e) {log.error("日期解析失败,字符串: {}, 格式: {}", dateStr, usePattern, e);throw new DateParseException("日期解析失败: " + dateStr, e);}}/*** 使用预设的格式转换日期* @param date 日期对象* @param formatType 格式类型,如"date"或"datetime"* @return 格式化后的日期字符串*/public static String formatWithPreset(Date date, String formatType) {String pattern = "datetime".equals(formatType) ? DEFAULT_DATETIME_FORMAT : DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT;return format(date, pattern);}
}
2.3 异常处理标准化:提升容错能力
统一的异常处理机制能让工具类在面对错误时表现得更加健壮,同时也方便使用者进行异常处理。
/*** 工具类通用异常基类* 所有工具类抛出的异常都应继承此类* @author ken*/
public class UtilityException extends RuntimeException {/*** 构造函数* @param message 异常信息*/public UtilityException(String message) {super(message);}/*** 构造函数* @param message 异常信息* @param cause 原始异常*/public UtilityException(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}
}/*** 日期解析异常* @author ken*/
public class DateParseException extends UtilityException {public DateParseException(String message) {super(message);}public DateParseException(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}
}/*** 无效日期格式异常* @author ken*/
public class InvalidDateFormatException extends UtilityException {public InvalidDateFormatException(String message) {super(message);}public InvalidDateFormatException(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}
}
2.4 通用验证工具类实战
下面是一个综合应用了上述原则的通用验证工具类,它具有高度的可复用性:
/*** 通用数据验证工具类* 提供常见数据类型的验证功能* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class ValidationUtils {// 邮箱正则表达式private static final String EMAIL_REGEX = "^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+(\\.[a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)+$";// 手机号正则表达式(中国大陆)private static final String PHONE_REGEX = "^1[3-9]\\d{9}$";// 身份证号正则表达式(18位)private static final String ID_CARD_REGEX = "^[1-9]\\d{5}(18|19|20)\\d{2}((0[1-9])|(1[0-2]))(([0-2][1-9])|10|20|30|31)\\d{3}[0-9Xx]$";private static final Pattern EMAIL_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(EMAIL_REGEX);private static final Pattern PHONE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(PHONE_REGEX);private static final Pattern ID_CARD_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(ID_CARD_REGEX);private ValidationUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 验证邮箱格式* @param email 邮箱地址* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isEmail(String email) {if (!StringUtils.hasText(email)) {return false;}return EMAIL_PATTERN.matcher(email).matches();}/*** 验证手机号格式* @param phone 手机号* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isPhone(String phone) {if (!StringUtils.hasText(phone)) {return false;}return PHONE_PATTERN.matcher(phone).matches();}/*** 验证身份证号格式* @param idCard 身份证号* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isIdCard(String idCard) {if (!StringUtils.hasText(idCard)) {return false;}return ID_CARD_PATTERN.matcher(idCard).matches();}/*** 验证字符串长度是否在指定范围内* @param str 待验证字符串* @param min 最小长度(包含)* @param max 最大长度(包含)* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isLengthBetween(String str, int min, int max) {if (str == null) {return min <= 0 && 0 <= max;}int length = str.length();return length >= min && length <= max;}/*** 验证集合大小是否在指定范围内* @param collection 待验证集合* @param min 最小大小(包含)* @param max 最大大小(包含)* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isCollectionSizeBetween(Collection<?> collection, int min, int max) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection)) {return min <= 0 && 0 <= max;}int size = collection.size();return size >= min && size <= max;}/*** 验证对象是否为指定类型或其子类型* @param obj 待验证对象* @param clazz 目标类型* @return 验证通过返回true,否则返回false*/public static boolean isInstanceOf(Object obj, Class<?> clazz) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(clazz, "目标类型不能为空");return obj != null && clazz.isInstance(obj);}/*** 执行验证并在失败时抛出异常* @param condition 验证条件* @param message 验证失败时的异常信息* @throws ValidationException 验证失败时抛出*/public static void validate(boolean condition, String message) {if (!condition) {log.error("验证失败: {}", message);throw new ValidationException(message);}}
}
三、线程安全:构建并发环境下的可靠工具
在多线程环境下,工具类的线程安全至关重要。一个线程不安全的工具类可能会导致数据错乱、程序崩溃等严重问题。
3.1 线程安全的根源与解决方案
线程安全问题通常源于共享状态的修改。工具类实现线程安全的主要策略有:
- 无状态设计:工具类不保存任何状态信息,所有方法仅依赖输入参数
- 不可变对象:使用 final 修饰字段,确保对象创建后状态不再改变
- 同步机制:使用 synchronized 或 Lock 保证临界区代码的原子性
- ThreadLocal 隔离:每个线程拥有独立的变量副本,避免共享
- 原子操作:使用 java.util.concurrent.atomic 包下的原子类
3.2 从线程不安全到线程安全的改造
以日期处理工具类为例,展示如何将线程不安全的实现改造为线程安全的版本:
/*** 线程不安全的日期工具类示例* 问题在于SimpleDateFormat是非线程安全的* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
@Deprecated
public final class UnsafeDateUtils {private static final SimpleDateFormat SDF = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");private UnsafeDateUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 格式化日期* 此方法在多线程环境下会出现线程安全问题*/public static String format(Date date) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(date, "日期对象不能为空");return SDF.format(date);}
}/*** 线程安全的日期工具类(方案一:每次创建新实例)* 优点:简单直接* 缺点:频繁创建对象可能影响性能* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class SafeDateUtilsV1 {private static final String DEFAULT_PATTERN = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";private SafeDateUtilsV1() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 格式化日期* 每次调用创建新的SimpleDateFormat实例,保证线程安全*/public static String format(Date date) {return format(date, DEFAULT_PATTERN);}/*** 格式化日期* @param date 日期对象* @param pattern 日期格式* @return 格式化后的字符串*/public static String format(Date date, String pattern) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(date, "日期对象不能为空");StringUtils.hasText(pattern, "日期格式不能为空");SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);return sdf.format(date);}
}/*** 线程安全的日期工具类(方案二:ThreadLocal)* 优点:性能好,每个线程只创建一次对象* 缺点:实现稍复杂,需要注意内存泄漏* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class SafeDateUtilsV2 {private static final String DEFAULT_PATTERN = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";// 使用ThreadLocal存储SimpleDateFormat,每个线程一个实例private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> SDF_THREAD_LOCAL = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat(DEFAULT_PATTERN));private SafeDateUtilsV2() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 格式化日期(默认格式)*/public static String format(Date date) {return format(date, DEFAULT_PATTERN);}/*** 格式化日期(指定格式)*/public static String format(Date date, String pattern) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(date, "日期对象不能为空");StringUtils.hasText(pattern, "日期格式不能为空");SimpleDateFormat sdf = SDF_THREAD_LOCAL.get();// 修改格式sdf.applyPattern(pattern);String result = sdf.format(date);// 清除ThreadLocal,防止内存泄漏SDF_THREAD_LOCAL.remove();return result;}
}/*** 线程安全的日期工具类(方案三:使用Java 8的DateTimeFormatter)* 优点:最简单,性能好,推荐使用* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class SafeDateUtilsV3 {private static final DateTimeFormatter DEFAULT_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");private SafeDateUtilsV3() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 格式化日期(默认格式)*/public static String format(LocalDateTime dateTime) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(dateTime, "日期时间对象不能为空");return DEFAULT_FORMATTER.format(dateTime);}/*** 格式化日期(指定格式)*/public static String format(LocalDateTime dateTime, String pattern) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(dateTime, "日期时间对象不能为空");StringUtils.hasText(pattern, "日期格式不能为空");DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern);return formatter.format(dateTime);}
}
3.3 线程安全的 ID 生成工具类
ID 生成器是分布式系统中常用的工具,需要保证在高并发环境下的线程安全和唯一性:
/*** 分布式ID生成工具类* 基于雪花算法(Snowflake)实现* 保证高并发环境下的线程安全和ID唯一性* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class IdGeneratorUtils {/*** 开始时间戳 (2023-01-01 00:00:00)*/private static final long START_TIMESTAMP = 1672502400000L;/*** 机器ID所占的位数*/private static final int WORKER_ID_BITS = 5;/*** 数据中心ID所占的位数*/private static final int DATA_CENTER_ID_BITS = 5;/*** 支持的最大机器ID,结果是31 (0b11111)*/private static final long MAX_WORKER_ID = ~(-1L << WORKER_ID_BITS);/*** 支持的最大数据中心ID,结果是31 (0b11111)*/private static final long MAX_DATA_CENTER_ID = ~(-1L << DATA_CENTER_ID_BITS);/*** 序列在ID中占的位数*/private static final int SEQUENCE_BITS = 12;/*** 机器ID向左移12位*/private static final int WORKER_ID_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS;/*** 数据中心ID向左移17位(12+5)*/private static final int DATA_CENTER_ID_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS + WORKER_ID_BITS;/*** 时间戳向左移22位(5+5+12)*/private static final int TIMESTAMP_LEFT_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS + WORKER_ID_BITS + DATA_CENTER_ID_BITS;/*** 生成序列的掩码,这里为4095 (0b111111111111)*/private static final long SEQUENCE_MASK = ~(-1L << SEQUENCE_BITS);/*** 机器ID*/private final long workerId;/*** 数据中心ID*/private final long dataCenterId;/*** 毫秒内序列(0~4095)*/private long sequence = 0L;/*** 上次生成ID的时间戳*/private long lastTimestamp = -1L;/*** 单例实例*/private static volatile IdGeneratorUtils instance;/*** 私有构造函数* @param workerId 机器ID (0~31)* @param dataCenterId 数据中心ID (0~31)*/private IdGeneratorUtils(long workerId, long dataCenterId) {if (workerId > MAX_WORKER_ID || workerId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", MAX_WORKER_ID));}if (dataCenterId > MAX_DATA_CENTER_ID || dataCenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("dataCenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0", MAX_DATA_CENTER_ID));}this.workerId = workerId;this.dataCenterId = dataCenterId;log.info("初始化ID生成器,workerId: {}, dataCenterId: {}", workerId, dataCenterId);}/*** 获取单例实例* 双重检查锁定确保线程安全* @param workerId 机器ID* @param dataCenterId 数据中心ID* @return 单例实例*/public static IdGeneratorUtils getInstance(long workerId, long dataCenterId) {if (instance == null) {synchronized (IdGeneratorUtils.class) {if (instance == null) {instance = new IdGeneratorUtils(workerId, dataCenterId);}}}return instance;}/*** 生成下一个ID* 同步方法确保线程安全* @return 生成的ID*/public synchronized long nextId() {long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();// 如果当前时间小于上一次ID生成的时间戳,说明系统时钟回退过,抛出异常if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {log.error("系统时钟回退,拒绝生成ID,上次时间戳: {}, 当前时间戳: {}", lastTimestamp, timestamp);throw new ClockBackwardsException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds", lastTimestamp - timestamp));}// 如果是同一时间生成的,则进行毫秒内序列自增if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {sequence = (sequence + 1) & SEQUENCE_MASK;// 毫秒内序列溢出if (sequence == 0) {// 阻塞到下一个毫秒,获得新的时间戳timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);}} else {// 时间戳改变,毫秒内序列重置sequence = 0L;}// 更新上次生成ID的时间戳lastTimestamp = timestamp;// 移位并通过或运算拼到一起组成64位的IDreturn ((timestamp - START_TIMESTAMP) << TIMESTAMP_LEFT_SHIFT)| (dataCenterId << DATA_CENTER_ID_SHIFT)| (workerId << WORKER_ID_SHIFT)| sequence;}/*** 阻塞到下一个毫秒,直到获得新的时间戳* @param lastTimestamp 上次生成ID的时间戳* @return 当前时间戳*/private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {long timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();}return timestamp;}/*** 生成字符串类型的ID* @return 字符串ID*/public String nextStringId() {return String.valueOf(nextId());}
}
3.4 线程安全的缓存工具类
缓存工具类在多线程环境下需要特别注意并发问题,下面是一个线程安全的本地缓存实现:
/*** 线程安全的本地缓存工具类* 基于ConcurrentHashMap实现,支持过期时间设置* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class LocalCacheUtils {/*** 缓存项实体类*/private static class CacheEntry {// 缓存值private final Object value;// 过期时间戳(毫秒),0表示永不过期private final long expireTimestamp;public CacheEntry(Object value, long expireTimestamp) {this.value = value;this.expireTimestamp = expireTimestamp;}/*** 判断缓存项是否已过期* @return 过期返回true,否则返回false*/public boolean isExpired() {return expireTimestamp > 0 && System.currentTimeMillis() > expireTimestamp;}public Object getValue() {return value;}}// 缓存容器,使用ConcurrentHashMap保证线程安全private static final ConcurrentMap<String, CacheEntry> CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();// 定时清理过期缓存的线程private static final ScheduledExecutorService CLEANER = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(runnable -> {Thread thread = new Thread(runnable, "local-cache-cleaner");thread.setDaemon(true); // 守护线程,当主线程退出时自动关闭return thread;});static {// 每5分钟清理一次过期缓存CLEANER.scheduleAtFixedRate(LocalCacheUtils::cleanExpiredEntries, 5, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);// 注册钩子,JVM关闭时清理资源Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {CLEANER.shutdown();try {if (!CLEANER.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {CLEANER.shutdownNow();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {CLEANER.shutdownNow();}log.info("本地缓存已关闭");}));}private LocalCacheUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 添加缓存项,永不过期* @param key 缓存键* @param value 缓存值*/public static void put(String key, Object value) {put(key, value, 0);}/*** 添加缓存项,设置过期时间* @param key 缓存键* @param value 缓存值* @param expireTime 过期时间* @param timeUnit 时间单位*/public static void put(String key, Object value, long expireTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) {StringUtils.hasText(key, "缓存键不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(value, "缓存值不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(timeUnit, "时间单位不能为空");long expireMillis = expireTime <= 0 ? 0 : timeUnit.toMillis(expireTime);long expireTimestamp = expireMillis > 0 ? System.currentTimeMillis() + expireMillis : 0;CACHE.put(key, new CacheEntry(value, expireTimestamp));log.debug("添加缓存,key: {}, 过期时间: {}", key, expireTime <= 0 ? "永不过期" : expireTime + timeUnit.name());}/*** 添加缓存项,设置过期时间(毫秒)* @param key 缓存键* @param value 缓存值* @param expireMillis 过期时间(毫秒),0表示永不过期*/public static void put(String key, Object value, long expireMillis) {StringUtils.hasText(key, "缓存键不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(value, "缓存值不能为空");long expireTimestamp = expireMillis > 0 ? System.currentTimeMillis() + expireMillis : 0;CACHE.put(key, new CacheEntry(value, expireTimestamp));log.debug("添加缓存,key: {}, 过期时间: {}毫秒", key, expireMillis <= 0 ? "永久" : expireMillis);}/*** 获取缓存项* @param key 缓存键* @param <T> 缓存值类型* @return 缓存值,如果不存在或已过期则返回null*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> T get(String key) {StringUtils.hasText(key, "缓存键不能为空");CacheEntry entry = CACHE.get(key);if (entry == null) {log.debug("缓存不存在,key: {}", key);return null;}if (entry.isExpired()) {CACHE.remove(key);log.debug("缓存已过期,key: {}", key);return null;}return (T) entry.getValue();}/*** 获取缓存项,如果不存在则执行加载函数并缓存结果* @param key 缓存键* @param loader 加载函数,当缓存不存在时执行* @param expireMillis 过期时间(毫秒)* @param <T> 缓存值类型* @return 缓存值*/public static <T> T getOrLoad(String key, Supplier<T> loader, long expireMillis) {StringUtils.hasText(key, "缓存键不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(loader, "加载函数不能为空");T value = get(key);if (value != null) {return value;}// 双重检查,减少并发时的重复加载synchronized (key.intern()) {value = get(key);if (value != null) {return value;}// 执行加载函数value = loader.get();ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(value, "加载函数返回值不能为空");// 缓存结果put(key, value, expireMillis);return value;}}/*** 移除缓存项* @param key 缓存键*/public static void remove(String key) {StringUtils.hasText(key, "缓存键不能为空");CACHE.remove(key);log.debug("移除缓存,key: {}", key);}/*** 清空所有缓存*/public static void clear() {CACHE.clear();log.debug("清空所有缓存");}/*** 获取缓存大小* @return 缓存项数量*/public static int size() {return CACHE.size();}/*** 清理过期的缓存项*/private static void cleanExpiredEntries() {log.debug("开始清理过期缓存,当前缓存大小: {}", CACHE.size());int removedCount = 0;long now = System.currentTimeMillis();for (Map.Entry<String, CacheEntry> entry : CACHE.entrySet()) {CacheEntry cacheEntry = entry.getValue();if (cacheEntry.expireTimestamp > 0 && now > cacheEntry.expireTimestamp) {CACHE.remove(entry.getKey());removedCount++;}}log.debug("清理过期缓存完成,移除缓存项数量: {}", removedCount);}
}
四、性能优化:让工具类高效运行
高性能的工具类能够在不增加系统负担的情况下提供所需功能。性能优化需要基于实际测试数据,而不是凭空猜测。
4.1 性能优化的基本原则
工具类性能优化应遵循以下原则:
- 避免过早优化:先确保功能正确,再考虑性能优化
- 基于数据优化:通过基准测试确定性能瓶颈,有针对性地优化
- 空间换时间:在内存允许的情况下,使用缓存等机制提高速度
- 时间换空间:在内存受限的情况下,适当增加计算时间减少内存占用
- 减少对象创建:避免频繁创建短期对象,减少 GC 压力
- 选择合适数据结构:根据使用场景选择最优的数据结构
4.2 集合操作工具类的性能优化
集合操作是工具类中常见的功能,优化集合操作能显著提升性能:
/*** 高性能集合操作工具类* 提供高效的集合转换、过滤、分组等操作* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class CollectionUtils {private CollectionUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 将集合转换为Map* 使用指定的键提取器和值提取器* 优化点:预先计算初始容量,避免Map扩容* @param collection 源集合* @param keyExtractor 键提取器* @param valueExtractor 值提取器* @param <K> 键类型* @param <V> 值类型* @param <T> 集合元素类型* @return 转换后的Map*/public static <K, V, T> Map<K, V> toMap(Collection<T> collection, Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyExtractor,Function<? super T, ? extends V> valueExtractor) {org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection, "源集合不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(keyExtractor, "键提取器不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(valueExtractor, "值提取器不能为空");// 计算初始容量,避免Map扩容int initialCapacity = computeInitialCapacity(collection.size());Map<K, V> map = Maps.newHashMapWithExpectedSize(initialCapacity);for (T element : collection) {K key = keyExtractor.apply(element);V value = valueExtractor.apply(element);map.put(key, value);}return map;}/*** 将集合分组* 优化点:使用并行流处理大数据量集合* @param collection 源集合* @param classifier 分组依据提取器* @param <T> 集合元素类型* @param <K> 分组键类型* @return 分组后的Map*/public static <T, K> Map<K, List<T>> groupBy(Collection<T> collection, Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier) {org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection, "源集合不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(classifier, "分组依据提取器不能为空");// 大数据量时使用并行流提高效率if (collection.size() > 1000) {return collection.parallelStream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(classifier, Collectors.toList()));} else {return collection.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(classifier, Collectors.toList()));}}/*** 过滤集合元素* 优化点:根据过滤条件预估结果大小,减少中间集合扩容* @param collection 源集合* @param predicate 过滤条件* @param <T> 集合元素类型* @return 过滤后的集合*/public static <T> List<T> filter(Collection<T> collection, Predicate<? super T> predicate) {org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection, "源集合不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(predicate, "过滤条件不能为空");List<T> result = Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(collection.size() / 2); // 预估一半元素会被保留for (T element : collection) {if (predicate.test(element)) {result.add(element);}}// 调整容量为实际大小,节省内存result.trimToSize();return result;}/*** 提取集合元素的某个属性并去重* 优化点:使用HashSet去重,同时转换为List* @param collection 源集合* @param mapper 属性提取器* @param <T> 集合元素类型* @param <R> 提取的属性类型* @return 去重后的属性列表*/public static <T, R> List<R> extractDistinct(Collection<T> collection, Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper) {org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection, "源集合不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(mapper, "属性提取器不能为空");// 使用HashSet去重,同时指定初始容量int initialCapacity = computeInitialCapacity(collection.size());Set<R> set = Sets.newHashSetWithExpectedSize(initialCapacity);for (T element : collection) {R value = mapper.apply(element);set.add(value);}return Lists.newArrayList(set);}/*** 计算Map的初始容量* 基于HashMap的加载因子(0.75)计算* @param size 预计元素数量* @return 初始容量*/private static int computeInitialCapacity(int size) {if (size < 3) {return size + 1;}if (size < 1073741824) {return (int) ((float) size / 0.75F + 1.0F);}return Integer.MAX_VALUE;}/*** 检查两个集合是否有交集* 优化点:使用较小的集合作为基准,减少比较次数* @param collection1 第一个集合* @param collection2 第二个集合* @param <T> 集合元素类型* @return 有交集返回true,否则返回false*/public static <T> boolean hasIntersection(Collection<T> collection1, Collection<T> collection2) {org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection1, "第一个集合不能为空");org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection2, "第二个集合不能为空");// 选择较小的集合作为基准,提高效率Collection<T> smaller = collection1.size() <= collection2.size() ? collection1 : collection2;Collection<T> larger = collection1.size() > collection2.size() ? collection1 : collection2;// 如果较小的集合是Set,直接使用containsAllif (smaller instanceof Set) {return larger.stream().anyMatch(smaller::contains);}// 否则将较小的集合转换为Set,提高查询效率Set<T> smallerSet = Sets.newHashSet(smaller);return larger.stream().anyMatch(smallerSet::contains);}
}
4.3 序列化工具类的性能优化
序列化和反序列化是常见的操作,优化其性能能显著提升系统响应速度:
/*** 高性能序列化工具类* 提供多种序列化方式,并选择最优实现* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class SerializationUtils {// 使用ThreadLocal缓存ObjectMapper实例,避免重复创建private static final ThreadLocal<ObjectMapper> OBJECT_MAPPER_THREAD_LOCAL = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();// 配置序列化特性,提高性能mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS);mapper.disable(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);mapper.enable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING);mapper.enable(DeserializationFeature.READ_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING);mapper.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));return mapper;});// FastJson2序列化器private static final JSONWriter.Feature[] FASTJSON_WRITE_FEATURES = {JSONWriter.Feature.WriteNulls,JSONWriter.Feature.PrettyFormat};private SerializationUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 将对象序列化为JSON字符串* 根据对象大小选择最优序列化方式* @param obj 要序列化的对象* @return JSON字符串*/public static String toJson(Object obj) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(obj, "序列化对象不能为空");// 对于小对象,使用FastJson2提高速度if (isSmallObject(obj)) {return JSON.toJSONString(obj, FASTJSON_WRITE_FEATURES);}// 对于大对象,使用Jackson,内存占用更优try {ObjectMapper mapper = OBJECT_MAPPER_THREAD_LOCAL.get();String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(obj);OBJECT_MAPPER_THREAD_LOCAL.remove(); // 清理ThreadLocalreturn json;} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {log.error("Jackson序列化失败", e);throw new SerializationException("对象序列化失败", e);}}/*** 将JSON字符串反序列化为对象* @param json JSON字符串* @param clazz 目标类* @param <T> 目标类型* @return 反序列化后的对象*/public static <T> T fromJson(String json, Class<T> clazz) {StringUtils.hasText(json, "JSON字符串不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(clazz, "目标类不能为空");// 对于小JSON,使用FastJson2if (json.length() < 1024) {return JSON.parseObject(json, clazz);}// 对于大JSON,使用Jacksontry {ObjectMapper mapper = OBJECT_MAPPER_THREAD_LOCAL.get();T result = mapper.readValue(json, clazz);OBJECT_MAPPER_THREAD_LOCAL.remove(); // 清理ThreadLocalreturn result;} catch (IOException e) {log.error("Jackson反序列化失败,JSON: {}", json, e);throw new SerializationException("JSON反序列化失败", e);}}/*** Java原生序列化* 注意:仅在必要时使用,性能较差* @param obj 要序列化的对象* @return 序列化后的字节数组*/public static byte[] serialize(Object obj) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(obj, "序列化对象不能为空");try (ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) {oos.writeObject(obj);oos.flush();return bos.toByteArray();} catch (IOException e) {log.error("Java原生序列化失败", e);throw new SerializationException("对象序列化失败", e);}}/*** Java原生反序列化* @param data 序列化后的字节数组* @param <T> 目标类型* @return 反序列化后的对象*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> T deserialize(byte[] data) {ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(data, "序列化数据不能为空");ObjectUtils.checkArgument(data.length > 0, "序列化数据不能为空");try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(data);ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis)) {return (T) ois.readObject();} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {log.error("Java原生反序列化失败", e);throw new SerializationException("对象反序列化失败", e);}}/*** 判断对象是否为小对象* 基于对象类型和估计大小* @param obj 要判断的对象* @return 是小对象返回true,否则返回false*/private static boolean isSmallObject(Object obj) {if (obj instanceof String) {return ((String) obj).length() < 1024;}if (obj instanceof Collection<?>) {return ((Collection<?>) obj).size() < 100;}if (obj instanceof Map<?, ?>) {return ((Map<?, ?>) obj).size() < 50;}return true;}
}
4.4 性能测试与对比
为了验证性能优化的效果,我们需要进行基准测试:
/*** 工具类性能测试* 使用JMH进行基准测试* @author ken*/
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
public class UtilityPerformanceTest {private List<User> userList;private String jsonString;/*** 测试准备工作*/@Setup(Level.Trial)public void setup() {// 初始化测试数据userList = Lists.newArrayList();for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {User user = new User();user.setId(i);user.setName("User_" + i);user.setAge(20 + i % 30);user.setEmail("user_" + i + "@example.com");user.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now().minusDays(i));userList.add(user);}// 生成测试JSON字符串jsonString = SerializationUtils.toJson(userList);}/*** 测试集合转换性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testToMapPerformance() {CollectionUtils.toMap(userList, User::getId, Function.identity());}/*** 测试分组性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testGroupByPerformance() {CollectionUtils.groupBy(userList, user -> user.getAge() / 10);}/*** 测试JSON序列化性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testJsonSerialization() {SerializationUtils.toJson(userList);}/*** 测试JSON反序列化性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testJsonDeserialization() {SerializationUtils.fromJson(jsonString, new TypeReference<List<User>>() {});}/*** 测试ID生成性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testIdGeneration() {IdGeneratorUtils.getInstance(1, 1).nextId();}/*** 测试缓存性能*/@Benchmark@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.SECONDS)public void testCachePerformance() {String key = "test_key_" + Thread.currentThread().getId();LocalCacheUtils.put(key, "test_value", 1000);LocalCacheUtils.get(key);LocalCacheUtils.remove(key);}/*** 测试主方法*/public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {Options options = new OptionsBuilder().include(UtilityPerformanceTest.class.getSimpleName()).warmupIterations(3).measurementIterations(5).threads(8).forks(1).build();new Runner(options).run();}/*** 测试用用户类*/@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructorpublic static class User {private Integer id;private String name;private Integer age;private String email;private LocalDateTime createTime;}
}
五、企业级工具类库的设计与实践
构建一个企业级的工具类库需要综合考虑可复用性、线程安全和性能,同时还要注重易用性和扩展性。
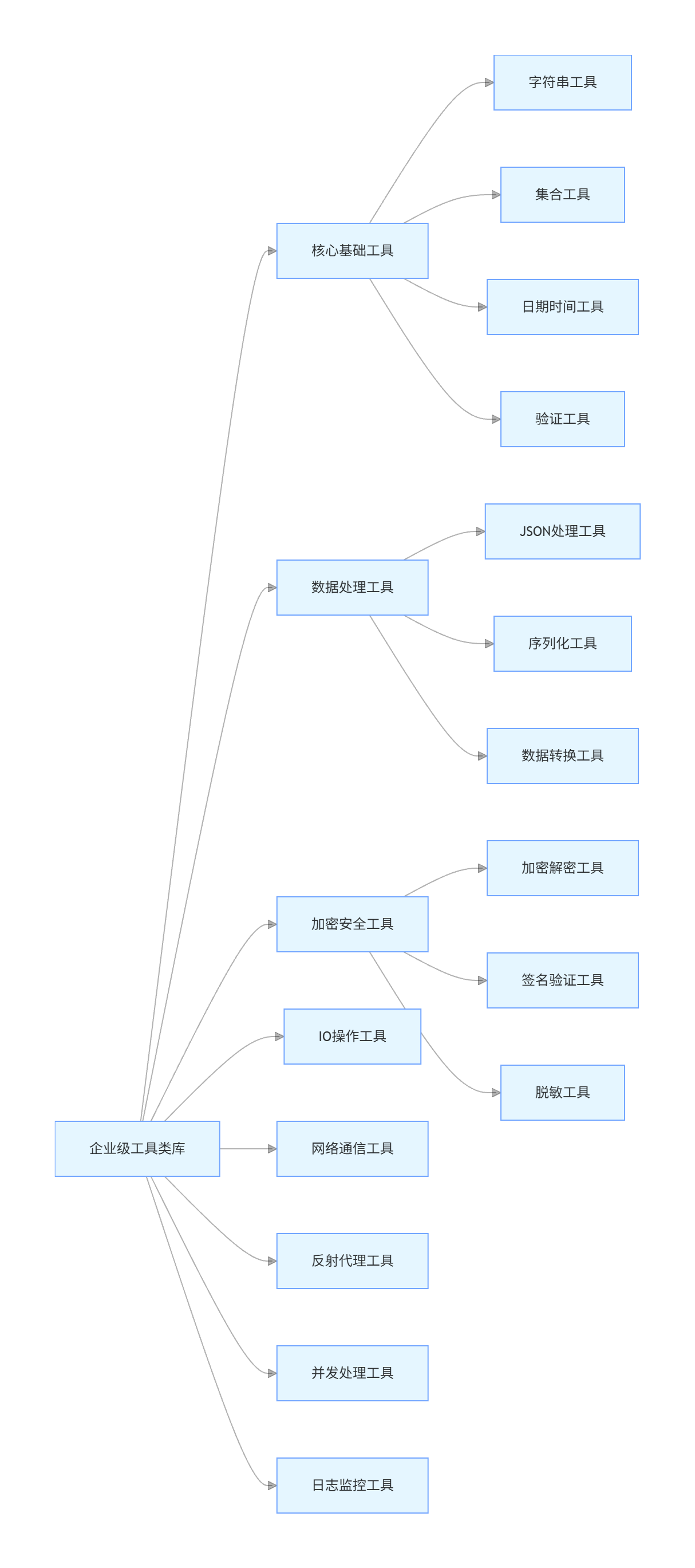
5.1 工具类库的整体架构
一个完善的工具类库应包含以下几个部分:
5.2 工具类库的依赖管理
使用 Maven 管理工具类库的依赖,确保依赖的稳定性和兼容性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.example</groupId><artifactId>enterprise-utils</artifactId><version>1.0.0</version><name>Enterprise Utility Library</name><description>A comprehensive utility library for enterprise Java applications</description><properties><maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding><!-- 依赖版本 --><lombok.version>1.18.30</lombok.version><spring.version>6.1.2</spring.version><fastjson2.version>2.0.45</fastjson2.version><guava.version>33.1.0-jre</guava.version><jackson.version>2.15.2</jackson.version><mybatis-plus.version>3.5.5</mybatis-plus.version><springdoc.version>2.2.0</springdoc.version><junit.version>5.10.1</junit.version><jmh.version>1.37</jmh.version></properties><dependencies><!-- Lombok --><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>${lombok.version}</version><scope>provided</scope></dependency><!-- Spring Core --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version></dependency><!-- Fastjson2 --><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId><artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId><version>${fastjson2.version}</version></dependency><!-- Guava --><dependency><groupId>com.google.guava</groupId><artifactId>guava</artifactId><version>${guava.version}</version></dependency><!-- Jackson --><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId><version>${jackson.version}</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId><artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId><version>${jackson.version}</version></dependency><!-- MyBatis-Plus --><dependency><groupId>com.baomidou</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-plus-core</artifactId><version>${mybatis-plus.version}</version></dependency><!-- Swagger3/SpringDoc --><dependency><groupId>org.springdoc</groupId><artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId><version>${springdoc.version}</version></dependency><!-- JUnit 5 --><dependency><groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId><artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId><version>${junit.version}</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId><artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId><version>${junit.version}</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><!-- JMH 基准测试 --><dependency><groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId><artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId><version>${jmh.version}</version><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId><artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId><version>${jmh.version}</version><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId><version>3.11.0</version><configuration><source>${maven.compiler.source}</source><target>${maven.compiler.target}</target><encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}</encoding><annotationProcessorPaths><path><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><version>${lombok.version}</version></path></annotationProcessorPaths></configuration></plugin><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId><version>3.2.2</version><configuration><testFailureIgnore>false</testFailureIgnore></configuration></plugin></plugins></build>
</project>
5.3 企业级通用脱敏工具类
在企业应用中,数据脱敏是常见需求,下面是一个功能完善的脱敏工具类:
/*** 数据脱敏工具类* 支持多种敏感信息的脱敏处理* @author ken*/
@Slf4j
public final class DesensitizationUtils {/*** 脱敏类型枚举*/public enum DesensitizationType {/** 姓名 */NAME,/** 身份证号 */ID_CARD,/** 手机号 */PHONE,/** 邮箱 */EMAIL,/** 银行卡号 */BANK_CARD,/** 地址 */ADDRESS,/** 密码 */PASSWORD}private DesensitizationUtils() {throw new AssertionError("Utility class should not be instantiated");}/*** 对敏感信息进行脱敏* @param content 原始内容* @param type 脱敏类型* @return 脱敏后的内容*/public static String desensitize(String content, DesensitizationType type) {StringUtils.hasText(content, "脱敏内容不能为空");ObjectUtils.requireNonNull(type, "脱敏类型不能为空");switch (type) {case NAME:return desensitizeName(content);case ID_CARD:return desensitizeIdCard(content);case PHONE:return desensitizePhone(content);case EMAIL:return desensitizeEmail(content);case BANK_CARD:return desensitizeBankCard(content);case ADDRESS:return desensitizeAddress(content);case PASSWORD:return desensitizePassword(content);default:log.warn("未知的脱敏类型: {}", type);return content;}}/*** 对姓名进行脱敏* 规则:只显示第一个字符,其余用*代替* 示例:张**,李** @param name 姓名* @return 脱敏后的姓名*/public static String desensitizeName(String name) {StringUtils.hasText(name, "姓名不能为空");if (name.length() == 1) {return name;}return name.substring(0, 1) + "*".repeat(name.length() - 1);}/*** 对身份证号进行脱敏* 规则:显示前6位和后4位,中间用*代替* 示例:110101********1234* @param idCard 身份证号* @return 脱敏后的身份证号*/public static String desensitizeIdCard(String idCard) {StringUtils.hasText(idCard, "身份证号不能为空");ValidationUtils.validate(idCard.length() >= 15, "身份证号格式不正确");if (idCard.length() == 15) {return idCard.substring(0, 6) + "*****" + idCard.substring(11);} else {return idCard.substring(0, 6) + "********" + idCard.substring(14);}}/*** 对手机号进行脱敏* 规则:显示前3位和后4位,中间4位用*代替* 示例:138****5678* @param phone 手机号* @return 脱敏后的手机号*/public static String desensitizePhone(String phone) {StringUtils.hasText(phone, "手机号不能为空");ValidationUtils.validate(phone.length() == 11, "手机号格式不正确");return phone.substring(0, 3) + "****" + phone.substring(7);}/*** 对邮箱进行脱敏* 规则:显示第一个字符和域名,中间用*代替* 示例:a**@example.com* @param email 邮箱* @return 脱敏后的邮箱*/public static String desensitizeEmail(String email) {StringUtils.hasText(email, "邮箱不能为空");ValidationUtils.validate(ValidationUtils.isEmail(email), "邮箱格式不正确");int atIndex = email.indexOf('@');if (atIndex <= 1) {return email;}return email.substring(0, 1) + "*".repeat(atIndex - 1) + email.substring(atIndex);}/*** 对银行卡号进行脱敏* 规则:显示前6位和后4位,中间用*代替* 示例:622260********1234* @param bankCard 银行卡号* @return 脱敏后的银行卡号*/public static String desensitizeBankCard(String bankCard) {StringUtils.hasText(bankCard, "银行卡号不能为空");ValidationUtils.validate(bankCard.length() >= 16, "银行卡号格式不正确");return bankCard.substring(0, 6) + "********" + bankCard.substring(bankCard.length() - 4);}/*** 对地址进行脱敏* 规则:只显示前6个字符,其余用*代替,最多显示10个字符* 示例:北京市海淀区**** @param address 地址* @return 脱敏后的地址*/public static String desensitizeAddress(String address) {StringUtils.hasText(address, "地址不能为空");if (address.length() <= 6) {return address;}int showLength = Math.min(address.length(), 10);return address.substring(0, 6) + "*".repeat(showLength - 6);}/*** 对密码进行脱敏* 规则:全部用*代替,长度保持不变* 示例:******* @param password 密码* @return 脱敏后的密码*/public static String desensitizePassword(String password) {StringUtils.hasText(password, "密码不能为空");return "*".repeat(password.length());}/*** 自定义脱敏* @param content 原始内容* @param prefixLength 前缀保留长度* @param suffixLength 后缀保留长度* @return 脱敏后的内容*/public static String desensitizeCustom(String content, int prefixLength, int suffixLength) {StringUtils.hasText(content, "脱敏内容不能为空");ValidationUtils.validate(prefixLength >= 0, "前缀保留长度不能为负数");ValidationUtils.validate(suffixLength >= 0, "后缀保留长度不能为负数");ValidationUtils.validate(prefixLength + suffixLength <= content.length(), "前缀保留长度与后缀保留长度之和不能超过内容长度");if (prefixLength + suffixLength >= content.length()) {return content;}String prefix = content.substring(0, prefixLength);String suffix = content.substring(content.length() - suffixLength);String mask = "*".repeat(content.length() - prefixLength - suffixLength);return prefix + mask + suffix;}
}
5.4 工具类的文档与测试
完善的文档和测试是企业级工具类库不可或缺的部分:
/*** 脱敏工具类测试* @author ken*/
@SpringBootTest
public class DesensitizationUtilsTest {@Testpublic void testDesensitizeName() {Assertions.assertEquals("张*", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeName("张三"));Assertions.assertEquals("李**", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeName("李四光"));Assertions.assertEquals("王", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeName("王"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeIdCard() {Assertions.assertEquals("110101********1234", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeIdCard("110101199001011234"));Assertions.assertEquals("110101*****123", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeIdCard("110101900101123"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizePhone() {Assertions.assertEquals("138****5678", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizePhone("13812345678"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeEmail() {Assertions.assertEquals("a**@example.com", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeEmail("abc@example.com"));Assertions.assertEquals("t*@test.com", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeEmail("to@test.com"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeBankCard() {Assertions.assertEquals("622260********1234", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeBankCard("62226000123456781234"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeAddress() {Assertions.assertEquals("北京市海淀区***", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeAddress("北京市海淀区中关村大街1号"));Assertions.assertEquals("上海市徐汇区", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeAddress("上海市徐汇区"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizePassword() {Assertions.assertEquals("******", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizePassword("123456"));Assertions.assertEquals("********", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizePassword("abcdefgh"));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeCustom() {Assertions.assertEquals("ab***yz", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeCustom("abcdefyz", 2, 2));Assertions.assertEquals("test", DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeCustom("test", 2, 2));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeWithType() {Assertions.assertEquals("张*", DesensitizationUtils.desensitize("张三", DesensitizationUtils.DesensitizationType.NAME));Assertions.assertEquals("138****5678", DesensitizationUtils.desensitize("13812345678", DesensitizationUtils.DesensitizationType.PHONE));}@Testpublic void testDesensitizeWithInvalidInput() {Assertions.assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> DesensitizationUtils.desensitizeName(null));Assertions.assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> DesensitizationUtils.desensitizePhone("12345"));}
}
六、总结:工具类设计的艺术与平衡
Java 工具类设计看似简单,实则蕴含着深厚的技术功底和设计智慧。一个优秀的工具类不仅要提供实用的功能,更要在可复用性、线程安全和性能之间找到完美的平衡。
6.1 工具类设计的核心要点
- 可复用性:通过单一职责、接口与实现分离、参数化配置等手段,让工具类能够在不同场景下被复用
- 线程安全:采用无状态设计、不可变对象、同步机制或 ThreadLocal 等方式,确保工具类在并发环境下的安全性
- 性能优化:基于实际测试数据,选择合适的数据结构,减少对象创建,合理使用缓存,提升工具类的执行效率
6.2 工具类设计的最佳实践
- 遵循 "高内聚、低耦合" 原则,每个工具类专注于特定领域的功能
- 对输入参数进行严格校验,采用防御性编程
- 提供清晰的文档和丰富的测试用例
- 避免过度设计,保持工具类的简洁性和易用性
- 定期进行性能测试和优化,持续改进工具类的质量
工具类作为 Java 开发中最基础也最常用的组件,其设计质量直接影响整个项目的代码质量和开发效率。希望本文所探讨的工具类设计精髓,能够帮助你打造出更加优秀、可靠、高效的 Java 工具类,让代码不仅能够工作,更能优雅地工作。
