数据结构与算法实验(黑龙江大学)
《数据结构与算法》实验内容及要求
实验一 顺序存储的线性表(2 学时)
实验二 单链表上的操作(2 学时)
实验三 循环链表和双链表(2 学时)
实验四 栈和队列(2 学时)
实验五 树的应用(2 学时)
实验六 综合设计与应用一(个人项目) (6 学时)
以下题目任选其中一个:
1.表达式求值问题
2.哈夫曼编码译码器
实验七 图的应用(2 学时)
实验八 综合设计与应用二(团队项目)(4 学时)
以下题目任选其中一个:
1.校园导游系统 (求最短路径算法: Dijkstra,Floyd)
2.最小生成树模拟程序(求最小生成树算法: Prim、Kruskal)
3.迷宫问题模拟程序(栈、队列、堆的应用,各种树形搜索算法)
4. 通讯录管理系统的设计与实现(各种查找算法)
5 内部排序性能分析演示程序(各种排序算法)
6. 教学计划编制系统的设计与实现 (拓扑排序)
7. 自选题目
实验九 排序和查找(2 学时)实验一 顺序存储的线性表(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导

四、考核标准

五、实验代码
package 实验一;import java.util.Scanner;public class MySeqListTest {private int[] arr;private int len;//顺序表长度,记载元素个数public MySeqListTest(int[] elem) {if (elem == null || elem.length == 0) {this.len = 0;} else {arr = elem;len = elem.length;}}/*** @description: 插入并排序* @date: 2023/10/28 19:59* @param: [x]* @return: void**/public void insert(int x) {int[] newArr = new int[len + 1];//将数组中元素按升序排列for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {if (arr[i] < arr[j]) {int temp = arr[i];arr[i] = arr[j];arr[j] = temp;}}}int i = 0, j = 0;// i 为element数组下标,j为newArr数组元素下标for (; i < arr.length; i++, j++) {//判断插入元素位置if (arr[i] >= x) {//如果element元素大于x,则将x置于newArr数组第j个位置newArr[j] = x;break;}else {//否则就将element数组中第i个元素置于newArr数组中第j个元素newArr[newArr.length-1] = x;newArr[j]=arr[i];}}while (i<arr.length){//复制element中元素,扩容4newArr[++j]=arr[i];i++;}arr=newArr;//更新数组len++;System.out.print("插入后的数组为:");for (int k=0;k<arr.length;k++){System.out.print(arr[k]+" ");}}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);int[] array = {1, 20, 6, 9, 27};MySeqListTest mySeqList = new MySeqListTest(array);System.out.println("请输入要插入的元素:");int n=sc.nextInt();mySeqList.insert(n);}
}
package 实验一;import java.util.Scanner;public class RightMoveTest {/*** @description: 循环右移* @date: 2023/10/28 19:59* @param: [move, num]* @return: void**/public void rightMove(int[] move, int num) {int i, j, temp;for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {//将原数组最后一位存入临时变量temptemp = move[move.length - 1];for (j = move.length - 2; j >= 0; j--) {//将剩下所有元素右移num次move[j + 1] = move[j];}move[0] = temp;//右移结束后temp存在数组第一位}System.out.println("循环右移结果如下:");for (i = 0; i < move.length; i++) {System.out.print(move[i] + "\t");}}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入数组元素个数:");int n = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请输入循环右移次数:");int m = sc.nextInt();int[] arr = new int[n];System.out.println("依次输入数组元素");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = sc.nextInt();}RightMoveTest r = new RightMoveTest();r.rightMove(arr, m);}
}
package 实验一;import java.util.Scanner;public class ArrayReverse {/*** @description: 数组逆置* @date: 2023/10/28 19:58* @param: [array]* @return: void**/public void reverse(int[] array) {for (int i = 0; i < array.length / 2; i++) {int temp = array[i];array[i] = array[array.length - i - 1];array[array.length - i - 1] = temp;}System.out.println("数组逆置结果如下:");for (int i : array) {System.out.print(i + " ");}}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入数组元素个数:");int num = sc.nextInt();int[] arr = new int[num];System.out.println("依次输入数组元素:");for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {arr[i] = sc.nextInt();}ArrayReverse a = new ArrayReverse();a.reverse(arr);}
}实验二 单链表 (2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容


三、实验指导

四、考核标准

五、实验代码
package 实验二;import java.util.Scanner;public class Node {private int data;private Node next;public Node() {Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);data= sc.nextInt();next = null;}public Node(Node next) {this.next = next;}public Node(int data) {this.data = data;}public Node(int data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public int getData() {return data;}public void setData(int data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + " "+next+" ";}
}
package 实验二;import java.util.Scanner;public class LinkList {private Node head;private int num;//初始化(建立)空链表public LinkList() {num = 0;head = null;}public LinkList(Node head) {this.head = head;}//初始化(建立)一个具有n个结点的链表public LinkList(int n) {num = n;head = new Node();Node p = head;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {p.setNext(new Node());p = p.getNext();}}/*** @description: 插入* @date: 2023/10/28 20:00* @param: [x]* @return: void**/public void insert(int x) {Node temp = new Node(x);num++;if (head == null) {head = temp;} else {if (x < head.getData()) {temp.setNext(head);head = temp;} else {Node p = head;while (p.getNext() != null && p.getNext().getData() < x) {p = p.getNext();}temp.setNext(p.getNext());p.setNext(temp);}}}/*** @description: 输出链表中所有结点data域的值* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01* @param: []* @return: void**/public void linkPrint() {Node p = head;if (head != null) {while (p.getNext() != null) {System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");p = p.getNext();}System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");} else {System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");}}/*** @description: 选择排序(升序)* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01* @param: [head]* @return: void**/public void sortList(Node head) {Node p = head;int temp = 0;while (p != null) {Node next = p.getNext();while (next != null) {if (next.getData() < p.getData()) {temp = p.getData();p.setData(next.getData());next.setData(temp);}next = next.getNext();}p = p.getNext();}}/*** @description: 选择排序(降序)* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01* @param: [head]* @return: void**/public void sortList_2(Node head) {Node q = head;int temp = 0;while (q != null) {Node next = q.getNext();while (next != null) {if (next.getData() > q.getData()) {temp = q.getData();q.setData(next.getData());next.setData(temp);}next = next.getNext();}q = q.getNext();}}/*** @description: 逆置 从原来的链表把第一个节点一个一个逮出来,然后头插到新链表中* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01* @param: [head]* @return: void**/public void reverse(Node head) {Node p = head; //head原链表头结点Node temp = null;//暂时保存的原来的头结点Node result = null;//新链表头结点while (p != null) {temp = p;p = p.getNext();temp.setNext(result);result = temp;}if (head != null) {while (result.getNext() != null) {System.out.print(result.getData() + " ");result = result.getNext();}System.out.print(result.getData() + " ");} else {System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");}}/*** @description: 连接* @date: 2023/10/28 20:02* @param: [p]* @return: void**/public void connect(LinkList p) {Node p1 = head;num = p.num + num;while (p1.getNext() != null) {p1 = p1.getNext();}Node p2 = p.head;while (p2 != null) {p1.setNext(new Node(p2.getData()));p1 = p1.getNext();p2 = p2.getNext();}}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);//插入测试System.out.println("请输入链表1的初始长度: ");int n1 = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请往链表1中输入数据: ");LinkList l1 = new LinkList(n1);System.out.println("显示链表1: ");l1.linkPrint();System.out.println();System.out.println("请输入插入的数据:");int x = sc.nextInt();l1.insert(x);l1.sortList(l1.head);System.out.println("显示插入之后的链表:");l1.linkPrint();//逆置测试System.out.println();System.out.println("请输入链表2的初始长度: ");int n2 = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请往链表2中输入数据: ");LinkList l2 = new LinkList(n2);System.out.println("显示链表2: ");l2.sortList(l2.head);l2.linkPrint();System.out.println();System.out.println("逆置后链表为:");l2.reverse(l2.head);//归并降序测试System.out.println();System.out.println("请输入链表3的初始长度: ");int n3 = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请往链表3中输入数据: ");LinkList l3 = new LinkList(n3);System.out.println("显示链表3: ");l3.linkPrint();System.out.println();System.out.println("请输入链表4的初始长度: ");int n4 = sc.nextInt();System.out.println("请往链表4中输入数据: ");LinkList l4 = new LinkList(n4);System.out.println("显示链表4: ");l4.linkPrint();System.out.println();System.out.println("连接链表3和链表4: ");l3.connect(l4);l3.linkPrint();System.out.println();System.out.println("将连接好的链表降序输出: ");l3.sortList_2(l3.head);l3.linkPrint();}
}实验三 循环链表和双链表(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导


四、考核标准

五、实验代码

package 实验三.题目一;import java.util.Objects;public class Node {private Object data;Node next;public Node(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node() {}public Node(Object data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + " ";}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;Node node = (Node) o;return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) &&Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());}
}
package 实验三.题目一;public class LinkedList1 {private Node head;public LinkedList1() {}public LinkedList1(Node head) {this.head = head;}public void create(int len) {head = new Node();Node p = head;if (len == 1) {p.setData(null);} else {for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (i < len - 1) {p.setData(i);p.setNext(new Node());p = p.getNext();}if (i==len-1){p.setData(i);p.setNext(head);}}}}public Node get (int index){if (head != null) {int i = 0;Node tmp = head;while (tmp.getNext() != null) {if (i == index) {return tmp;}i++;tmp = tmp.getNext();}if (i == index) {return tmp;}}return null;}public void delete(int n){Node curr=head;while(!curr.getNext().getData().equals(n)){curr=curr.getNext();}curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext());curr.setData(n);}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList1 l=new LinkedList1();l.create(2);System.out.println("显示链表:");for (int i=0;i<2;i++){System.out.print(l.get(i));}System.out.println();System.out.println("删除后的链表:");l.delete(0);for (int i=0;i<1;i++){System.out.print(l.get(i));}}
}
package 实验三.题目二;public class Node {private char data;private Node next;public Node() {this('0',null);}public Node(Node next) {this.next = next;}public Node(char data) {this.data = data;}public Node(char data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public char getData() {return data;}public void setData(char data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + " "+next+" ";}
}
package 实验三.题目二;public class LinkedList2 {private Node head;int size;public LinkedList2() {this.head = new Node('0', null);this.size = 0;}public void create(Node head, int len) {head = new Node();Node p = head;if (len == 1) {p.setData('\0');} else {for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if (i < len - 1) {p.setNext(new Node());p = p.getNext();}if (i == len - 1) {p.setNext(head);}}}}public void insert(char t) {Node n = head;while (n.getNext() != null) {n = n.getNext();}Node newNode = new Node(t, null);n.setNext(newNode);size++;}public Node get(int i) {Node p = head;for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {p = p.getNext();}return p;}public void linkPrint() {Node p = head.getNext();if (head != null) {while (p.getNext() != null) {System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");p = p.getNext();}System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");System.out.println();} else {System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");}}public void result() {Node current = head;LinkedList2 a1 = new LinkedList2();LinkedList2 a2 = new LinkedList2();LinkedList2 a3 = new LinkedList2();while (current != null) {if ((current.getData() >= 'A' && current.getData() <= 'Z') || (current.getData() >= 'a' && current.getData() <= 'z')) {a1.insert(current.getData());} else if (current.getData() >= '0' && current.getData() <= '9') {a2.insert(current.getData());} else {a3.insert(current.getData());}current = current.getNext();}System.out.print("字母:");a1.linkPrint();System.out.print("数字:");a2.linkPrint();System.out.print("符号:");a3.linkPrint();}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList2 l = new LinkedList2();l.insert('1');l.insert('2');l.insert('a');l.insert('e');l.insert('f');l.insert('b');l.insert('5');l.insert('c');l.insert('7');l.insert('9');l.insert('d');l.insert('e');l.insert('@');l.insert('#');l.insert('$');l.insert('%');l.insert('^');l.insert('&');l.insert('*');l.insert('?');l.create(l.head, 20);l.linkPrint();l.result();}
}
package 实验三.题目三;import java.util.Objects;public class Node {private Object data;private int freq;Node prior;Node next;public Node(Object data, int freq, Node prior, Node next) {this.data = data;this.freq = freq;this.prior = prior;this.next = next;}public Node(Object data) {this.data=data;}public Node(){}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public int getFreq() {return freq;}public void setFreq(int freq) {this.freq = freq;}public Node getPrior() {return prior;}public void setPrior(Node prior) {this.prior = prior;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data+" " ;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;Node node = (Node) o;return getFreq() == node.getFreq() && Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getPrior(), node.getPrior()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getData(), getFreq(), getPrior(), getNext());}
}
package 实验三.题目三;public class LinkList {private Node head;public LinkList() {}public LinkList(Node head) {this.head = head;}public Node getHead() {return head;}public void setHead(Node head) {this.head = head;}public Node get(int index) {if (head != null) {int count = 0;Node temp = head;while (temp.getNext() != null) {if (count == index) {return temp;}count++;temp = temp.getNext();}if (count == index) {return temp;}}return null;}public void add(Object data) {Node node = new Node(data);if (head == null) {head = node;} else {Node temp = head;while (temp.getNext() != null) {temp = temp.getNext();}temp.setNext(node);}}public int size() {if (head == null) {return 0;} else {Node temp = head;int count = 0;while (temp.getNext() != null) {temp = temp.getNext();count++;}count++;return count;}}public void Locate(LinkList l, int x) {Node temp = l.head;while (temp.getNext() != null) {if (temp.getData().equals(x)) {temp.setFreq(temp.getFreq() + 1);}temp = temp.getNext();}if (temp.getData().equals(x)) {temp.setFreq(temp.getFreq() + 1);}}//冒泡排序(升序)public void order(LinkList l) {int size = l.size();int temp;for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) {if (l.get(j).getFreq() <= l.get(j + 1).getFreq()) {temp = (int) l.get(j + 1).getData();l.get(j + 1).setData(l.get(j).getData());l.get(j).setData(temp);}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkList l1 = new LinkList();l1.add(1);l1.add(2);l1.add(3);l1.add(4);l1.Locate(l1, 1);l1.Locate(l1, 1);l1.Locate(l1, 1);l1.Locate(l1, 2);l1.Locate(l1, 2);l1.Locate(l1, 2);l1.Locate(l1, 2);l1.Locate(l1, 3);System.out.println("链表为:");System.out.println(l1.get(0) + " " + l1.get(1) + " " + l1.get(2) + " " + l1.get(3));System.out.println("该链表中个数据频度为:");System.out.println(l1.get(0).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(1).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(2).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(3).getFreq());System.out.println("排序后:");l1.order(l1);System.out.println(l1.get(0) + " " + l1.get(1) + " " + l1.get(2) + " " + l1.get(3));}
}
实验四 栈和队列(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导

四、考核标准

五、实验代码

package 实验四.题目一;import java.util.Objects;public class Node {private Object data;Node next;public Node(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node(Object data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public Node() {}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + "" ;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;Node node = (Node) o;return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());}
}
package 实验四.题目一;import java.util.Objects;public class Stack {private Node head;private int N;public Stack() {this.head = new Node(null, null);this.N = 0;}/*** @description: 判断当前栈中元素个数是否为0* @param: []* @return: boolean*/public boolean isEmpty() {return N == 0;}/*** @description: 获取栈中元素个数* @param: []* @return: int*/public int size() {return N;}/*** @description: 把t元素压入栈* @param: [t]* @return: void*/public void push(Object t) {//找到首结点指向的第一个结点Node oldFirst = head.getNext();//创建新节点Node newNode = new Node(t, null);//让首结点指向新结点head.setNext(newNode);//让新结点指向原来的第一个结点newNode.setNext(oldFirst);//元素个数+1N++;}/*** @description: 弹出栈顶元素* @param: []* @return: java.lang.Object*/public Object pop() {//找到首结点指向的第一个结点Node oldFirst = head.getNext();if (oldFirst == null) {return null;}//让首结点指向原来的第一个结点的下一个结点head.setNext(oldFirst.getNext());//元素个数-1N--;return oldFirst.getData() + "";}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Stack)) return false;Stack stack = (Stack) o;return N == stack.N && Objects.equals(head, stack.head);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(head, N);}
}
package 实验四.题目一;import java.util.Objects;public class LinkedList {private Node head;public LinkedList() {}public LinkedList(Node head) {this.head = head;}public Node getHead() {return head;}public void setHead(Node head) {this.head = head;}public Node get(int index) {if (head != null) {int count = 0;Node temp = head;while (temp.getNext() != null) {if (count == index) {return temp;}count++;temp = temp.getNext();}if (count == index) {return temp;}}return null;}public int size() {if (head == null) {return 0;} else {Node temp = head;int count = 1;while (temp.getNext() != null) {temp = temp.getNext();count++;}return count;}}public void add(Object data) {Node node = new Node(data);if (head == null) {head = node;} else {Node temp = head;while (temp.getNext() != null) {temp = temp.getNext();}temp.setNext(node);}}public boolean isCentrallySymmetric(LinkedList l) {int size = l.size();int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < size / 2; i++) {if (l.get(i).getData().equals(l.get(size - 1 - i).getData())) {count++;}}if (count == size / 2 || count == (size / 2) + 1) {return true;}return false;}public void linkPrint() {Node p = head;if (head != null) {while (p.getNext() != null) {System.out.print(p.getData() + "");p = p.getNext();}System.out.print(p.getData() + "");} else {System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");}}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList l = new LinkedList();l.add('a');l.add('b');l.add('a');l.add('b');l.add('a');boolean b = l.isCentrallySymmetric(l);l.linkPrint();System.out.println("是否为中心对称的字符串:");System.out.println(b);}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof LinkedList)) return false;LinkedList that = (LinkedList) o;return Objects.equals(getHead(), that.getHead());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getHead());}
}
package 实验四.题目一;public class CentrallySymmetric {public static boolean isCentrallySymmetric(LinkedList l) {Stack s = new Stack();Node p = l.getHead();for (int i = 0; i < l.size() / 2; i++) {s.push(p.getData());p = p.getNext();}if (l.size()%2==1){p=p.getNext();}int count=0;for (int i = 0; i < l.size() / 2; i++) {Object pop = s.pop();if (p!=null&&pop.equals(p.getData())){count++;p=p.getNext();}}System.out.println(count);if (count== l.size()/2){return true;}else {return false;}}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList l = new LinkedList();l.add("a");l.add("a");l.add("b");l.add("b");l.add("a");l.add("a");boolean b = CentrallySymmetric.isCentrallySymmetric(l);l.linkPrint();System.out.println("是否为中心对称的字符串:");System.out.println(b);}
}
package 实验四.题目二;import java.util.Objects;public class Node {private Object data;Node next;public Node(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node() {}public Node(Object data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + " " ;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;Node node = (Node) o;return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) &&Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());}
}
package 实验四.题目二;public class Stack {private Node head;private int N;public Stack() {this.head = new Node(null, null);this.N = 0;}//判断当前栈中元素个数是否为0public boolean isEmpty() {return N == 0;}//获取栈中元素个数public int size() {return N;}//把t元素压入栈public void push(Object t) {//找到首结点指向的第一个结点Node oldFirst = head.getNext();//创建新节点Node newNode = new Node(t, null);//让首结点指向新结点head.setNext(newNode);//让新结点指向原来的第一个结点newNode.setNext(oldFirst);//元素个数+1N++;}//弹出栈顶元素public String pop() {//找到首结点指向的第一个结点Node oldFirst=head.getNext();if (oldFirst==null){return null;}//让首结点指向原来的第一个结点的下一个结点head.setNext(oldFirst.getNext());//元素个数-1N--;return oldFirst.getData()+"";}}
package 实验四.题目二;public class BracketsMatchTest {public static boolean isMatch(String str) {//建栈Stack chars = new Stack();//从左到右遍历字符串for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {String currChar = str.charAt(i) + "" ;//如果检测到左括号,压入栈中if (currChar.equals("(")) {chars.push(currChar);//如果检测到右括号,从栈中弹出一个左括号} else if (currChar.equals(")")) {String pop = chars.pop();if (pop == null) {return false;}}}//栈中是否有剩余的左括号if (chars.size() == 0){return true;}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "({[]})" ;boolean match = isMatch(str);System.out.println(str + " 中的括号是否配对: "+"\t");System.out.println(match+"\t");}
}
package 实验四.题目三;import java.util.Objects;public class Node {private Object data;Node next;public Node(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node(Object data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public Node() {}public Object getData() {return data;}public void setData(Object data) {this.data = data;}public Node getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Node next) {this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return data + "" ;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;Node node = (Node) o;return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());}
}
package 实验四.题目三;public class LinkedList {private Node head;public LinkedList(Node head) {this.head = head;}public LinkedList() {}public Node getHead() {return head;}public void setHead(Node head) {this.head = head;}public void createList(int size) {head = new Node();Node temp = head;if (size == 1) {temp.setData(null);} else {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {if ((i < size - 1)) {temp.setData(i);temp.setNext(new Node());temp = temp.getNext();} else if (i == size - 1) {temp.setData(i);temp.setNext(head);}}}}public Node get(int index) {if (head != null) {int count = 0;Node tmp = head;while (tmp.getNext() != null) {if (count == index) {return tmp;}count++;tmp = tmp.getNext();}if (count == index) {return tmp;}}return null;}public int size() {if (head == null) {return 0;} else {Node tmp = head;int count = 1;while (tmp.getNext() != null) {tmp = tmp.getNext();count++;}return count;}}public void delete(int num) {Node tmp = head;while (!tmp.getNext().getData().equals(num)) {tmp = tmp.getNext();}tmp.setNext(tmp.getNext().getNext());tmp.setData(num);}//置队空public LinkedList setNull(LinkedList l) {// l.createList(5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {l.get(i).setData(null);}return l;}//进队public void enqueue(LinkedList l, int data) {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {if (l.get(i).getData() == null) {l.get(i).setData(data);break;}}}//出队public void dequeue(LinkedList l, int size) {for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {l.delete((int) l.get(1).getData());}}}
package 实验四.题目三;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList l=new LinkedList();l.createList(5);LinkedList l1=l.setNull(l);for (int i=0;i<5;i++){System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");}l1.enqueue(l1,4);l1.enqueue(l1,5);l1.enqueue(l1,6);l1.enqueue(l1,7);l1.enqueue(l1,8);System.out.println();System.out.println("入队之后链表里的数据为");for (int i=0;i<5;i++){System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");}l1.dequeue(l1,2);System.out.println();System.out.println("出队之后的数据为");for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");}}
}
实验五 树的应用(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导

四、考核标准

五、实验代码
package 实验五.题目一;public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {private Node root;private int N;private class Node {public Key key;//存储键private Value value;//存储值public Node left;public Node right;public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.left = left;this.right = right;}}//获取树中元素个数public int size() {return N;}//向树中添加元素key-valuepublic void put(Key key, Value value) {root = put(root, key, value);}//向指定树x中添加 key-value,并返回添加元素后的新树private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {//如果x子树为空if (x == null) {N++;return new Node(key, value, null, null);}//如果x子树不为空//比较x结点的键和key的大小int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);if (cmp > 0) {//如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树x.right = put(x.right, key, value);} else if (cmp < 0) {//如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树x.left = put(x.left, key, value);} else {//如果key等于x结点的键,则替换x结点的值为valuex.value = value;}return x;}//查询树中指定key对应的valuepublic Value get(Key key) {return get(root, key);}//从指定的树x中,查找key对应的值public Value get(Node x, Key key) {//x树为空if (x == null) {return null;}//x树不为空//比较x结点的键和key的大小int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);if (cmp > 0) {//如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树return get(x.right, key);} else if (cmp < 0) {//如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树return get(x.left, key);} else {//如果key等于x结点的键,就找到了键为key的结点,只需要返回x结点的值即可return x.value;}}//获取整个树的最大深度public int maxDepth() {return maxDepth(root);}//获取指定树x的最大深度private int maxDepth(Node x) {if (x == null) {return 0;}int max = 0;//x的最大深度int maxL = 0;//的最大深度int maxR = 0;//的最大深度//计算x结点左子树的最大深度if (x.left != null) {maxL = maxDepth(x.left);}//计算x结点右子树的最大深度if (x.right != null) {maxR = maxDepth(x.right);}//比较左右子树最大深度,取最大值+1if (maxL > maxR) {max = maxL + 1;} else {max = maxR + 1;}return max;}
}
package 实验五.题目一;public class BinaryTreeMaxDepthTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建树对象BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();//往树中添加数据tree.put("E", "5");tree.put("B", "2");tree.put("G", "7");tree.put("A", "1");tree.put("D", "4");tree.put("F", "6");tree.put("H", "8");tree.put("C", "3");int maxDepth = tree.maxDepth();System.out.println(maxDepth);}
}

package 实验五.题目二;public class LinkedList {public void preorder(int[] tree) {int p = 0;int k = 0;while (k != tree.length) {if (p < tree.length) {System.out.println(tree[p] + " ");p = 2 * p + 1;k++;} else {p = p / 2;if (p % 2 == 0) {p = p / 4 - 1;p = 2 * p + 2;} else {p = p + 1;if (p >= tree.length) {p = 2 * p + 1;}}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList linkedlist = new LinkedList();int[] tree = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};linkedlist.preorder(tree);}
}
package 实验五.题目三;public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {public Node root;public int N;public class Node {public Key key;public Value value;public Node left;public Node right;public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.left = left;this.right = right;}}public int size() {return N;}public void put(Key key, Value value) {root = put(root, key, value);}//向指定的树x中添加key-value,并返回添加元素后新的树private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {if (x == null) {N++;return new Node(key, value, null, null);}//如果x子树不为空,比较x结点的键和key的大小int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);if (cmp > 0) {//如果key大于x节点的键,则继续找x节点的右子树x.right = put(x.right, key, value);} else if (cmp < 0) {x.left = put(x.left, key, value);} else {x.value = value;}return x;}public int maxDepth() {return maxDepth(root);}//获取指定树x的最大深度private int maxDepth(Node x) {if (x == null) {return 0;}int max = 0;int maxL = 0;int maxR = 0;if (x.left != null) {maxL = maxDepth(x.left);}if (x.right != null) {maxR = maxDepth(x.right);}max = maxL > maxR ? maxL + 1 : maxR + 1;return max;}
}
package 实验五.题目三;import java.util.Stack;public class LinkedList {/*** @description: 前序* @param: [root]* @return: void*/static void preOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {if (root == null) return;Stack<BinaryTree.Node> s = new Stack<>();while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {while (root != null) {System.out.print(root.value + " ");s.push(root);root = root.left;}if (!s.isEmpty()) {BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();root = t.right;}}}/*** @description: 中序* @param: [root]* @return: void*/static void inOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {if (root == null) return;Stack<BinaryTree.Node> s = new Stack<>();while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {while (root != null) {s.push(root);root = root.left;}if (!s.isEmpty()) {BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();System.out.print(t.value + " ");root = t.right;}}}/*** @description: 后序* @param: [root]* @return: void*/static void postOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {if (root == null) return;Stack<BinaryTree.Node> s = new Stack<>();BinaryTree.Node last = null;while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {while (root != null) {s.push(root);root = root.left;}if (!s.isEmpty()) {BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();if (t.right == null || last == t.right) {//在这里面打印t并处理last之后,并不用处理root,因为之所以能进入这里,是因为root一定等于null,所以下一轮循环一定还能进入这里,然后弹出t的父结点做处理System.out.print(t.value + " ");last = t;} else {//右孩子还没有打印过s.push(t);//因为当前结点未打印,所以要重新放回去,等右孩子打印完之后回来打印root = t.right;}}}}public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTree<String, String> tree = new BinaryTree<>();tree.put("E", "5");tree.put("B", "2");tree.put("G", "7");tree.put("A", "1");tree.put("D", "4");//preOrder(tree.root);System.out.println();//inOrder(tree.root);System.out.println();//postOrder(tree.root);}
}实验六 综合设计与应用一(个人项目) (6 学时)
本单元为个人综合项目,上机实现部分占 5 分,报告占 3 分,总计 8 分,共占 6 学时。
一、实验目的
1.熟练掌握线性结构(线性表、栈、队列等)的存储方式,及在其上进行复杂操作的方式。
2.熟练掌握非线性结构----树形结构的存储方式,及在其上进行复杂操作的方式。
3.提高学生设计能力以及编写综合性大实验的编程能力。
二、实验内容 (以下题目任选其中一个)
1.表达式求值问题
2.哈夫曼编码译码器
三、实验指导
1.表达式求值问题




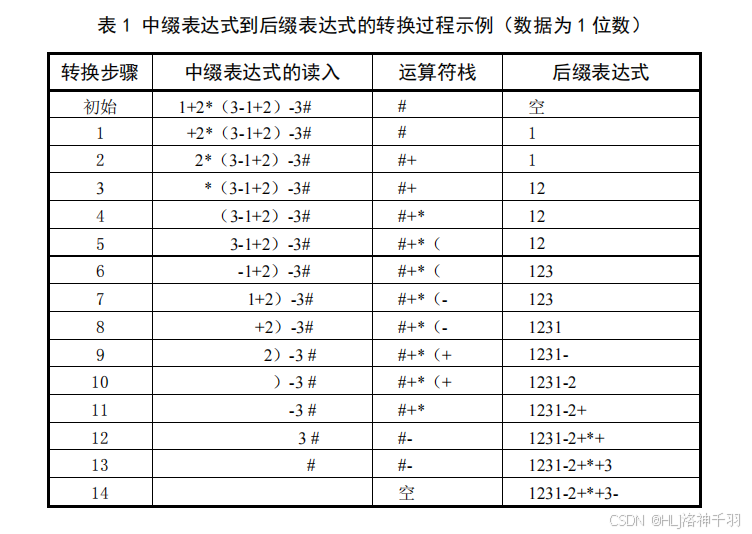

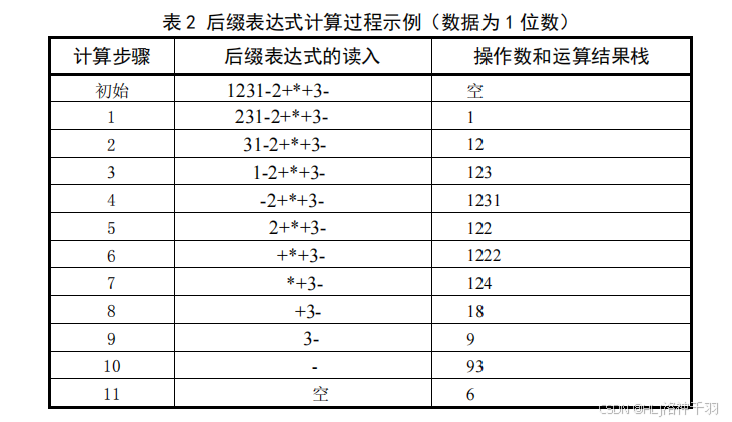

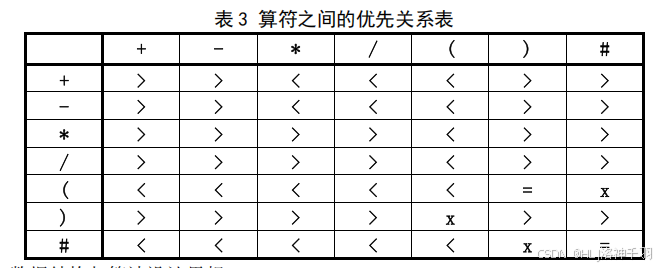






四、实验代码
package 实验六;public class Operation {/*** @description: 返回对应的优先级* @param: [operation]* @return: int*/public static int get(String operation) {int result = 0;if ("+".equals(operation) || "-".equals(operation)) {result = 1;} else if ("*".equals(operation) || "/".equals(operation)) {result = 2;} else {result = 0;}return result;}
}
package 实验六;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;public class SuffixExpression {/*** @description: 先将中缀表达式转 换成list集合* @param: [s]* @return: java.util.List<java.lang.String>*/public static List<String> zhongZhuiList(String s) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();String str;//用于拼接多位数char c;//每遍历到一个字符,就放入到cint i = 0;//指针,用于遍历中缀表达式do {//先判断是不是运算符if ((c = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = s.charAt(i)) > 57) {//ASCII码48~57为0到9十个阿拉伯数字list.add(c + "");i++;} else {//是数字,需要考虑多位数str = "";while (i < s.length() && (c = s.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c = s.charAt(i)) <= 57) {str = str + c;i++;}list.add(str);}} while (i < s.length());return list;}/*** @description: 将得到的中缀表达式对应的list转换成后缀表达式对应的list* @param: [list]* @return: java.util.List<java.lang.String>*/public static List<String> houZhuiList(List<String> list) {Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>();List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>();//遍历中缀表达式集合for (String item : list) {//如果是一个数字,加入到s2if (item.matches("\\d+")) {//matches() 方法用于检测字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式s2.add(item);} else if (item.equals("(")) {s1.push(item);} else if (item.equals(")")) {//如果是右括号,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这对括号丢弃while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {s2.add(s1.pop());}s1.pop();//将(弹出s1} else {//当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符的优先级时,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到s2while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.get(s1.peek()) >= Operation.get(item)) {s2.add(s1.pop());}s1.push(item);//还需要将item压入栈}}while (s1.size() != 0) {//将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入s2s2.add(s1.pop());}return s2;}/*** @description: 计算中缀表达式* @param: [list]* @return: java.util.List<java.lang.String>*/public static List<String> calzhongZhui(List<String> list) {Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>();Stack<String> num = new Stack<>();List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>();for (String item : list) {if (item.matches("\\d+")) {num.push(item);} else if (item.equals("(")) {s1.push(item);} else if (item.equals(")")) {while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {cal2(s1, num);s1.pop();}s1.pop();} else {while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.get(s1.peek()) >= Operation.get(item)) {cal2(s1, num);s1.pop();}s1.push(item);}}while (s1.size() != 0) {cal2(s1, num);s1.pop();}s2.add(num.pop());return s2;}public static Stack<String> cal2(Stack<String> s1, Stack<String> s2) {int num2 = Integer.parseInt(s2.pop());int num1 = Integer.parseInt(s2.pop());int res = 0;if (s1.peek().equals("+")) {res = num1 + num2;} else if (s1.peek().equals("-")) {res = num1 - num2;} else if (s1.peek().equals("*")) {res = num1 * num2;} else if (s1.peek().equals("/")) {res = num1 / num2;} else {throw new RuntimeException("运算符有错误");}//把计算结果入栈s2.push(res + "");return s2;}/*** @description: 完成对后缀表达式的运算* @param: [list]* @return: int*/public static int cal(List<String> list) {Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();//遍历listfor (String p : list) {//使用正则表达式来取数if (p.matches("\\d+")) {//匹配的是多位数stack.push(p);//如果是数字,则入栈,如果是符号则进行运算} else {int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());int res = 0;if (p.equals("+")) {res = num1 + num2;} else if (p.equals("-")) {res = num1 - num2;} else if (p.equals("*")) {res = num1 * num2;} else if (p.equals("/")) {res = num1 / num2;} else {throw new RuntimeException("运算符有错误");}//把计算结果入栈stack.push(res + "");}}return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());}public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";System.out.println(s);System.out.println("中缀表达式转成后缀表达式:");List<String> list = houZhuiList(zhongZhuiList(s));for (String str : list) {System.out.print(str + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("计算后缀表达式:");System.out.println(cal(houZhuiList(zhongZhuiList(s))));System.out.println("计算中缀表达式:");List<String> strings = calzhongZhui(zhongZhuiList(s));for (String string : strings) {System.out.println(string);}}
}实验七 图的应用(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导


四、考核标准

五、实验代码

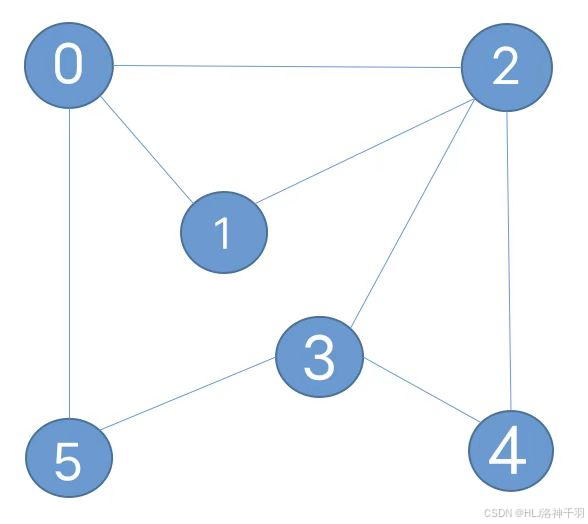
package 实验七.first;public class Graph {private final int v;//顶点数目private int e;//边的数目private Queue<Integer>[] adj;//邻接表public Graph(int v) {this.v = v;//初始化顶点数目this.e = 0;//初始化边的数目this.adj = new Queue[v];//初始化邻接表for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++) {adj[i] = new Queue<Integer>();}}//获取顶点数目public int V() {return v;}//获取边的数目public int E() {return e;}//向图中添加一条边v-wpublic void addEdge(int v, int w) {adj[v].enqueue(w);adj[w].enqueue(v);//边的数量+1e++;}//获取和顶点v相邻的所有顶点public Queue<Integer> adj(int v) {return adj[v];}
}
package 实验七.first;import java.util.Iterator;public class Queue<T> implements Iterable<T> {private Node head;private Node last;private int N;private class Node {public T item;public Node next;public Node(T item, Node next) {this.item = item;this.next = next;}}public Queue() {this.head = new Node(null, null);this.last = null;this.N = 0;}public Queue(Node head, Node last, int n) {this.head = head;this.last = last;N = n;}public boolean isEmpty() {return N == 0;}public int size() {return N;}public void enqueue(T t) {if (last == null) {last = new Node(t, null);head.next = last;} else {Node oldLast = last;last = new Node(t, null);oldLast.next = last;}N++;}public T dequeue() {if (isEmpty()) {return null;}Node oldFirst = head.next;head.next = oldFirst.next;N--;if (isEmpty()) {last = null;}return oldFirst.item;}@Overridepublic Iterator<T> iterator() {return new QIterator();}private class QIterator implements Iterator {private Node n;private QIterator() {this.n = head;}@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return n.next != null;}@Overridepublic Object next() {n = n.next;return n.item;}}
}
package 实验七.first;import java.util.Stack;public class DepthFirstPaths {//索引代表顶点,值表示当前顶点是否已经被搜索private boolean[] marked;//起点private int s;//索引代表顶点,值代表从起点s到当前顶点路径上的最后一个顶点private int[] edgeTo;//构造深度优先搜索对象,使用深度优先搜索找出G图中起点为s的所有路径public DepthFirstPaths(Graph g, int s) {//初始化marked数组this.marked = new boolean[g.V()];//初始化起点this.s = s;//初始化edgeTo数组this.edgeTo = new int[g.V()];dfs(g, s);}//使用深度优先搜索找出G图中v顶点的所有相邻顶点private void dfs(Graph g, int v) {//把v顶点标识为已搜索marked[v] = true;//遍历顶点v的邻接表,拿到每一个相邻的顶点,继续递归搜索for (Integer w : g.adj(v)) {//如果顶点w没有被搜索,则继续递归搜索if (!marked[w]) {edgeTo[w] = v;//到达顶点w的路径上的最后一个顶点是vdfs(g, w);}}}//判断w顶点与s顶点是否存在路径public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {return marked[v];}//找出从起点s到顶点v的路径(就是该路径经过的顶点)public Stack<Integer> pathTo(int v) {if (!hasPathTo(v)) {return null;}//创建栈对象,保存路径中的所有顶点Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();//通过循环,从顶点v开始,一直往前找直到找到起点为止for (int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x]) {path.push(x);}path.push(s);return path;}
}
package 实验七.first;import java.util.Stack;public class DepthFirstPathsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Graph graph = new Graph(6);graph.addEdge(0, 2);graph.addEdge(0, 1);graph.addEdge(2, 1);graph.addEdge(2, 3);graph.addEdge(2, 4);graph.addEdge(3, 5);graph.addEdge(3, 4);graph.addEdge(0, 5);DepthFirstPaths paths = new DepthFirstPaths(graph, 0);Stack<Integer> path = paths.pathTo(4);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();while (!path.empty()) {// System.out.print(path.pop()+"-");sb.append(path.pop()).append("-");}sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);System.out.println(sb);}
}
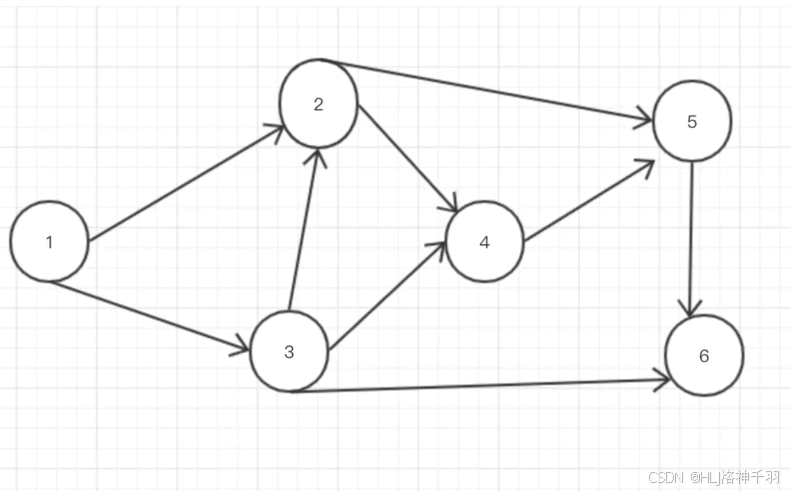
package 实验七.two;import java.util.*;public class GraphBfs {private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> adjList = new HashMap<>();//key是编号 value是邻居LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();/*** @description: 初始化图* @param: []* @return: void*/public void createGraph() {List<Integer> l1 = new LinkedList<>();l1.add(2);l1.add(3);List<Integer> l2 = new LinkedList<>();l2.add(4);l2.add(5);List<Integer> l3 = new LinkedList<>();l3.add(4);l3.add(6);List<Integer> l4 = new LinkedList<>();l4.add(5);List<Integer> l5 = new LinkedList<>();l5.add(6);List<Integer> l6 = new LinkedList<>();this.adjList.put(1, l1);this.adjList.put(2, l2);this.adjList.put(3, l3);this.adjList.put(4, l4);this.adjList.put(5, l5);this.adjList.put(6, l6);}/*** @description: 广度优先 寻找最短路径* @param: [startId, endId]* @return: void*/public void bfs(int startId, int endId) {Queue<Node> waitSearchQueue = new LinkedList<>();//等待被搜索的队列Map<Integer, Node> visitedList = new HashMap<>(); //访问过的节点列表waitSearchQueue.offer(new Node(startId, -1));//将开始节点入队while (!waitSearchQueue.isEmpty()) {//队列不空Node currentNode = waitSearchQueue.poll();//从队列头弹出System.out.println("当前目标:" + currentNode.id);if (currentNode.id == endId) {//如果找到了System.out.println("找到目标:" + currentNode.id);printPath(currentNode, visitedList); //打印出来路径return;}if (visitedList.containsKey(currentNode.id)) { //如果搜索过的就不第二次搜索了continue;}//将当前节点的邻居都入队for (int i = 0; i < this.adjList.get(currentNode.id).size(); i++) {int nodeId = this.adjList.get(currentNode.id).get(i);//如果访问过的就不用入队了。入队的话parentId就错了if (!visitedList.containsKey(nodeId)) {waitSearchQueue.offer(new Node(nodeId, currentNode.id));}}//标示当前节点访问过了visitedList.put(currentNode.id, currentNode);}System.out.println("没有路径");}/*** @description: 打印出路径* @param: [targetNode, visitList]* @return: void*/public void printPath(Node targetNode, Map<Integer, Node> visitList) {int parentId = targetNode.parentId;while (parentId != -1) {int id = visitList.get(parentId).id;parentId = visitList.get(parentId).parentId;list.add(id);}ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator(list.size());while (it.hasPrevious()) {Object O = it.previous();System.out.print(O + "-->");}System.out.print(targetNode.id);}//每一个节点的抽象 这里只存储idstatic class Node {private final int id;private final int parentId;public Node(int id, int parentId) {this.id = id;this.parentId = parentId;}}public static void main(String[] args) {GraphBfs g = new GraphBfs();g.createGraph();g.bfs(1, 5);}
}
实验八 综合设计与应用二(团队项目)(4 学时)
本单元为团队项目,系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性占 2 分,总计 5 分。
一、实验目的
综合运用所学的数据结构与算法实现一个小系统。
二、实验内容
1.校园导游系统(求最短路径算法: Dijkstra,Floyd)
2.最小生成树模拟程序(求最小生成树算法: Prim、Kruskal)
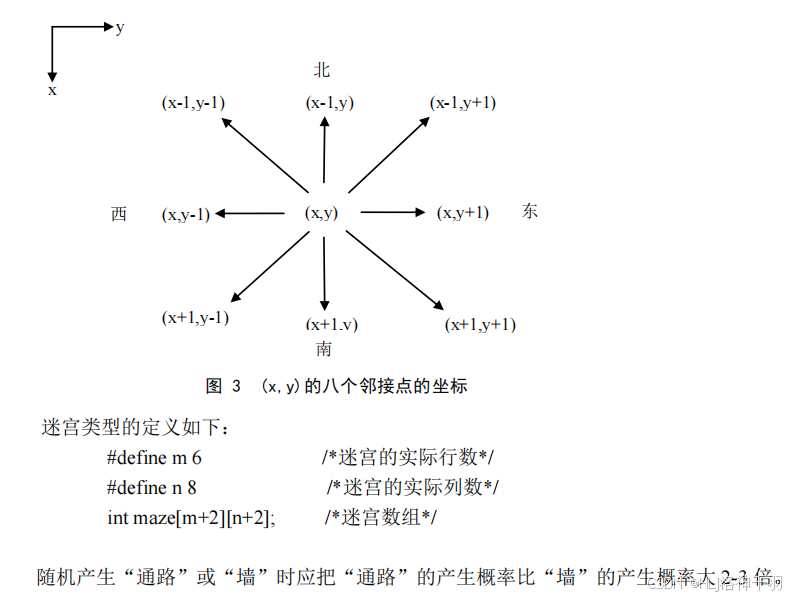
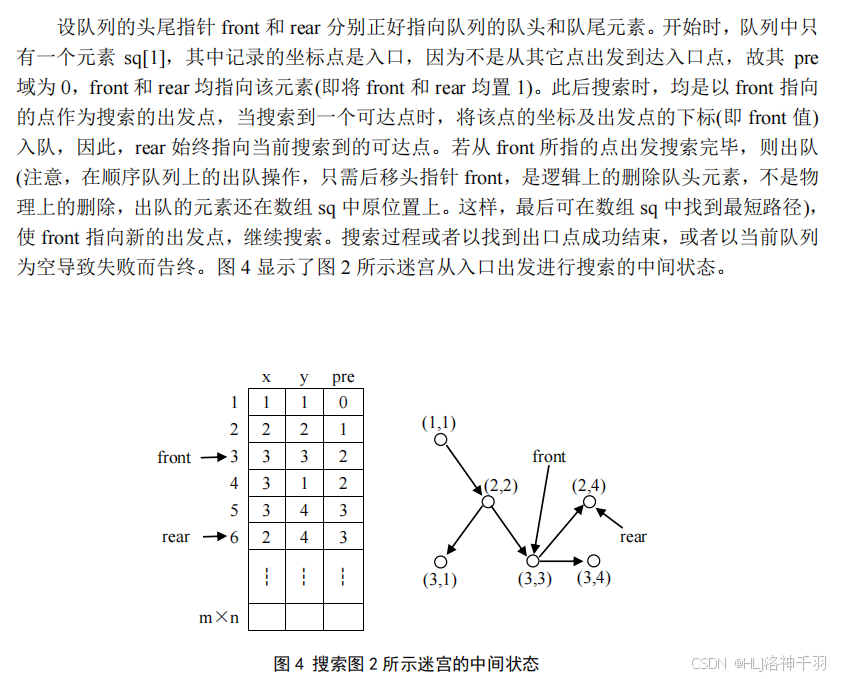
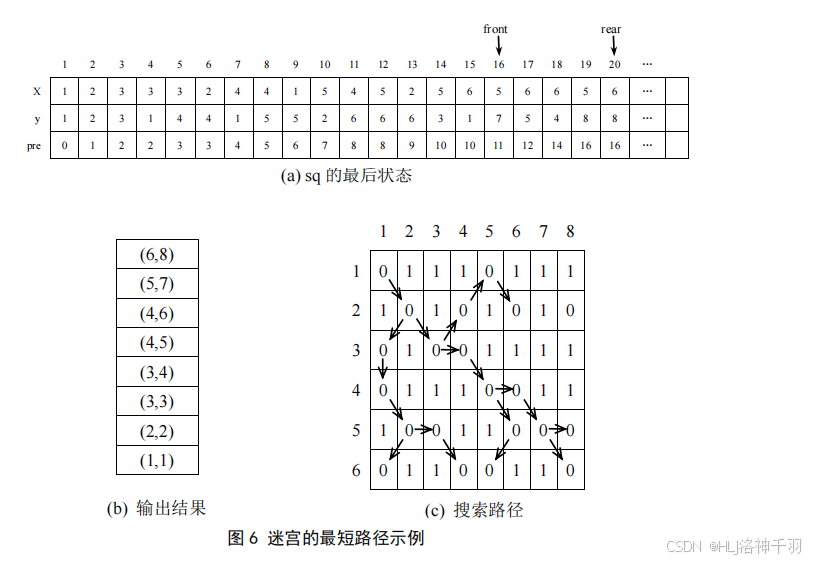
3.迷宫问题模拟程序(栈、队列、堆的应用,各种树形搜索算法)
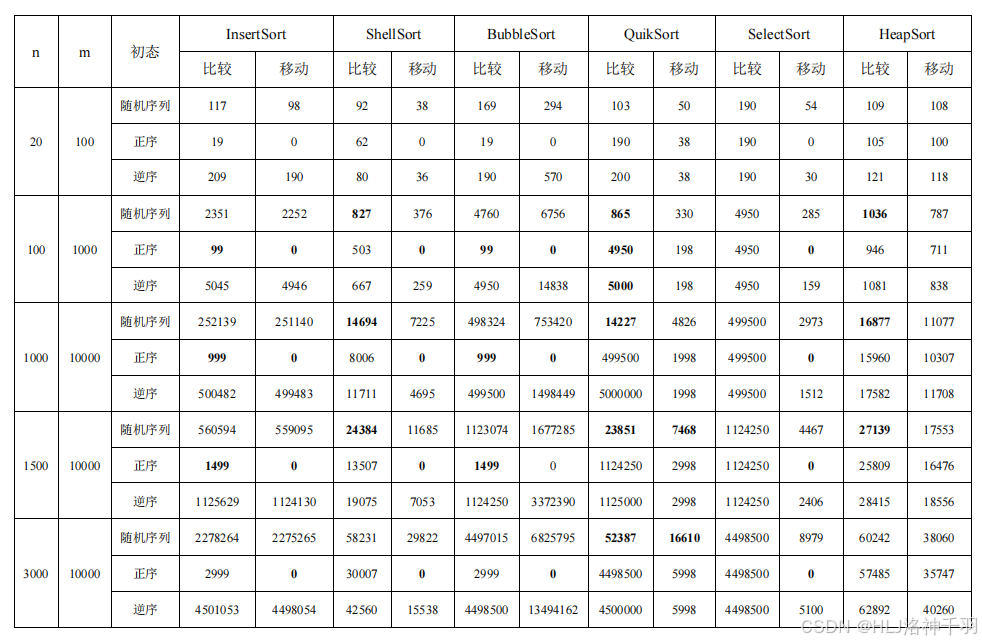
4.内部排序性能分析演示程序(各种排序算法)
5.通讯录管理系统的设计与实现(各种查找算法)
6.(拓扑排序算法)
7. 自选题目
三、实验指导





















四、实验代码
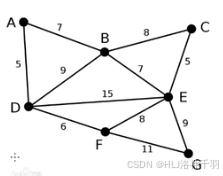
package 实验八;import java.util.Arrays;public class KruskalTree {public void t2() {char[] vertexes = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};int vertexSize = vertexes.length;int[][] edges = {{0, 7, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0},{7, 0, 8, 9, 7, 0, 0},{0, 8, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0},{5, 9, 0, 0, 15, 6, 0},{0, 7, 5, 15, 0, 8, 9},{0, 0, 0, 6, 8, 0, 11},{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 11, 0}};//创建一个图Graph graph = new Graph(vertexSize);//定义KruskalMinTreeKruskalMinTree kruskalMinTree = new KruskalMinTree();//初始化参数int edgeNum = kruskalMinTree.createGraph(graph, vertexSize, vertexes, edges);//遍历我们的邻接数组kruskalMinTree.showGraph(graph);//输出边//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(kruskalMinTree.getEdges(edgeNum, vertexes, edges)));kruskalMinTree.Kruskal(edgeNum, vertexes, edges);}static class KruskalMinTree {public int createGraph(Graph graph, int vertexSize, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {int edgeNum = 0;//初始化 vertexes edgesfor (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {graph.vertexes[i] = vertexes[i];for (int j = 0; j < vertexSize; j++) {graph.edges[i][j] = edges[i][j];}}//找到所有边数for (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j < vertexSize; j++) {if (edges[i][j] != 0) {edgeNum++;}}}return edgeNum;}public void showGraph(Graph graph) {for (int[] edge : graph.edges) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));}}/*** @description: 给一个字符,如果找到,返回相应的下标,反之,返回-1* @param: [ch, vertexes] 传入的顶点 字符数组* @return: int*/public int getPosition(char ch, char[] vertexes) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexes.length; i++) {if (vertexes[i] == ch) {return i;}}return -1;}/*** @description: 返回 Edge{ start=A end=D weight=5 }* @param: [edgeNum, vertexes, edges] 边的数目 字符数组 权值* @return: 实验八.KruskalTree.Edge[]*/public Edge[] getEdges(int edgeNum, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {int index = 0;//存放边的数组 Edge{ start=A end=D weight=5 }Edge[] edge = new Edge[edgeNum];for (int i = 0; i < vertexes.length; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j < vertexes.length; j++) {if (edges[i][j] != 0) {edge[index++] = new Edge(vertexes[i], vertexes[j], edges[i][j]);}}}return edge;}/*** @param ends 对应终点数组* @param i 起点下标* @return*/public int getEnd(int[] ends, int i) {while (ends[i] != 0) {i = ends[i];}return i;}/*** @param edgeNum 边的数目* @param vertexes 字符数组* @param edges 权值*/public void Kruskal(int edgeNum, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {//当前结果序列的索引int index = 0;//存放结果数组Edge[] rets = new Edge[edgeNum];//存放每个顶点在最小生成树中的终点int[] ends = new int[edgeNum];//边的序列Edge[] edge = getEdges(edgeNum, vertexes, edges);// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));Arrays.sort(edge);// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));//判断是否形成回路for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {// 给一个字符,如果找到,返回相应的下标,反之,返回-1//拿到第一个顶点的起始位置int p1 = getPosition(edge[i].start, vertexes);//拿到第一个顶点的终点位置int p2 = getPosition(edge[i].end, vertexes);//拿到第一个顶点的起始位置的终点int m = getEnd(ends, p1);//拿到第一个顶点的终点位置的终点int n = getEnd(ends, p2);if (m != n) {ends[m] = n;rets[index++] = edge[i];}}System.out.println("最小生成树");for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {System.out.println(rets[i]);}}}static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {char start;//边的起始位置char end;//边的结束位置int weight;//权值public Edge(char start, char end, int weight) {this.start = start;this.end = end;this.weight = weight;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Edge o) {return this.weight - o.weight;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Edge{" +"start=" + start +", end=" + end +", weight=" + weight +'}';}}static class Graph {int vertexSize;//存放顶点个数char[] vertexes;//存放顶点的数据int[][] edges;//存放权值public Graph(int vertexSize) {this.vertexSize = vertexSize;this.vertexes = new char[vertexSize];this.edges = new int[vertexSize][vertexSize];}}
}
package 实验八;import java.util.Arrays;public class PrimTree {public void t1() {char[] vertex = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};int vertexSize = vertex.length;int[][] edges = {{0, 7, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0},{7, 0, 8, 9, 7, 0, 0},{0, 8, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0},{5, 9, 0, 0, 15, 6, 0},{0, 7, 5, 15, 0, 8, 9},{0, 0, 0, 6, 8, 0, 11},{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 11, 0}};//生成一个图Graph graph = new Graph(vertexSize);//最小生成树MinTree minTree = new MinTree();minTree.createGraph(graph, vertexSize, vertex, edges);//显示邻接矩阵minTree.showGraph(graph);//显示路径minTree.prim(graph, 3);}static class MinTree {//生成一个邻接矩阵/* graph 图对象* vertexSize 图中顶点个数* vertex 图中顶点值* edges 图权值(邻接矩阵)*/public void createGraph(Graph graph, int vertexSize, char[] vertex, int[][] edges) {for (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {graph.vertex[i] = (char) vertex[i];for (int j = 0; j < vertexSize; j++) {graph.edges[i][j] = edges[i][j];}}}public void showGraph(Graph graph) {for (int[] edge : graph.edges) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));}}/** graph 一个图* v 当前我们开始顶点的下标*/public void prim(Graph graph, int v) {//用来标记当前顶点是否被访问int[] visited = new int[graph.vertexSize];//当前顶点记录成访问visited[v] = 1;//用于记录存放未被遍历的顶点中与已被遍历顶点的最小权值的顶点int minV = -1;int minI = -1;//寻找最小权值并记录 默认为无穷大int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//循环遍历k个顶点for (int k = 1; k < graph.vertexSize; k++) {//我们需要确定每一次生成子图中最短一条路径并记录for (int i = 0; i < graph.vertexSize; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < graph.vertexSize; j++) {if (visited[i] == 1 && visited[j] == 0 && graph.edges[i][j] != 0 && graph.edges[i][j] < minDistance) {//找到当前子图最小路径并记录minDistance = graph.edges[i][j];//记录最小路径的下标minV = i;minI = j;}}}System.out.println(graph.vertex[minV] + "-->" + graph.vertex[minI] + " " + minDistance);visited[minI] = 1;minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;}}}static class Graph {int vertexSize;//存放顶点个数char[] vertex;//存放顶点的数据int[][] edges;//存放权值public Graph(int vertexSize) {this.vertexSize = vertexSize;this.vertex = new char[vertexSize];this.edges = new int[vertexSize][vertexSize];}}
}
package 实验八;import java.util.Scanner;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);PrimTree primTree = new PrimTree();KruskalTree kruskalTree = new KruskalTree();int option;while (true){System.out.println("***********************************************");System.out.println("* 1、普里姆(Prim)算法构造最小生成树 *");System.out.println("* 2、克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法构造最小生成树 *");System.out.println("* 3、退出 *");System.out.println("************************************************");option=scanner.nextInt();switch (option) {case 1:primTree.t1();continue;case 2:kruskalTree.t2();break;case 3:System.out.println("成功退出!");System.exit(0);default:}}}
}
实验九 排序和查找(2 学时)
一、实验目的

二、实验内容

三、实验指导

四、考核标准

五、实验代码
package 实验九.快速排序;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;public class QuickSort {public static void main(String[] args) {Random random = new Random();int[] arr = new int[8];for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;arr[i]=randNum;}System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));}/*** @param arr 传进来的数组int* @param begin 左位置* @param end 右位置*/public static void sort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {if (begin < end) {//定义一个基准数int temp = arr[begin];int left = begin;int right = end;while (left < right) {//处理右边找到右边所有大于基准数的元素//退出循环时,右边都是大于基准数的元素while (left < right && arr[right] >= temp) {right--;}//把右边小于基准数的元素给左边arr[left] = arr[right];//处理左边找到左边所有小于基准数的元素//退出循环时,左边都小于基准数的元素while (left < right && arr[left] < temp) {left++;}//把左边大于基准数的元素给右边arr[right] = arr[left];}arr[left] = temp;//划分为两部分//处理左边用到递归sort(arr, begin, left - 1);//处理右边用到递归sort(arr, left + 1, end);}}
}
package 实验九.快速排序;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;public class QuickSort {public static void main(String[] args) {Random random = new Random();int[] arr = new int[8];for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;arr[i]=randNum;}System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));}/*** @param arr 传进来的数组int* @param begin 左位置* @param end 右位置*/public static void sort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {if (begin < end) {//定义一个基准数int temp = arr[begin];int left = begin;int right = end;while (left < right) {//处理右边找到右边所有大于基准数的元素//退出循环时,右边都是大于基准数的元素while (left < right && arr[right] >= temp) {right--;}//把右边小于基准数的元素给左边arr[left] = arr[right];//处理左边找到左边所有小于基准数的元素//退出循环时,左边都小于基准数的元素while (left < right && arr[left] < temp) {left++;}//把左边大于基准数的元素给右边arr[right] = arr[left];}arr[left] = temp;//划分为两部分//处理左边用到递归sort(arr, begin, left - 1);//处理右边用到递归sort(arr, left + 1, end);}}
}
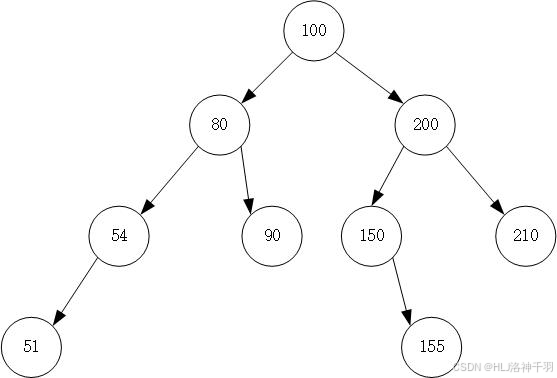
package 实验九.二叉排序树;public class BinarySearchTree {private int data;private BinarySearchTree left;private BinarySearchTree right;public BinarySearchTree() {}public BinarySearchTree(int data) {this.data = data;}public int getData() {return data;}public void setData(int data) {this.data = data;}public BinarySearchTree getLeft() {return left;}public void setLeft(BinarySearchTree left) {this.left = left;}public BinarySearchTree getRight() {return right;}public void setRight(BinarySearchTree right) {this.right = right;}
}
package 实验九.二叉排序树;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;public class BinarySearchTreeOpts {static BinarySearchTree root;public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("************************");System.out.println("* 1—建立 *");System.out.println("* 2—输出 *");System.out.println("* 3—插入 *");System.out.println("* 4—查找 *");System.out.println("* 5—删除 *");System.out.println("* 0—退出 *");System.out.println("************************");while (true) {System.out.println("请选择:");Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);int option = scanner.nextInt();switch (option) {case 1://建立Random random = new Random();int[] dataS = new int[7];for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;dataS[i] = randNum;}System.out.println("随机数据:" + Arrays.toString(dataS));for (int data : dataS) {insert(data);}break;case 2://输出System.out.println("中序遍历输出:");mid(root);System.out.println();break;case 3://插入System.out.println("请输入要插入的数据:");int in = scanner.nextInt();insert(in);break;case 4://查找System.out.println("请输入要查找的数据:");int fn = scanner.nextInt();find(fn);break;case 5://删除System.out.println("请输入要删除的数据:");int rn = scanner.nextInt();remove(rn);break;case 0://退出System.exit(0);default:System.out.println("请重新选择!");}}}//插入public static void insert(int data) {if (root == null) {root = new BinarySearchTree(data);return;}BinarySearchTree node = root;while (node != null) {if (data < node.getData()) {if (node.getLeft() == null) {node.setLeft(new BinarySearchTree(data));return;}node = node.getLeft();} else {if (node.getRight() == null) {node.setRight(new BinarySearchTree(data));return;}node = node.getRight();}}}//中序public static void mid(BinarySearchTree cur) {if (cur == null) {return;}mid(cur.getLeft());System.out.print(cur.getData() + " ");mid(cur.getRight());}//查找public static void find(int data) {BinarySearchTree node = root;while (node != null) {if (data < node.getData()) {node = node.getLeft();} else if (data > node.getData()) {node = node.getRight();} else {System.out.println("找到数据!");return;}}System.out.println("没找到数据!");}//删除public static void remove(int data) {BinarySearchTree node = root;BinarySearchTree parent = null;//查找要删除的结点,并且记录其父节点while (node != null && node.getData() != data) {parent = node;if (data < node.getData()) {node = node.getLeft();} else {node = node.getRight();}}if (node == null) {return;}//找到该节点//删除的节点有两个子结点if (node.getLeft() != null && node.getRight() != null) {//找最小的节点BinarySearchTree minNode = node.getRight();BinarySearchTree minNodeParent = node;while (minNode.getLeft() != null) {minNodeParent = minNode;minNode = minNode.getLeft();//找最小节点}node.setData(minNode.getData());//节点转换节点,删除实际数据node = minNode;//真正要删除的节点parent = minNodeParent;}//删除结点BinarySearchTree child = null;if (node.getLeft() != null) {child = node.getLeft();} else if (node.getRight() != null) {child = node.getRight();} else {child = null;}if (parent == null) {//删除根节点,并且根节点没有右子树root = child;} else if (parent.getLeft() == node) {parent.setLeft(child);} else if (parent.getRight() == node) {parent.setRight(child);}}}
若觉得有帮助,欢迎点赞关注,一起成长进步~
声明:本文仅供学习交流,禁作商用;禁篡改、歪曲及有偿传播,引用需标明来源。侵权必究。