【优选算法】LinkedList-Concatenate:链表的算法之契
文章目录
- 1.概念解析
- 2.两数相加
- 3.两两交换链表中的节点
- 4.重排链表
- 5.合并 K 个升序链表
- 6.K 个一组翻转链表
- 希望读者们多多三连支持
- 小编会继续更新
- 你们的鼓励就是我前进的动力!
1.概念解析
链表是一种线性数据结构,通过节点(含数据 + 指向下一节点的引用 / 指针)串联存储,不要求内存连续;核心特点是插入 / 删除无需移动大量元素(改指针即可),但访问元素需从头遍历(无随机访问能力),常见类型有单链表、双链表、循环链表
2.两数相加
✏️题目描述:

✏️示例:
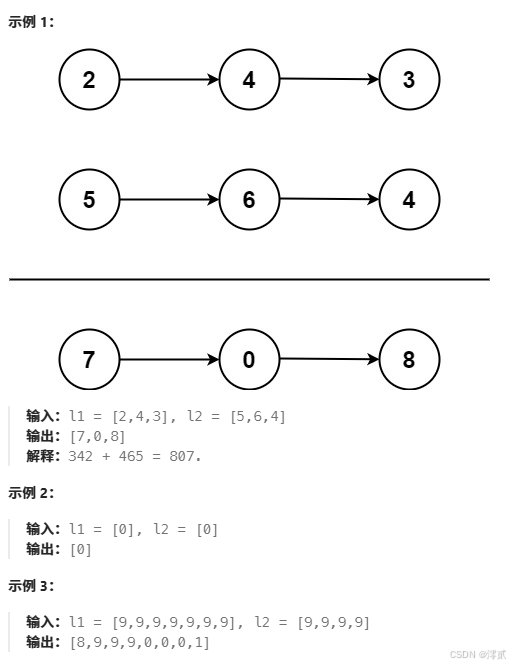
传送门: 两数相加
题解:
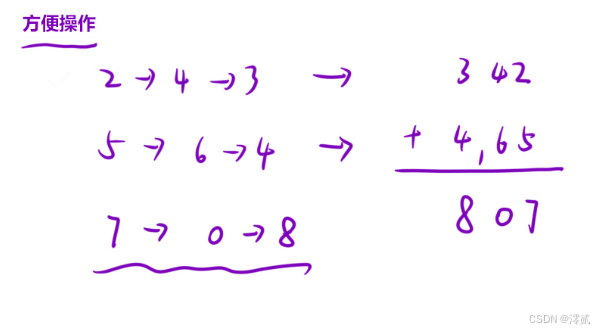
用两个指针指向要相加的链表,创建一个虚拟头节点,用于方便接收新的链表,创建一个变量 t 统计进位,通过不断的 / 和 % 得到答案并尾插新节点到新链表中
💻细节问题: 要注意 h1 指针、h2 指针、t 都为 nullptr 或 0 才能停止循环
💻代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode* h1 = l1, *h2 = l2;ListNode* head = new ListNode();ListNode* tail = head;int data = 0;while(h1 || h2 || data){if(h1){data += h1->val;h1 = h1->next;}if(h2){data += h2->val;h2 = h2->next;}ListNode* node = new ListNode();tail->next = node;tail = tail->next;node->val = (data % 10);data /= 10;}return head->next;}
};
3.两两交换链表中的节点
✏️题目描述:

✏️示例:
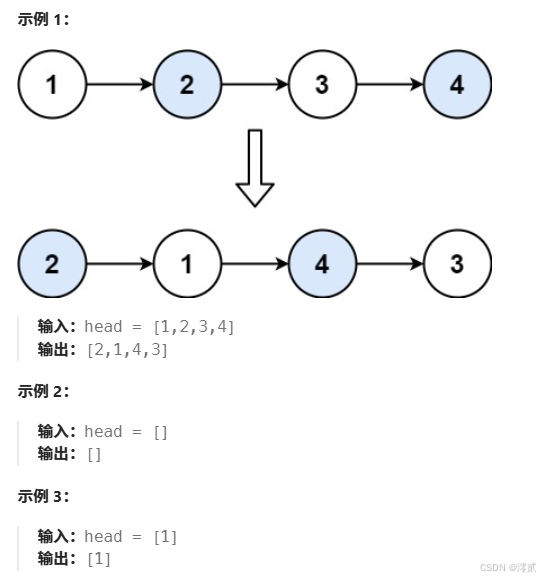
传送门: 两两交换链表中的节点
题解:
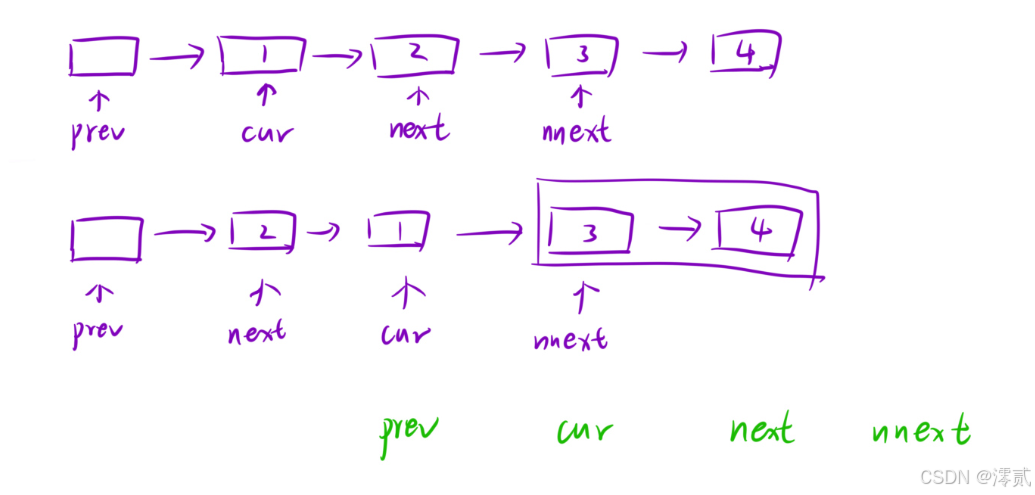
这题实际上是一道很基础的模拟,不要吝啬你的变量定义,因为相邻两个节点交换涉及四个节点的指针变化,不如给这四个节点都定义一个变量,就不怕被覆盖的问题了
💻代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr){return head;}ListNode* headnode = new ListNode();headnode->next = head;ListNode* prevNode = headnode;ListNode* cur = head;ListNode* nextNode = head->next;ListNode* nnextNode = head->next->next;while(cur && nextNode){prevNode->next = nextNode;cur->next = nnextNode;nextNode->next = cur;prevNode = cur;cur = nnextNode;if(cur) nextNode = cur->next;if(nextNode) nnextNode = nextNode->next;}return headnode->next;}
};
4.重排链表
✏️题目描述:

✏️示例:
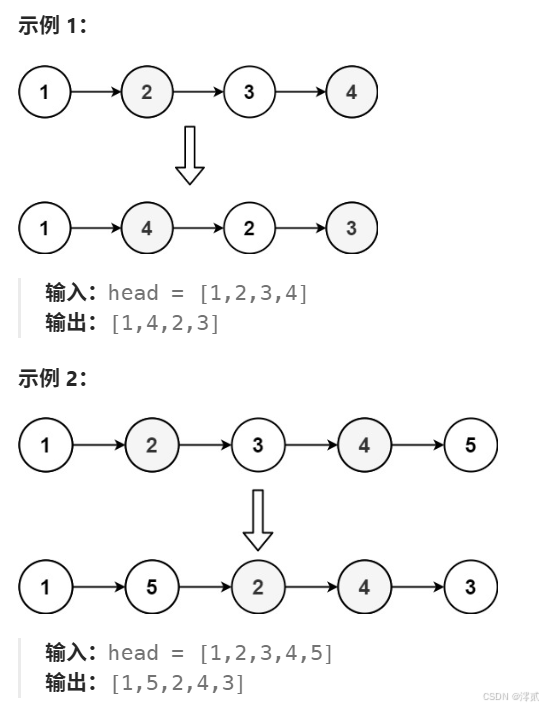
传送门: 重排链表
题解:
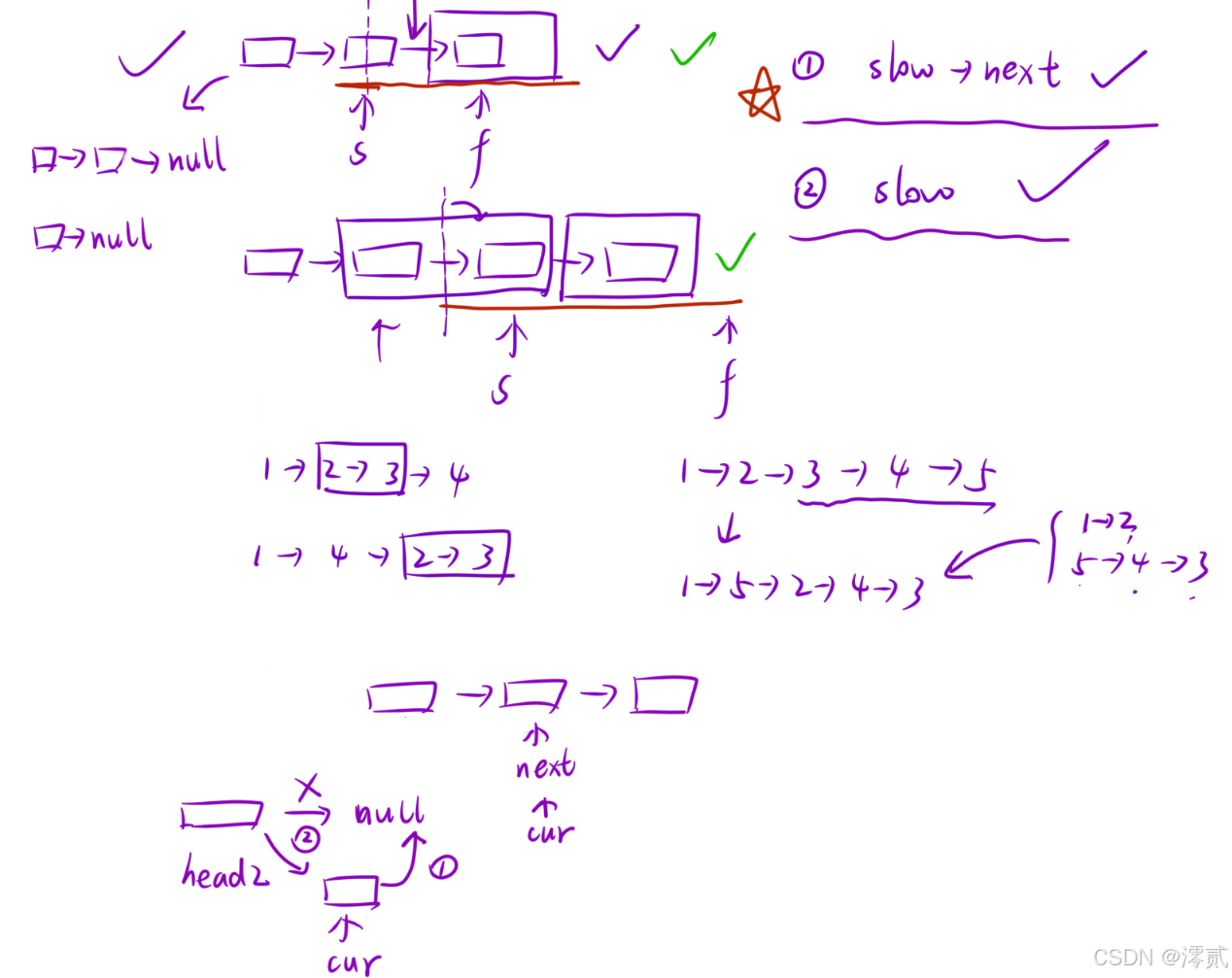
这是一道综合性很强的题目,可以看到是依次取链尾和链首的的节点重排链表,那么就需要用到快慢指针找到中间节点,然后通过不断头插逆序链表,获得新链表,那么按照题意合并新链表即可
💻代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void reorderList(ListNode* head) {if(!head || !head->next || !head->next->next){return;}ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}ListNode* head2 = new ListNode();ListNode* cur = slow->next;slow->next = nullptr;while(cur){ListNode* nextNode = cur->next;cur->next = head2->next;head2->next = cur;cur = nextNode;}ListNode* ret = new ListNode();ListNode* prev = ret;ListNode* cur1 = head, *cur2 = head2->next;while(cur1){prev->next = cur1;prev = prev->next;cur1 = cur1->next;if(cur2){prev->next = cur2;prev = prev->next;cur2 = cur2->next;}}delete head2;delete ret;}
};
5.合并 K 个升序链表
✏️题目描述:

✏️示例:

传送门: 合并 K 个升序链表
题解:
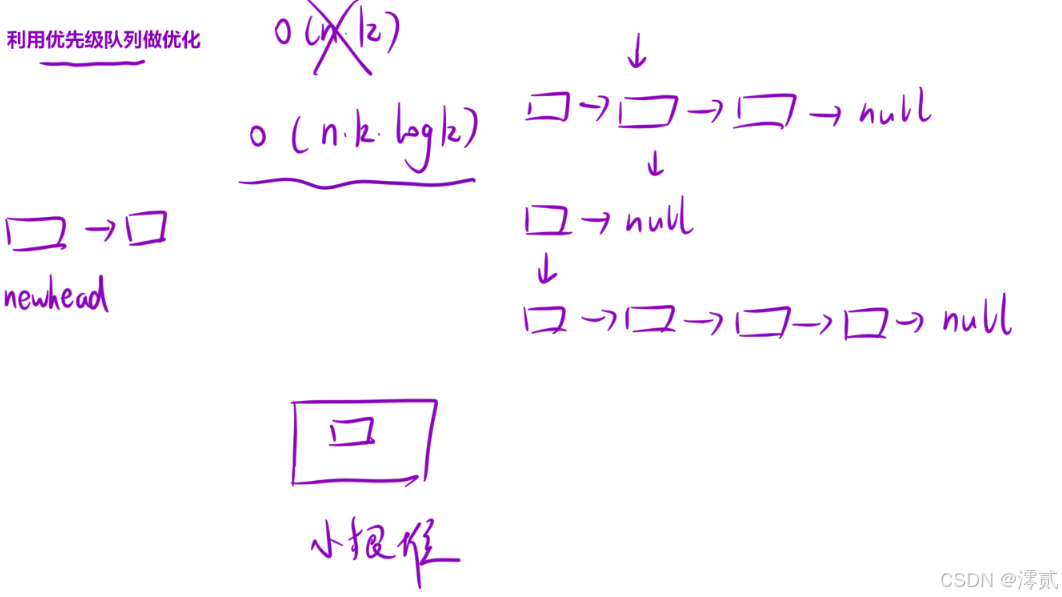
其实这题最先想到的方法就是每条链表定义一个指针指向,因为是升序的,所以依次从小到大放进新链表就行了,但是这几个链表的指针又要取 value 小的那个,进而我们可以想到使用优先级队列,建立小根堆,这样每次取堆顶的都是最小的数
💻代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution
{struct cmp{bool operator()(const ListNode* l1, const ListNode* l2){return l1->val > l2->val;}};
public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, cmp> heap;for(auto l : lists){if(l){heap.push(l);}}ListNode* ret = new ListNode();ListNode* prev = ret;while(!heap.empty()){ListNode* t = heap.top();prev->next = t;heap.pop();prev = t;if(t->next){t = t->next;heap.push(t);}}prev = ret->next;delete ret;return prev;}
};
6.K 个一组翻转链表
✏️题目描述:

✏️示例:
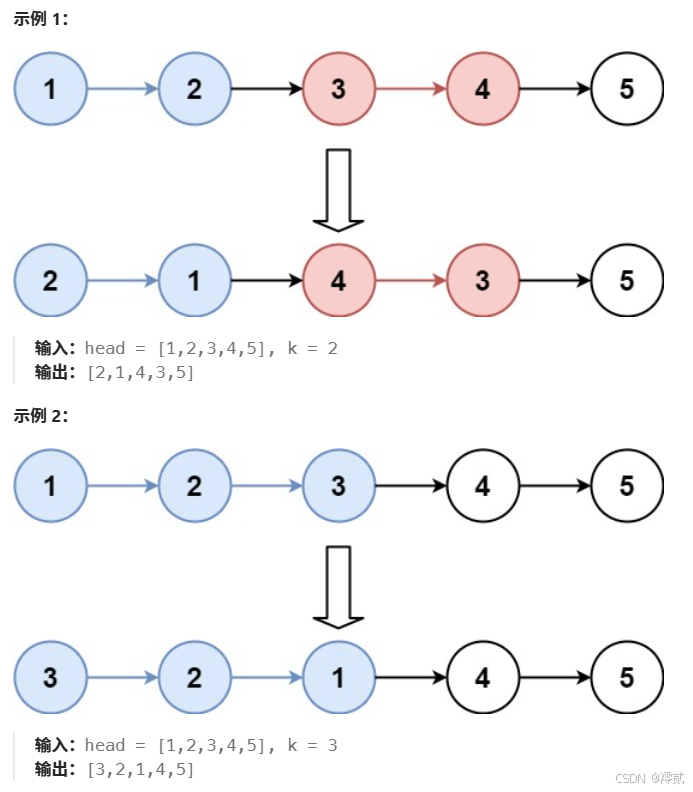
传送门: K 个一组翻转链表
题解:
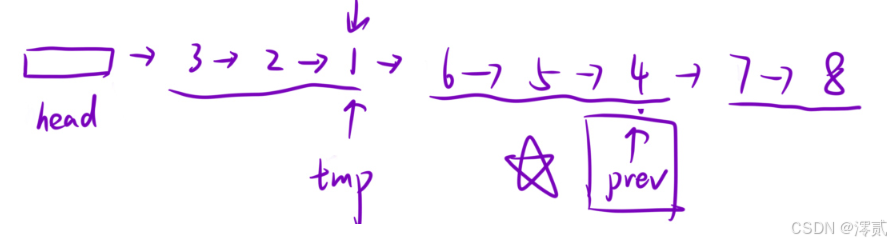
这题和 两两交换链表中的节点 那一题思路差不多,不过要注意提前保存节点,和计算有多少组需要翻转
💻代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {int sum = 0;ListNode* cur = head;while(cur){sum++;cur = cur->next;}int n = sum / k;ListNode* ret = new ListNode();ListNode* prev = ret;cur = head;for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ListNode* tmp = cur;for(int j = 0; j < k; ++j){ListNode* nextNode = cur->next;cur->next = prev->next;prev->next = cur;cur = nextNode;}prev = tmp;}prev->next = cur;cur = ret->next;delete ret;return cur;}
};
希望读者们多多三连支持
小编会继续更新
你们的鼓励就是我前进的动力!

