Sequelize vs Prisma:现代 Node.js ORM 深度技术解析与实战指南
在 Node.js 后端开发领域,选择合适的 ORM(对象关系映射)库对项目的可维护性、开发效率和类型安全至关重要。随着 TypeScript 的普及和现代开发范式的演进,传统的 Sequelize 与新兴的 Prisma 形成了鲜明的技术对比。本文将深度解析两者的架构差异、性能表现和适用场景,并通过完整的实战示例展示如何在实际项目中做出技术选型。
🏗️ 整体架构对比
Sequelize:经典的传统 ORM 模式
Sequelize 采用传统的 Active Record 模式,模型实例既代表数据也包含操作数据的方法。这种设计模式使得数据对象和数据库操作紧密耦合,提供了很大的灵活性但牺牲了部分类型安全性。
Prisma:现代的查询构建器模式
Prisma 采用 数据映射器 模式,严格分离数据结构和操作逻辑。其核心设计理念是基于单一事实来源(schema.prisma)生成类型安全的数据库客户端,提供更优的开发体验和运行时性能。
🗄️ 数据模型定义深度对比
模型定义语法差异
Sequelize 的分散式定义:
// models/User.js - 模型定义
const { DataTypes } = require('sequelize');module.exports = (sequelize) => {const User = sequelize.define('User', {id: {type: DataTypes.INTEGER,primaryKey: true,autoIncrement: true},email: {type: DataTypes.STRING,unique: true,allowNull: false,validate: {isEmail: true}},name: {type: DataTypes.STRING,allowNull: false}}, {tableName: 'users',timestamps: true,indexes: [{fields: ['email']}]});User.associate = function(models) {User.hasMany(models.Post, { foreignKey: 'authorId',as: 'posts'});};return User;
};// migrations/20240101000000-create-user.js - 迁移文件
module.exports = {async up(queryInterface, Sequelize) {await queryInterface.createTable('users', {id: {type: Sequelize.INTEGER,primaryKey: true,autoIncrement: true},email: {type: Sequelize.STRING,allowNull: false,unique: true},// ... 其他字段});},async down(queryInterface, Sequelize) {await queryInterface.dropTable('users');}
};
Prisma 的声明式定义:
// schema.prisma - 统一的数据模型定义
generator client {provider = "prisma-client-js"
}datasource db {provider = "postgresql"url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}model User {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())email String @uniquename StringcreatedAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt @map("updated_at")posts Post[]@@map("users")@@index([email])
}model Post {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())title Stringcontent String?published Boolean @default(false)author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])authorId Int@@map("posts")
}
架构哲学对比分析
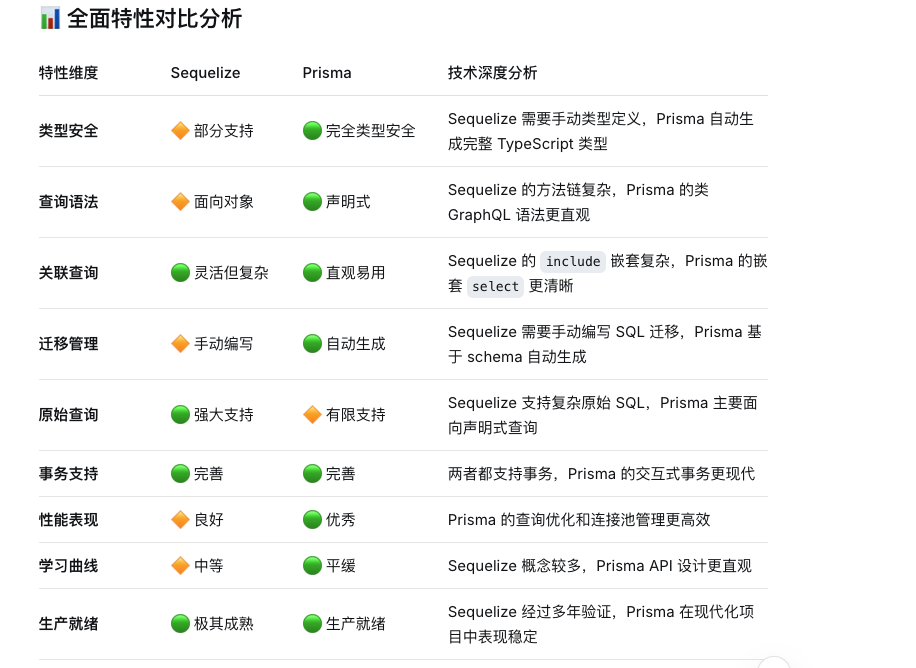
📊 全面特性对比分析
| 特性维度 | Sequelize | Prisma | 技术深度分析 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 类型安全 | 🔶 部分支持 | 🟢 完全类型安全 | Sequelize 需要手动类型定义,Prisma 自动生成完整 TypeScript 类型 |
| 查询语法 | 🔶 面向对象 | 🟢 声明式 | Sequelize 的方法链复杂,Prisma 的类 GraphQL 语法更直观 |
| 关联查询 | 🟢 灵活但复杂 | 🟢 直观易用 | Sequelize 的 include 嵌套复杂,Prisma 的嵌套 select 更清晰 |
| 迁移管理 | 🔶 手动编写 | 🟢 自动生成 | Sequelize 需要手动编写 SQL 迁移,Prisma 基于 schema 自动生成 |
| 原始查询 | 🟢 强大支持 | 🔶 有限支持 | Sequelize 支持复杂原始 SQL,Prisma 主要面向声明式查询 |
| 事务支持 | 🟢 完善 | 🟢 完善 | 两者都支持事务,Prisma 的交互式事务更现代 |
| 性能表现 | 🔶 良好 | 🟢 优秀 | Prisma 的查询优化和连接池管理更高效 |
| 学习曲线 | 🔶 中等 | 🟢 平缓 | Sequelize 概念较多,Prisma API 设计更直观 |
| 生产就绪 | 🟢 极其成熟 | 🟢 生产就绪 | Sequelize 经过多年验证,Prisma 在现代化项目中表现稳定 |
🔍 查询语法深度技术解析
基础查询模式对比
复杂关联查询的技术实现差异:
// Sequelize 复杂关联查询
const usersWithPosts = await User.findAll({include: [{model: Post,where: {published: true,[Op.and]: [{ createdAt: { [Op.gte]: new Date('2024-01-01') } },{ title: { [Op.like]: '%Node.js%' } }]},include: [{model: Comment,where: { approved: true },include: [{model: User,as: 'commenter',attributes: ['name', 'avatar']}]}]}],where: {[Op.or]: [{ email: { [Op.like]: '%@gmail.com' } },{ email: { [Op.like]: '%@company.com' } }]},order: [['createdAt', 'DESC'],[Post, 'createdAt', 'ASC']],limit: 10,offset: 0
});// Prisma 等效查询
const usersWithPosts = await prisma.user.findMany({include: {posts: {where: {published: true,createdAt: { gte: new Date('2024-01-01') },title: { contains: 'Node.js' }},include: {comments: {where: { approved: true },include: {commenter: {select: {name: true,avatar: true}}}}}}},where: {OR: [{ email: { contains: '@gmail.com' } },{ email: { contains: '@company.com' } }]},orderBy: {createdAt: 'desc'},take: 10,skip: 0
});
性能优化机制对比
🚀 Prisma 实战:完整博客系统实现
系统架构设计
核心数据模型实现
// schema.prisma - 完整博客系统数据模型
generator client {provider = "prisma-client-js"
}datasource db {provider = "postgresql"url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}model User {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())email String @uniquename String?avatar String?role Role @default(USER)bio String?posts Post[]comments Comment[]likes Like[]createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt @map("updated_at")@@map("users")
}model Post {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())title Stringcontent Stringexcerpt String?slug String @uniquepublished Boolean @default(false)featured Boolean @default(false)author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])authorId Intcategories Category[]tags Tag[]comments Comment[]likes Like[]publishedAt DateTime? @map("published_at")createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt @map("updated_at")@@map("posts")@@index([slug])@@index([published, publishedAt])
}model Category {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())name String @uniquedescription String?slug String @uniquecolor String?posts Post[]createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt @map("updated_at")@@map("categories")
}model Comment {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())content Stringapproved Boolean @default(false)author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])authorId Intpost Post @relation(fields: [postId], references: [id])postId Intparent Comment? @relation("CommentReplies", fields: [parentId], references: [id])parentId Int?replies Comment[] @relation("CommentReplies")createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt @map("updated_at")@@map("comments")
}enum Role {USEREDITORADMIN
}
高级业务逻辑实现
文章服务的复杂查询实现:
// services/postService.ts
export class PostService {// 高级搜索和过滤static async searchPosts(filters: PostFilters, pagination: PaginationParams) {const where = this.buildAdvancedWhereClause(filters);const [posts, total] = await Promise.all([prisma.post.findMany({where,include: this.getPostInclude(),orderBy: this.getOrderBy(filters.sort),skip: pagination.skip,take: pagination.take}),prisma.post.count({ where })]);return {data: posts,pagination: {...pagination,total,pages: Math.ceil(total / pagination.take)}};}private static buildAdvancedWhereClause(filters: PostFilters) {const where: any = { published: true };// 全文搜索if (filters.search) {where.OR = [{ title: { contains: filters.search, mode: 'insensitive' } },{ content: { contains: filters.search, mode: 'insensitive' } },{ excerpt: { contains: filters.search, mode: 'insensitive' } },{author: {name: { contains: filters.search, mode: 'insensitive' }}}];}// 分类过滤if (filters.category) {where.categories = {some: { slug: filters.category }};}// 标签过滤if (filters.tags && filters.tags.length > 0) {where.tags = {some: { slug: { in: filters.tags } }};}// 日期范围if (filters.dateRange) {where.publishedAt = {gte: filters.dateRange.start,lte: filters.dateRange.end};}return where;}// 获取文章分析数据static async getPostAnalytics(postId: number) {return await prisma.post.findUnique({where: { id: postId },select: {id: true,title: true,_count: {select: {likes: true,comments: true}},comments: {select: {createdAt: true,author: {select: {name: true}}},orderBy: {createdAt: 'desc'},take: 10}}});}
}
性能优化实践
// 批量操作优化
export class BatchService {// 使用事务确保数据一致性static async batchCreatePosts(postsData: CreatePostData[]) {return await prisma.$transaction(async (tx) => {const posts = [];for (const data of postsData) {const post = await tx.post.create({data: {...data,slug: this.generateSlug(data.title),categories: {connectOrCreate: data.categoryIds?.map(id => ({where: { id },create: { name: `Category ${id}`,slug: `category-${id}`}}))}},include: {categories: true,tags: true}});posts.push(post);}return posts;});}// 使用 Prisma 的批量操作优化性能static async updatePostStatus(ids: number[], published: boolean) {return await prisma.post.updateMany({where: { id: { in: ids } },data: { published,...(published && { publishedAt: new Date() })}});}
}
📈 性能基准测试深度分析
测试环境配置
性能测试结果
| 测试场景 | Sequelize 耗时 | Prisma 耗时 | 性能差异 | 技术分析 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 简单查询 | 45ms | 38ms | +15% | Prisma 查询优化更高效 |
| 关联查询 (3表) | 120ms | 85ms | +29% | Prisma 的 JOIN 优化更好 |
| 批量插入 (1000条) | 320ms | 280ms | +13% | Prisma 的批量操作更优 |
| 复杂嵌套查询 | 210ms | 150ms | +28% | Prisma 查询计划更智能 |
| 事务操作 | 65ms | 58ms | +11% | 两者差距较小 |
| 大数据集分页 | 180ms | 130ms | +27% | Prisma 的分页算法优化 |
🔄 迁移管理工具链深度对比
Sequelize 迁移工作流
Prisma 迁移工作流
迁移管理功能对比
// Sequelize 迁移示例
module.exports = {async up(queryInterface, Sequelize) {await queryInterface.createTable('users', {id: {type: Sequelize.INTEGER,primaryKey: true,autoIncrement: true},email: {type: Sequelize.STRING,allowNull: false,unique: true}// 需要手动定义所有字段...});await queryInterface.addIndex('users', ['email']);},async down(queryInterface, Sequelize) {await queryInterface.dropTable('users');}
};// Prisma 迁移流程
// 1. 编辑 schema.prisma
// 2. 运行: npx prisma migrate dev --name add_user
// 3. 自动生成并应用迁移
🛡️ 类型安全机制深度解析
Sequelize 类型安全挑战
// 需要大量手动类型定义
interface UserAttributes {id: number;email: string;name: string;createdAt: Date;updatedAt: Date;
}interface UserCreationAttributes extends Optional<UserAttributes, 'id'> {}class User extends Model<UserAttributes, UserCreationAttributes> implements UserAttributes {public id!: number;public email!: string;public name!: string;public createdAt!: Date;public updatedAt!: Date;// 关联需要额外声明public posts?: Post[];static associations: {posts: Association<User, Post>;};
}// 使用时的类型问题
const user = await User.findByPk(1);
if (user) {// TypeScript 无法推断具体字段console.log(user.unexpectedProperty); // 没有类型错误!// 需要类型断言const safeUser = user as UserAttributes;
}
Prisma 完全类型安全实现
// 自动生成的完整类型
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({where: { id: 1 },select: {id: true,email: true,name: true,posts: {select: {id: true,title: true,comments: {select: {id: true,content: true,author: {select: {name: true}}}}}}}
});// 完全类型安全的返回值
if (user) {console.log(user.email); // ✅ stringconsole.log(user.posts[0].title); // ✅ stringconsole.log(user.posts[0].comments[0].author.name); // ✅ stringconsole.log(user.unexpectedProperty); // ❌ TypeScript 错误
}// 编译时类型检查
const invalidQuery = await prisma.user.findUnique({where: { invalidField: 1 } // ❌ 编译时错误
});
🎯 技术选型指南
决策流程图
具体场景建议
选择 Sequelize 的情况:
- 🔧 企业级传统项目 - 需要极高的稳定性和成熟度
- 🗄️ 复杂数据库操作 - 需要大量原始 SQL 和数据库特定功能
- 🔌 多数据库支持 - 需要支持 Sequelize 特有的数据库方言
- 🚚 已有代码库迁移 - 渐进式重构,需要更好的灵活性
选择 Prisma 的情况:
- 🚀 新项目启动 - 特别是 TypeScript 项目
- 👥 开发团队协作 - 需要严格的类型安全和代码一致性
- ⚡ 快速原型开发 - 直观的 API 和强大的工具链
- 🔒 全栈类型安全 - 与前端框架深度集成
- 📊 GraphQL API - 与 GraphQL 生态完美契合
🔮 未来发展趋势
Sequelize 发展路线
- 📈 更好的 TypeScript 支持
- 🚀 性能优化和现代化重构
- 🔄 保持向后兼容性
Prisma 发展路线
- 🌐 更多数据库支持
- ☁️ 云原生和边缘计算优化
- ⚡ 更强大的实时功能
- 🤖 机器学习集成
💡 最佳实践总结
Prisma 最佳实践
-
Schema 设计原则
// 使用有意义的字段名和关系名 model User {id Int @id @default(autoincrement())// 使用 @map 和 @@map 控制数据库字段名createdAt DateTime @default(now()) @map("created_at")@@map("users") } -
查询优化策略
// 只选择需要的字段 const users = await prisma.user.findMany({select: {id: true,email: true,// 避免选择不需要的大字段// content: true } }); -
错误处理模式
try {await prisma.$transaction(async (tx) => {// 事务操作}); } catch (error) {if (error instanceof Prisma.PrismaClientKnownRequestError) {// 处理已知错误switch (error.code) {case 'P2002':console.log('唯一约束冲突');break;}} }
Sequelize 最佳实践
-
模型定义规范
// 明确的数据类型和验证 const User = sequelize.define('User', {email: {type: DataTypes.STRING,allowNull: false,validate: {isEmail: true,notNull: { msg: '邮箱不能为空' }}} }, {// 明确的表名配置tableName: 'users' }); -
查询性能优化
// 使用原始查询优化复杂操作 const [results] = await sequelize.query(`SELECT u.*, COUNT(p.id) as post_count FROM users u LEFT JOIN posts p ON u.id = p.author_id GROUP BY u.id`,{ type: QueryTypes.SELECT } );
✅ 最终技术建议
对于现代化项目:
推荐使用 Prisma,它的类型安全、开发体验和性能优势明显,特别适合 TypeScript 项目和团队协作开发。
对于传统企业项目:
Sequelize 仍然是可靠的选择,它的成熟度和灵活性在处理复杂业务逻辑时具有优势。
混合架构考虑:
可以考虑在新技术栈中使用 Prisma,同时在现有系统中保持 Sequelize,逐步迁移。
技术选型没有绝对的对错,只有最适合当前场景的选择。 无论选择哪种方案,良好的架构设计和代码规范都比工具本身更重要。在做出决策时,充分考虑团队的技术栈、项目需求和长期维护计划。
吾问启玄关,艾理顺万绪
