Langgraph研究
目录
一、综合解释
二、核心概念
三、简单的图构建
四、Agent理解
4.1 Langgraph中的Agent
4.2 Agent 的执行流程
4.3 关键组件讲解
ToolNode
InjectedState / InjectedStore
tools_condition
状态 schema、context schema
remaining_steps / recursion limit
4.4 LangGraph实现Agent最小示例
一、综合解释
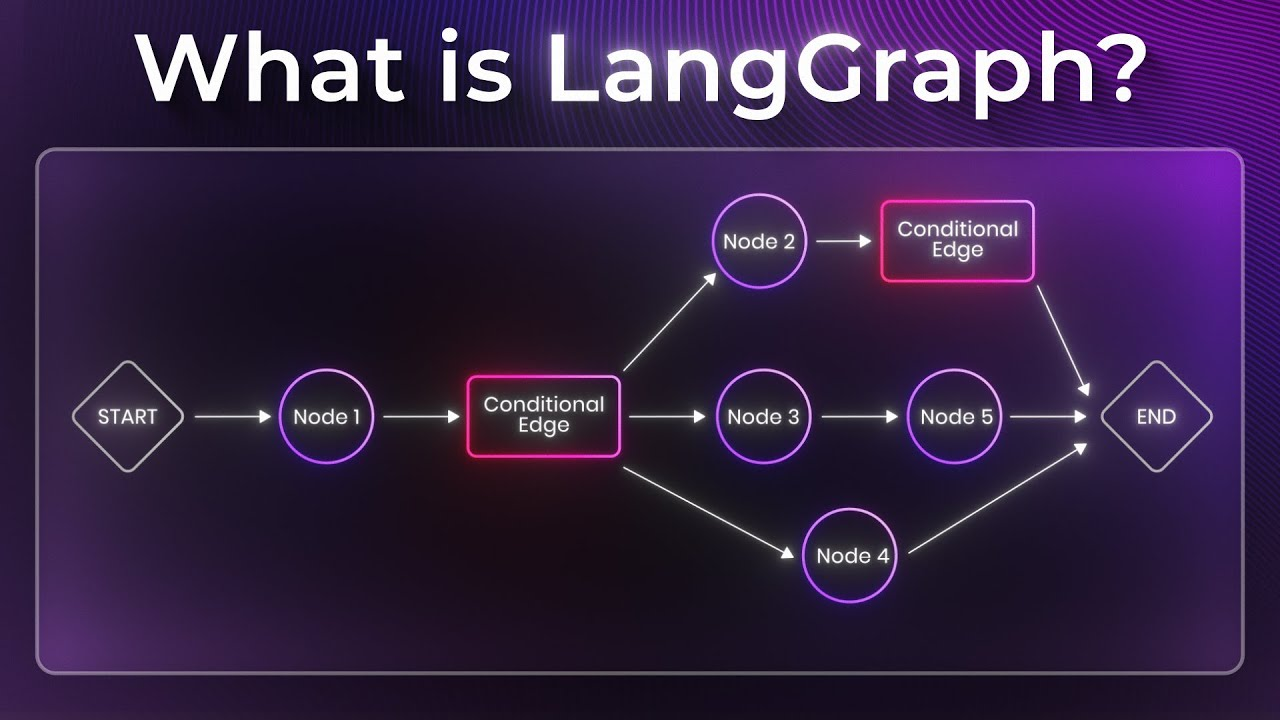
LangGraph 是一个非常热门的开源框架,用于构建多步骤、可控的语言模型(LLM)工作流或智能体(Agent)系统。它相当于是 LangChain 的“图式版本”,但设计更现代、更简洁,核心思想是用 有向图(DAG)来定义 LLM 调用流程。
参考文档:https://reference.langchain.com/python/langgraph/
LangGraph = “可视化 + 可控制 + 有状态”的 LLM 流程编排框架。
二、核心概念
| 概念 | 含义 |
| Node(节点) | 图中的基本执行单元(比如调用一个模型、执行一个函数、检索数据库等)。 |
| Edge(边) | 描述节点之间的执行依赖(谁执行完触发谁)。 |
| State(状态) | 每个节点都可以共享或修改全局上下文状态。LangGraph 天生支持有状态执行。 |
| Graph(图) | 将节点与边组合成一个完整的工作流或智能体系统。 |
三、简单的图构建
| 方法 | 描述 |
| add_node | 向状态图添加一个新节点。 |
| add_edge | 从开始节点(或开始节点列表)向结束节点添加一条有向边。 |
| add_conditional_edges | 从起始节点向任意数量的目标节点添加条件边。 |
| add_sequence | 添加将按提供的顺序执行的节点序列。 |
| compile | 将状态图编译为CompiledStateGraph对象。 |
-
例子1
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from typing import TypedDict# 定义状态
class State(TypedDict):message: str# 定义节点函数
def greet(state: State):return {"message": f"Hello, {state['message']}"}def end(state: State):print(state["message"])return state# 构建图
graph = StateGraph(State)
graph.add_node("greet", greet)
graph.add_node("end", end)graph.add_edge("greet", "end")
graph.set_entry_point("greet")
graph.set_finish_point("end")# 执行
app = graph.compile()
app.invoke({"message": "LangGraph!"})
# Hello, LangGraph!-
例子2
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from typing_extensions import Annotated, TypedDict
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.runtime import Runtimedef reducer(a: list, b: int | None) -> list:if b is not None:return a + [b]return aclass State(TypedDict):x: Annotated[list, reducer]class Context(TypedDict):r: floatgraph = StateGraph(state_schema=State, context_schema=Context)def node(state: State, runtime: Runtime[Context]) -> dict:r = runtime.context.get("r", 1.0)x = state["x"][-1]next_value = x * r * (1 - x)return {"x": next_value}graph.add_node("A", node)
graph.set_entry_point("A")
graph.set_finish_point("A")
compiled = graph.compile()step1 = compiled.invoke({"x": 0.5}, context={"r": 3.0})
print(step1)
# {'x': [0.5, 0.75]}四、Agent理解
4.1 Langgraph中的Agent
在 LangGraph 中,Agent 是一种“工具调用 + 语言模型循环执行”的结构。简单来说:
-
模型(LLM)接收输入(如用户消息)→ 输出可能包含“调用工具(tool_calls)”的指令。
-
如果模型决定调用工具,那么工具节点(ToolNode)被触发,执行对应函数/API,将结果返回。
-
模型再基于新的状态继续推理/调用工具,如此循环,直到没有工具调用为止。
-
最终,Agent 输出最终的消息/状态。
这种模式其实对应了很多“ReAct”范式(Reasoning + Acting)——模型不仅回答,还决定是否执行操作,再依据反馈继续。 LangGraph 提供了对应的 graph 构建、工具节点、状态注入等机制来支持这个流程。
4.2 Agent 的执行流程
分为如下步骤:
-
初始输入(通常是
messages包含用户消息)被送入 agent node。 -
Agent node 调用模型,模型生成输出。如果输出里指定调用工具(tool_calls)的话,进入下一步。
-
工具节点(ToolNode)执行每一个 tool_call,返回
ToolMessage添加到messages列表中。 -
回到 agent node,再次调用模型,基于扩展后的
messages。 -
重复上述步骤,直到模型输出不包含
tool_calls,然后流程结束,返回最终状态。
该流程在文档中用一个序列图也描述了:U(User)→ A(LLM)→ (loop) → T(Tools) → A → … → U。
4.3 关键组件讲解
ToolNode
ToolNode 是负责工具调用执行的节点。文档指出它支持:
-
并行执行多个工具调用。
-
错误处理(当工具参数错了、工具执行出错时) 。
-
注入状态(InjectedState)或者持久化存储(InjectedStore)让工具访问更多上下文或跨会话数据。
InjectedState / InjectedStore
-
InjectedState:注入当前 graph 状态(如消息列表、其他状态字段)到工具中,但模型并不能直接看到这些注入字段以避免泄露内部状态。 -
InjectedStore:注入持久存储(如跨会话记忆),工具可以读写,但模型仍不可直接访问。
tools_condition
这是一个条件路由函数,当最后一个 AIMessage 包含 tool_calls 时,它会让流程跳转到 ToolNode,否则结束流程。
状态 schema、context schema
-
state_schema:定义 graph 状态结构(例如必须包含messages和remaining_steps等字段) 。 -
context_schema:运行时的上下文结构(如用户、会话元数据) 。
remaining_steps / recursion limit
文档提到 remaining_steps 用于限制 Agent 最大执行步数。如果剩余步数 <2 且模型还想调用工具,则 Agent 会提前停止并返回提示“需要更多步骤”而不是抛出错误。
4.4 LangGraph实现Agent最小示例
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optionalfrom openai import OpenAI
import os
import random# ========== Qwen ==========
client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1"
)def llm(prompt: str) -> str:r = client.chat.completions.create(model="qwen-plus",messages=[{"role":"user","content":prompt}])return r.choices[0].message.content.strip()# ========== tools ==========
def cam1():print("[tool] camera1")return random.choice(["状态1","状态2"])def cam3():print("[tool] camera3")return random.choice(["状态1","状态2"])# ========== state ==========
class S(BaseModel):q: strobs: dict = {}answer: Optional[str] = None_step: int = 0 # 内部计数,防止死循环# ========== agent logic ==========
def agent_node(state:S) -> S:state._step += 1 # 增加步数计数# 强制安全停机if state._step > 5 and not state.answer:state.answer = "无法继续判断,超出最大循环"return state# 构建 promptprompt = f"""
任务:{state.q}
现有观测:{state.obs}规则:
- 如果未观测 cam1 并判断需要 -> 写 cam1
- 如果未观测 cam3 并判断需要 -> 写 cam3
- 如果已经观测足够 -> 写 final:你的结论
- 必须只输出一行,不要解释。
""".strip()r = llm(prompt)print("LLM:", r)if "cam1" in r.lower() and "cam1" not in state.obs:state.obs["cam1"] = cam1()elif "cam3" in r.lower() and "cam3" not in state.obs:state.obs["cam3"] = cam3()elif "final:" in r.lower():state.answer = r.split("final:")[-1].strip()return statedef should_continue(state:S) -> str:return "end" if state.answer else "loop"if __name__ == "__main__":# ========== graph ==========g = StateGraph(S)g.add_node("agent", agent_node)g.set_entry_point("agent")g.add_conditional_edges("agent",should_continue,{"loop":"agent","end":END})workflow = g.compile()# ========== run ==========init = S(q="拆包机是否正常投料?")result = workflow.invoke(init)# workflow.invoke 返回 dict,所以用 result.get("answer")print("FINAL =>", result.get("answer"))